Abstract
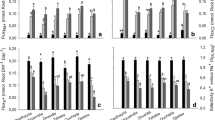
The effects of increasing relative humidity on the growth and salt tolerance of two melon (Cucumis melo L.) cultivars, Revigal C-8 (salt sensitive) and Galia (salt tolerant) was investigated. One month after germination, the plants were exposed for 15 d to 0 (control) and 80 mM NaCl, under relative humidity (RH), 30 and 70 %. The growth of the whole plant, leaf, stem and root of cv. Revigal C-8 was increased with increasing RH. On the other hand, cv. Galia showed an increase in root growth with increasing RH only under the NaCl treatment. Under salinity, most of the Na+ was withheld in the stems. An increase in RH in the NaCl treatment significantly decreased Na+ and Cl− concentrations in leaves of cv. Revigal C-8, while it had no effect on their concentrations in cv. Galia. In both cultivars, increasing RH under NaCl condition significantly decreased water contents in leaves and stems, and increased osmotic potential in roots. The amount of the root exudate of cv. Galia was significantly decreased with increasing RH, while it was not affected in cv. Revigal C-8. Under the NaCl treatment, cv. Galia had significantly higher leaf osmotic potential than cv. Revigal C-8 at both relative humidities and higher amount of root exudate at 30 % RH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, P.: Coping with the environment.-In: Barnes, R.S.K., Birks, H.J.B., Connor, E.F., Harper, J.L., Paine, R.T. (ed.): Saltmarsh Ecology. Pp. 207–308. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1990.
An, P., Inanaga, S., Cohen, Y., Kafkafi, U., Sugimoto, Y.: Salt tolerance in two soybean cultivars.-J. Plant Nutr.: in press, 2002.
An, P., Inanaga, S., Kafkafi, U., Lux, A., Sugimoto, Y.: Different effect of humidity on growth and salt tolerance of two soybean cultivars.-Biol. Plant. 44: 405–410, 2001.
Asagawa, M.: [Hydroponics.]-In: Hozyo, Y., Ishizuka, J. (ed.): Sakumotsu Seiri Ijikenhou (Experimental Method of Crop Physiology). Pp. 387–388, Nougyo Gijyutsu Kyokai, Tokyo 1985. [In Jap.]
Ball, M.C.: Salinity tolerance in the mangroves Aegiceras corniculatum and Avicennia marina I. Water use in relation to growth, carbon partitioning, and salt balance.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 15: 447–464, 1988.
Ball, M.C., Cochrane, M.J., Rawson, H.M.: Growth and water use of the mangroves Rhizophora apiculata and R. stylosa in response to salinity and humidity under ambient and elevated concentrations of atmospheric CO2.-Plant Cell Environ. 20: 1158–1166, 1997.
Borochov-Neori, H., Shani, U.: Response of melon plants to salt: 2. Modulation by root growth temperature — the role of root membrane properties.-J. Plant Physiol. 145: 545–550, 1995.
Botia, P., Carvajal, M., Cerdá, A., Martínez, V.: Response of eight Cucumis melo cultivars to salinity during germination and early vegetative growth.-Agronomie 18: 503–513, 1998.
Carvajal, M., Cerdá, A., Martínez, V.: Does calcium ameliorate the negative effect of NaCl on melon root water transport by regulation aquaporin activity?-New Phytol. 145: 439–447, 2000.
Carvajal, M., Del Amor, F.M. Fernandez-Ballester, G., Martínez, V., Cerdá, A.: Time course of solute accumulation and water relations in muskmelon plants exposed to salt during different growth stages.-Plant Sci. 138: 103–112, 1998.
Chaudhary, M.T., Wainwright, S.J., Merrett, M.J.: Comparative NaCl tolerance of lucerne plants regenerated from saltselected suspension cultures.-Plant Sci. 114: 221–232, 1996.
Dudley, L.M.: Salinity in the soil environment.-In: Pessarakli, M. (ed.): Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress. Pp. 13–30. Marcel Dekker, New York 1992.
Durand, M., Lacan, D.: Sodium partitioning within the shoot of soybean.-Physiol. Plant. 91: 65–71, 1994.
Franco, J.A., Esteban, C., Rodriguez, C.: Effect of salinity on various growth stages of muskmelon cv. Revigal.-J. hort. Sci. 68: 899–904. 1993.
Gislerod, H.R., Mortensen, L.M.: Relative humidity and nutrient concentration affect nutrient uptake and growth of Begonia hiemalis.-Hort. Sci. 25: 524–526, 1990.
Gislerod, H.R., Selmer-Olsen, A.R., Mortensen, L.M.: The effect of air humidity on nutrient uptake of some greenhouse plants.-Plant Soil 102: 193–196, 1987.
Greenway, H., Munns, R.: Mechanism of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31: 149–190, 1980.
Hoffman, G.J., Jobes, J.A.: Growth and water relations of cereal crops as influence by salinity and relative humidity.-Agron. J. 70: 765–769, 1978.
Hoffman, G.J., Rawlins, S.L.: Design and performance of sunlit climate chambers.-Trans. Amer. Soc. Agr. Eng. 13: 656–660, 1970.
Hoffman, G.J., Rawlins, S.L., Garber, M.J., Cullen, E.M.: Water relations and growth of cotton as influenced by salinity and relative humidity.-Agron. J. 63: 822–826, 1971.
Katou, K.: [Exudation and root pressure.]-In: Morita, S., Abe, J. (ed.): Ne No Jiten. [Roots Cyclopedia.] Pp. 353–355. Asakura, Tokyo 1998. [In Jap.]
Kirdmanee, C., Chaum, S., Wanussakul, R.: Morphological and physiological comparations plantlets in vitro: Responses to salinity.-In: Scannerini, S., Baker, A., Charlwood, B.V., Damiano, C., Franz, C., Gianinazzi, S. (ed.): Symposium on Plant Biotechnology as a Tool for the Exploitation of Mountain Lands. Pp. 181–186. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1998.
Kuehny, J.S., Morales, B.: Effects of salinity and alkalinity on pansy and impatiens in three different growing medial.-J. Plant Nutr. 21: 1011–1023, 1998.
Läuchli, A.: Salt exclusion: An adaptation of legumes for crops and pastures under saline conditions.-In: Staples, R.C., Toeniessen, G.H. (ed.): Salinity Tolerance in Plants. Strategies for Crop Improvement. Pp. 171–187. Wiley, New York 1984.
Leidi, E.O., Saiz, J.F.: Is salinity tolerance related to Na accumulation in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) seedlings?-Plant Soil 190: 67–75, 1997.
Lissner, J., Schierup, H.H., Comin, F.A., Astorga, V.: Effect of climate on the salt tolerance of two Phragmites australis populations. I. Growth, inorganic solutes, nitrogen relations and osmoregulation.-Aquat. Bot. 64: 317–333, 1999a.
Lissner, J., Schierup, H.H., Comin, F.A., Astorga, V.: Effect of climate on the salt tolerance of two Phragmites australis populations. II. Diurnal CO2 exchange and transpiration.-Aquat. Bot. 64: 335–350, 1999b.
Maas, E.V.: Salt tolerance of plants.-Appl. agr. Res. 1: 12–26, 1986.
Mangal, J.L., Hooda, P.S., Lal, S.: Salt tolerance of five muskmelon cultivars.-J. agr. Sci. 67: 535–540, 1988.
Martinez-Ballesta, M. del C., Martinez, V., Carvajal, M.: Regulation of water channel activity in whole roots and in protoplasts from roots of melon plants grown under saline conditions.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 27: 685–691, 2000.
Mavrogianopoulos, G.N., Spanakis, J., Tsikalas, P.: Effect of carbon dioxide enrichment and salinity on photosynthesis and yield in melon.-Sci. Hort. 79: 51–63, 1999.
Meiri, A., Plaut, Z., Pincas, L.: Salt tolerance of glasshouse-grown muskmelon.-Soil Sci. 131: 189–193, 1981.
Mendlinger, S., Pasternak, D.: Screening for salt tolerance in melons.-HortScience 27: 905–907, 1992.
Munns, R., Termaat, A.: Whole plant responses to salinity.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 13: 143–160, 1986.
Navarro, J.M., Angeles Botella, M., Cerdá, A., Martínez, V.: Effect of salinity × calcium interaction on cation balance in melon plants grown under two regimes of orthophosphate.-J. Plant Nutr. 23: 991–1006, 2000.
Navarro, J.M., Botella, M.A., Martinez, V.: Yield and fruit quality of melon plants grown under saline conditions in relation to phosphate and calcium nutrition.-J. hort. Sci. Biotechnol. 74: 573–578, 1999.
Paiva, E.A.S., Martinez, H.E.P., Casali, V.W.D., Padilha, L.: Occurrence of blossom-end rot in tomato as a function of calcium dose in the nutrient solution and air relative humidity.-J. Plant Nutr. 21: 2663–2670, 1998.
Rekika, D., Nachit, M.M., Araus, J.L., Monneveux, P.: Effects of water deficit on photosynthetic rate and osmotic adjustment in tetraploid wheat.-Photosynthetica. 35: 129–138, 1998.
Romero, L., Belakbir, A., Ragala, L., Ruiz, J.M.: Response of plant yield and leaf pigments to saline conditions: Effectiveness of different rootstocks in melon plants (Cucumis melo L.).-Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 43: 855–862, 1997.
Salim, M.: Effects of salinity and relative humidity on growth and ionic relations of plants.-New Phytol. 113: 13–20, 1989.
Shannon, M.C., Bohn, G.W., McCreight, J.D.: Salt tolerance among muskmelon genotypes during seed emergence and seedling growth.-Hort. Sci. 19: 828–830, 1984.
Shannon, M.C., Catherine, M.G., Francois, L.E.: Whole-plant response to salinity.-In: Robert, E.W. (ed.): Plant-Environment Interactions. Pp. 204–206. Marcel Dekker, New York 1994.
Shannon, M.C., Francois, L.E.: Salt tolerance of three muskmelon cultivars.-J. amer. Soc. hort. Sci. 103: 127–130, 1978.
Shmueli, M., Goldberg, D.: Sprinkle, furrow and trickle irrigation of musk-melon in an arid zone.-Hort. Sci. 6: 557–559, 1971.
Yonezawa, K., Sasaki, Y., Imanisi, S., Fujii, K.: [Analysis of variance.]-In: Seibutsu Toukei Gaku [Biostatistical Analysis.] Pp. 46–106. Asakura, Tokyo 1988. [In Jap.]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, P., Inanaga, S., Lux, A. et al. Effects of Salinity and Relative Humidity on Two Melon Cultivars Differing in Salt Tolerance. Biologia Plantarum 45, 409–415 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016273818726
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016273818726