Abstract
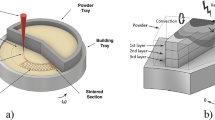
Direct Metal Laser Re-Melting is a variant of the Selective Laser Sintering process, a Rapid Prototyping (RP) technology. This tool-less manufacturing technology has the potential of producing complex, high quality components from single-phase metal powders in short time scales. This is made possible by the production of consecutive two-dimensional layers. Unfortunately, finished components manufactured by this technique have their integrity and material properties dictated by the porosity within the laser re-melted structure. In order to maintain structural integrity comparable to conventionally produced components, metal components produced by the rapid prototyping method should exhibit a porosity of the order of maximum of ∼2% with corresponding bulk material properties. To achieve these objectives, process and laser parameters require optimisation for maximum densities to be attained. This paper reports on the development of a scanning strategy that produces stainless steel (316L) laser re-melted components which exhibit porosities of <1%, while maintaining the concept of rapid prototyping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. P. KRUTH, M. C. LU and T. MAKAGAWA, CIRP Annals, Mfg. Tech. 47(2) (1998) 525.
C. K. CHUA, S. M. CHOU and T. S. WONG, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 14 (1998) 146.
I. GIBSON and D. SHI, Rapid Prototyping J. 3(4) (1997) 129.
C. NELSON, N. K. VAIL, J. W. BARLOW, J. J. BEAMAN, D. L. BOURELL and H. L. MARCUS, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 34 (1995) 1641.
D. L. BOURELL, H. L. MARCUS, J. W. BARLOW and J. J. BEAMAN, Int. Journ. Powder Metallurgy 28(4) (1992) 369.
C. NELSON, Rapid steel 2.0 mold inserts for plastic injection molding, DTM Corporation, www.dtm-corp.com (1998).
J. P. KRUTH, B. VAN DER SCHUEREN, J. E. BONSE and B. MORREN, CIRP Annals 45(1) (1996) 183.
W. MEINERS, K. WISSENBACH and R. PROPAWE, in Laser Assisted Net Shape Engineering 2, Proc. LANE (1997) p. 615.
C. HAUSER, T. H. C. CHILDS, K. W. DALGARNO and R. B. EANE, in Proc. Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, (1999) Vol. 10, p. 265.
R. MORGAN, C. J. SUTCLIFFE and W. O'NEILL, Rapid Prototyping J. 7(3) (2001) 159.
Idem., Optics and Laser in Engineering, submitted.
R. MORGAN, A. PAPWORTH, C. SUTCLIFFE, P. FOX and W. O'NEILL, in Proc. Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium 2001, Accepted.
G. ARTHUR, J. Inst. Mat. 83 (1954) 329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, R.H., Papworth, A.J., Sutcliffe, C. et al. High density net shape components by direct laser re-melting of single-phase powders. Journal of Materials Science 37, 3093–3100 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016185606642
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016185606642