Abstract
Purpose. Flexible parametric models describing the input process after extravascular drug administration are needed for the assessment of absorption rate and the use of population methods in bioavailability and bioequivalence studies.
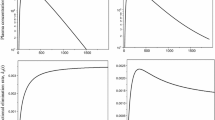
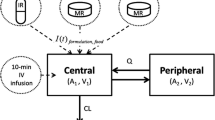
Methods. The oral concentration-time curve modeled as the product of the input and disposition function in the Laplace domain was obtained by numerical inversion methods for parameter estimation. The utility of the inverse Gaussian input density was examined using bioavailability data of an extended-release dosage form. Measures of rate of absorption and the cumulative absorbed amount profile were defined in terms of the estimated model parameters.
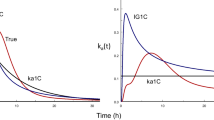
Results. Accurate estimation of absorption parameters was achieved by simultaneous fitting of the extravascular and intravascular data (describing the latter by a triexponential function). The new input function allowed a direct estimation of both extent of absorption and mean absorption time.
Conclusions. The findings suggest that the inverse Gaussian density is a useful input function. Its flexibility may reduce the effect of model misspecification in parameter estimation. All parameters can be readily interpreted in terms of the absorption process.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Weiss, J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:635–657 (1986).
M. Weiss, J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:57–74 (1986).
M. Weiss, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 43:571–579 (1992).
Y. G. Sinai, Probability Theory, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 1992.
M. Weiss, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 25:695–702 (1983).
R. S. Chhikara and J. L. Folks, Technometrics. 19:461–468 (1977).
M. K. Charter, In W. T. Grandy, Jr. and L. H. Schick (eds.), Maximum Entropy and Bayesian Methods., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, 1991, pp. 245–252.
R. D. Purves, J. Pharm. Sci. 84:71–74 (1995).
J. M. van Rossum and C. A. M. van Ginneken, In E. Gladtke and H. Heimann (eds.), Pharmacokinetics, Fischer, Stuttgart, 1980, pp. 53–73.
D. Brockmeier, H. J. Dengler and D. Voegele, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28:291–300 (1985).
K. L. H. Chan and M. Gibaldi, J. Pharm. Sci. 74:388–393 (1985).
K. E. Fattinger and D. Verotta, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58:595–599 (1995).
F. Bressolle, J. M. Laurelli, R. Gomeni, J. G. Bechier, N. R. Wynn, M. Galtier and J. J. Eledjam, J. Pharm. Sci. 82:1175–1178 (1993).
F. Bressolle, R. Gomeni, R. Alric, M. J. Royer-Morrot and J. Necciari, J. Pharm. Sci. 83:1461–1464 (1994).
F.-Y. Liu, N. C. Sambol, R. P. Giannini and C. Y. Liu, Pharm. Res. 12:720–728 (1995).
L. Endrenyi, S. Fritsch, and W. Yan, Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 29:394–399 (1991).
F. Y. Bois, T. N. Tozer, W. W. Hauck, M.-L. Chen, R. Patnaik and R. L. Williams, Pharm. Res. 11:966–974 (1994).
A. Rostami-Hodjegan, P. R. Jackson and G. T. Tucker, J. Pharm. Sci. 83:1554–1557 (1994).
G. Paintaud, L. Helleday, C. W. Maboundou and G. Alvàn, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 49:139–143 (1995).
K. E. Fattinger and D. Verotta, J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 23:581–610 (1995).
N. H. G. Holford, R. J. Ambros and K. Stoeckel, J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 20:421–442 (1992).
R. Miller and T. M. Ludden, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 44:231–235 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, M. A Novel Extravascular Input Function for the Assessment of Drug Absorption in Bioavailability Studies. Pharm Res 13, 1547–1553 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016039931663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016039931663