Abstract
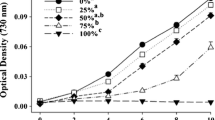
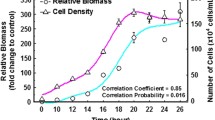
This study describes effects of exposure of the freshwater ciliate Tetrahymena pyriformis to the "classic" weak acid respiratory uncoupler pentachlorophenol (PCP) on the population growth kinetics and membrane lipid profiles. The assessment of growth kinetics of naive populations exposed to PCP, at concentrations eliciting <50% growth inhibition, showed generation times of exposed cultures similar to generation times of controls but preceded by a short lag phase (<2 h). Assessment of exposed cultures exhibiting >50% growth inhibition revealed generation times that increased with increasing concentrations of toxicant. In addition, the relative percentages of selected fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) in both pellicle and mitochondrial membranes were examined. Upon exposure to PCP the relative percentages of FAMEs 12:0, 14:0, 16:0, 16:1, and 18:0 did not change. However, with exposure to PCP a decrease was observed for FAMEs 15:0 and 17:0. Conversely, with PCP exposure there was an increase in FAME 18:1. A comparison of these results with those elicited upon exposure to the model narcotic 1-octanol reveals marked differences in both growth kinetics and fatty acid shifts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy SG, Mackay D, McCarty LS. Volume fraction correlation for narcosis in aquatic organisms: the key role of partitioning. Environ ToxicolChem. 1988:7:469-81.
Bearden AP, Gregory BW, Schultz TW. Population growth kinetics of Tetrahymena pyriformis exposed to selected nonpolar narcotics. Arch Environ Contam. 1997:33:401-6.
Bearden AP, Sinks GD, Schultz TW. Acclimation to sublethal exposure to a model nonpolar narcotic: population growth kinetics and membrane lipid alterations in Tetrahymena pyriformis. AquaticToxicol. 1999:46:11-21.
Beavan MJ, Charpentier C, Rose AH. Production and toler-ance of ethanol in relation to phospholipid fatty-acyl composition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCLC 431. J Gen Microbiol. 1982:128:1447-55.
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959:37:911-7.
Cajina-Quezada M, Schultz TW. Structure-toxicity relation-ships for selected weak acid respiratory uncouplers. Aquatic Toxicol. 1990:17:239-52.
Franks NB, Lieb WR. Mechanisms of general anesthesia. Environ Health Perspect. 1990:87:199-205.
Guckert JB, Antworth CP, Nichols PD, White DC. Phospholi-pid, ester-linked fatty acid profiles as reproducible assays for changes in prokaryotic community structure of estruarine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 1985:31:147-58.
Heipeper HJ, deBont JAM. Adaptation of Pseudomonas putida S12 to ethanol and toluene at the level of fatty acid composition of membranes. Appi Environ Microbiol. 1994; 60:4440-4.
Ingram L. Adaptation of membrane lipids to alcohols. J Bacteriol. 1976:125:670-8.
Larsen J, Schultz TW, Rasmussen L, Hoofman R, Pauli W. Progress in an ecotoxicological standard protocol with protozoa: results from a pilot ring test with Tetmhymena pyriformis. Chemosphere. 1997:35:1023-41.
McLaughlin SGA, Dilger J. Transport of protons across membranes by weak acids. Physiol Rev. 1980:60:825-63.
Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosyn-thetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev. 1966:41:445-502.
Nilsson JR. pH-dependent effects of 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) on proliferation, endocytosis, fine structure and DNP resistance in Tetrahymena. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1995;42: 248-55.
Nozawa Y, Thompson GA. Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis: II. Isolation and lipid analysis of cell fractions. J Cell Biol. 1971:49:712-21.
Ramesha CS, Thompson GA. Changes in lipid composition and physical properties of Tetrahymena ciliary membranes following low-temperature acclimation. Biochemistry. 1982; 21:3612-7.
SAS. SAS/STAT User's Guide, version 6, 4th edn,Vol. 2. Gary, NC: SAS Institute, Inc.; 1989:846.
Schultz TW. TETRATOX: Tetrahymena pyriformis population growth impairment endpoint: a surrogate for fish lethality. Toxicol Methods. 1997:7:289-309.
Schultz TW, Cronin MTD. QSARs for weak acid respiratory uncouplers to Vibrio fischeri. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1997; 16:357-60.
Schultz TW, Seward JR. Health-effects related structure-toxi-city relationships: a paradigm for the millennium. Sci Total Environ. 2000:249:73-84.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste-water. Bioassay procedures for ciliated protozoa (Tentative). Prepared and published jointly by American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Olution Control. 1976:795-62.
Terada H. Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. Environ Health Perspect. 1990:87:213-8.
Umeki S, Fukushima H, Nozawa Y. Variations in the activity of fatty acyl-CoA desaturates and electron-transport compo-nents in Tetrahymena microsomes with temperature and age of culture. J Therm Biol. 1983:8:353-60.
van Wezel AP, Opperhuizen A. Narcosis due to environmental pollutants in aquatic organisms: residue-based toxicity, mechanisms, and membrane burdens. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1995:25:255-79.
Weber FJ, Isken S, deBont JAM. Cis/trans isomerization of fatty acids as a defense mechanism of Pseudomonas putida strains to toxic concentrations of toluene. Microbiology. 1994:140:2013-7.
White DC, Davis WM, Nichols JS, King JD, Bobbie RJ. Determination of sedimentary microbial biomass by extrac-table lipid phosphate. Oecologia. 1979:40:51-62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schultz, T., Sinks, G. & Bearden-Lowit, A. Population growth kinetics and bulk membrane lipid alterations in Tetrahymena pyriformis: Exposure to pentachlorophenol. Cell Biol Toxicol 18, 271–278 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016007128759
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016007128759