Abstract
Purpose. Transdermal administration of the peptides [Mpa1, D-Tyr (Ethyl)2, Thr4, Orn8]-oxytocin (antocin) and [Mpa1, D-Arg8]-vasopressin (dDAVP) was studied in healthy volunteers.
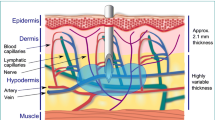
Methods. A standardized skin erosion was formed preliminary by suctioning. The peptides were administered in plastic reservoirs through a 5 mm erosion and the absorption was followed for a six-day period with plasma concentration determinations on days 1, 3 and 6 with refilling the reservoirs daily with 15 µm and 10 mM solutions of dDAVP and antocin, respectively. Fourteen healthy non-smoking volunteers divided equally between the sexes, participated in the study. Plasma concentrations were measured using specific radioimmunoassays. Reservoir concentrations and metabolic stability of the peptides were determined using reverse-phase HPLC.
Results. Both antocin and dDAVP were absorbed across the skin erosion. The absorption pattern was biphasic with a high initial absorption during days 1 and 2 followed by a lower absorption on days 3 and 6. The absorption on day 1, which was estimated at more than 50% for both peptides during a 24 h period, corresponded to a simultaneous decrease in peptide concentration in the reservoirs. The extent of absorption for antocin on days 3 and 6 was 1/3 to 1/6, respectively, of that observed on day 1. Antocin was minimally degraded in the skin reservoir while dDAVP was intact. However, accumulation of cellular material appeared in the antocin reservoirs. The absorption of antocin was reduced by exposure to intact skin surrounding the skin erosion. No pain was experienced and no scar formation was observed.
Conclusions. The observed biphasic absorption may be a consequence of the mild inflammatory response occurring subsequent to eroding the skin. The standardized skin erosion may provide a route for the short-term delivery of otherwise poorly absorbable peptide and protein drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Wearley, L L. Recent progress in protein and peptide delivery by noninvasive routes. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 8, 331–394 (1991).
Cullander, C. and R. H. Guy. (D) Routes of delivery: Case Studies (6) Transdermal delivery of peptides and proteins. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 8, 291–329 (1992).
Svedman, P., S. Lundin and C. Svedman. Administration of antidiuretic peptide (DDAVP) by way of suction-depithelialised skin. Lancet 337, 1506–1509 (1991b).
Westerling, D., P. Höglund, S. Lundin and P. Svedman. Transdermal administration of morphine to healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 37, 571–576 (1994).
Melin, P. Oxytocin antagonists in preterm labour and delivery. Baillieres. Clin Obstet Gynecol 7, 577–600 (1993).
Lundin, S., P. Melin and H. Vilhardt. Plasma concentrations of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin after intragastric administration in the rat. Acta Endocrinol 108, 179–183 (1985).
Lundin, S., A. Broeders and P. Melin. Pharmacokinetic properties of the tocolytic agent [Mpa1, D-Tyr2(Et), Thr4, Orn8]-oxytocin in healthy volunteers. Clin Endocrinol 39, 369–374 (1993).
Lundin, S., N. Pantzar, A., Broeders, M. Ohlin and B. R. Weström. Differences in transport rate of oxytocin and vasopressin analogues across proximal and distal isolated intestinal segments of the rat. Pharm Res 8, 1274–1280 (1991).
Fjellestad-Paulsen, A., P. Höglund, S. Lundin and O. Paulsen. Pharmacokinetics of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin after various routes of administration in healthy volunteers. Clin Endocrinol 38, 177–182 (1993).
Kiistala, U. and K. K. Mustakallio. Dermo-epidermal separation with suction. Electron-microscopic and histochemical study of initial events of blistering on human skin. J Invest Dermatol 48, 466–477 (1967).
Kiistala, U. The suction blister method for the in vivo separation of epidermis from dermis in human skin. Thesis, University of Helsinki (1976).
Kutlu, N. and P. Svedman. Structural microvessel response in dermis of suction blister wounds on upper and lower limbs in healthy volunteers. Vasc Surg 26, 290–299 (1992b).
Svedman, P., C. Svedman and T. Njalsson. Epithelialization and blood flow in suction blister wounds on healthy volunteers. J Invest Sur 4, 175–189 (1991c).
Svedman, C., C. Hammarlund, N. Kutlu and P. Svedman. Skin suction blister wound exposed to UV-irradiation. A burn wound model for use in humans. Burns 17, 41–46 (1991a).
Kutlu, N. and P. Svedman. The microcirculation in suction blister wounds on upper and lower limbs in healthy volunteers. Vasc Surg 26, 706–711 (1992a).
Kuhns, D. B., B. Decarlo, D. M. Hawk and J. I. Gallin. Dynamics of the cellular and humoral components of the inflammatory response elicited in skin blisters in humans. J Clin Invest 89, 1734–1740 (1992).
Renkin, E. M. Capillary transport of macromolecules: pores and other endothelial pathways. J Appl Physiol 58, 315–325 (1985).
Manning, M. and W. H. Sawyer. Discovery, development and some uses of vasopressin and oxytocin antagonists. J Lab Clin Med 114, 617–632 (1989).
Hurley, J. V. In Acute Inflammation, Churchill Livingstone, Melbourne, Australia (1983).
Grega, G. J. and G. J. Adamski. Differential effects of inhibitors of cellular function on inflammatory mediator-stimulated increase in vascular permeability. Microcirc, Endothel, Lymphatics 7, 217–244 (1991).
Crone, C. Modulation of solute permeability in microvascular endothelium. Fed Proc 45, 77–83 (1986).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lundin, S., Svedman, P., Höglund, P. et al. Absorption of an Oxytocin Antagonist (Antocin) and a Vasopressin Analogue (dDAVP) Through a Standardized Skin Erosion in Volunteers. Pharm Res 12, 2024–2029 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016272729556
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016272729556