Abstract
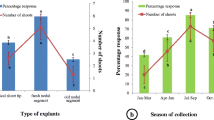
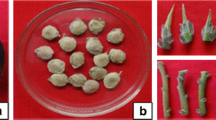
Stackhousia tryonii Bailey, a rare species whichhyperaccumulates nickel and with a potential to be exploited inphytoremediation/phytomining, is difficult to propagate via seeds. This studyinvestigated the development of a micropropagation protocol for the productionof large stocks of S. tryonii. Disinfested shoot tips andnodal buds were precultured on Gamborg's (B5) basal medium toobtain aseptic shoots for the optimisation of the protocol. 6-Benzyl aminopurine(BAP) at 1.0 mg l−1 produced the highest number ofshoots per explant in B5 medium. Comparison betweenB5 and MS media showed similar responses, but with marked influenceof BAP concentration on shoot numbers. Transfer of shoots from MS(multiplication) medium to MS medium supplemented with indole-3-acetic acid(IAA) and indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), individually or in combination, indicatedthat a combination of IAA and IBA (0.75 mg l−1each) is required to produce roots on young shoots (75%) compared to IBA(15–45%) or IAA (0–10%) alone. This study demonstrated that by usingthis protocol, a high multiplication rate (up to 18 shoots per explant) could be produced within 4 weeks, andthey can be readily hardened (98% survival) in a glasshouse by transplantingthem into a potting mixture of sand and perlite (4:1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banik R.L. and Islam S.A.M.N. 1997. In vitro clonal propagation of hybrid acacia (A. auriculiformis 3 A. mangium). Bangladesh Journal of Forest Science 25: 1–7.
Batianoff G.N. and Specht R.L. 1992. Queensland (Australia) serpentinite vegetation. In: Baker A.J.M., Proctor J. and Reeves R.D. (eds), TheVegetation of Ultramafic (Serpentine) Soils. Intercept Limited, Andover, UK, pp. 109–128.
Batianoff G.N., Reeves R.D. and Specht R.L. 1990. Stackhousia tryonii Bailey: a nickel-accumulating serpentine-endemic species of central Queensland. Australian Journal of Botany 38: 121–130.
Briggs J.D. and Leigh J.H. 1996. Rare and Threatened Australian Plants. CSIRO, Canberra, Australia.
Brooks R.R., Lee J., Reeves R.D. and Jaffre T. 1977. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 7: 49–57.
Castelli J.P. 1997. The effects of population size and soil characteristics on the germination and growth of the rare serpentinite endemic Ceratium velutinum Raf. (Caryophyllaceae) compared in small serpentine barren fragments and large intact serpentine barrens in southeastern Pennsylvania. American Journal of Botany 84: 75–76.
Cunningham S.D. and Berti W.R. 1993. Remediation of contaminated soils with green plants — an overview. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology — Plant 29P: 207–212.
Gamborg O.L., Miller R. and Ojima K. 1968. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Experimental Cell Research 50: 151–158.
George E. 1993. Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture, Part 1. 2nd edn. Exegetics Ltd, London, UK.
Harrison S. 1997. How natural habitat patchiness affects the distribution of diversity in Californian serpentine chaparral. Ecology 78: 1898–1906.
Khadeeva N.V., Degtyarenko L.V., Gordon N.Y. and Yakovleva E.Y. 1995. Introduction of Stachys sieboldii Mig. to tissue culture. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 42: 815–820.
Murashige T. and Skoog F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia Plantarum 15: 473–497.
Naik S.K., Patnaik S. and Chand P.K. 1999. In vitro propagation of pomegranate (Punica granatum L. cv. Ganesh) through axillary shoot proliferation from nodal segments of mature tree. Scientia Horticulturae 79: 175–183.
Nicks L.J. and Chambers M.F. 1995. Farming for metals. Mining Environment and Management 3: 15–18.
Parthasarthy V.A., Parthasarthy U. and Nagaraju V. 1996. Morphogenetic response of gerbera shoots to media and benzyl amino purine. Annals of Plant Physiology 10: 34–39.
Rabinowitz D. 1981. Seven forms of rarity. In: Synge H. (ed.), The Biological Aspects of Rare Plant Conservation. Wiley, London, pp. 205–218.
Ralph M. 1997. Growing Australian Native Plants from Seed. Bushland Horticulture, Fitzroy, Australia.
Rashid A.A.H.A., Aziz M.A. and Alang Z.C. 1992. In vitro organogenesis of carambola. Acta Horticulturae 321: 579–588.
Reeves R.D. 1991. The hyperaccumulation of nickel by serpentine plants. In: Baker A.J.M., Proctor J., Reeves R.D. (eds), The Vegetation of Ultramafic (Serpentine) Soils. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Serpentine Ecology. University of California, Davis. Intercept, Andover, UK, pp. 253–277.
Reeves R.D. and Baker A.J.M. 2000. Metal-accumulating plants. In: Raskin I. and Ensley B.D. (eds), Phytoremediation of Toxic Metals: using Plants to Clean up the Environment. Wiley, New York, pp. 193–229.
Robinson B.H., Brooks R.R. and Clothier B.E. 1999. Soil amendments affecting nickel and cobalt uptake by Berkheya coddii: potential use for phytomining and phytoremediation. Annals of Botany 84: 689–694.
Stanley T.D. and Ross E.M. 1986. Flora of Southeastern Queensland, Vol II. Queensland Department of Primary Industries, Brisbane, Australia.
Sudha C.G., Krishnan P.N. and Pushpahgadan P. 1998. In vitro propagation of Holostemma annulare (Roxb.) K. Schum., a rare medicinal plant. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology — Plant 34: 57–63.
Sudha C.G. and Seeni S. 1996. In vitro propagation of Rauwolfia micrantha, a rare medicinal plant. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 44: 243–248.
Zalba S.M. and Nebbia A.J. 1999. Neosparton darwinii (Verbenaceae), a restricted endemic species. Is it also endangered? Biodiversity and Conservation 8: 1585–1593.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, P., Bhatia, N.P. & Ashwath, N. In vitro propagation of Stackhousia tryonii Bailey (Stackhousiaceae): a rare and serpentine-endemic species of central Queensland, Australia. Biodiversity and Conservation 11, 1469–1477 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016252207054
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016252207054