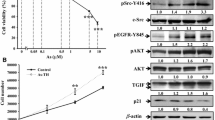
Abstract
Environmental and occupational exposure to arsenic is associated with increased risk of skin, urinary bladder and respiratory tract cancers. Increasing evidence indicates that arsenic acts at the level of tumor promotion by modulating the signaling pathways responsible for cell growth. One of this pathways might include c-Src dependent EGFR and MAPK activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welch AH, Helsel DR, Focazio MJ, Watkins SA: Arsenic in ground water supplies of the United States. In: W.R. Chappell, C.O. Abernathy, R.L. Calderon (eds). Arsenic Exposure and Health Effects. Elsevier Science Ltd., Oxford, UK, 1999, pp 9–17
Thornton I: Arsenic in the global environment: Looking towards the millennium. In: W.R. Chappell, C.O. Abernathy, R.L. Calderon (eds). Arsenic Exposure and Health Effects. Elsevier Science, Oxford, UK, 1999, pp 1–7
Tsuda T, Babazono A, Yamamoto E, Kurumatini N, Mino Y, Ogawa T, Kishi Y, Aoyama H: Ingested arsenic and internal cancer: A historical cohort study followed for 33 years. Am J Epidemiol 141: 198–209, 1995
Nriagu JO: Human health and ecosystem effects. In: Wiley and Sons Inc. (eds). Arsenic in the Environment. Wiley and Sons Inc., 1994
Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertz-Picciotto P, Duggan HM, Wood R, Kornett MJ, Smith MT: Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 97: 259–267, 1992
Chiou HY, Hsueh YM, Liaw KF, Horng SF, Chiang MH, Pu YS, Lin JS, Huang CH, Chen CJ: Incidence of internal cancers and ingested inorganic arsenic: A 7 year follow-up study in Taiwan. Cancer Res 55: 1296–1300, 1995
Cebrian ME, Albores A, Garcia-Vargas G, Razo LMD, Ostrosky-Wegman P: Chronic arsenic poisoning in humans: The case of Mexico. In: J.O. Nriagu (ed). Arsenic in the Environment, Part II: Human Health and Ecosystem Effects. John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1994, pp 93–107
Mazumder DNG, Gupta JD, Santra A, Pal A, Ghose A, Sarkar S: Chronic arsenic toxicity in West Bengal - the worst calamity in the world. J Indian Med Assoc 96: 4–8, 1997
Maloney ME: Arsenic in dermatology. Dermatol Surg 22: 301–304, 1996
Chai C-Y, Yu H-S, Yen H-T, Tsai K-B, Chen S-S, Yu C-L: The inhibitory effect of UVB irradiation on the expression of p53 and Ki-67 proteins in arsenic-induced Bowen's disease. J Cutan Pathol 24: 8–13, 1997
IARC (eds): Arsenic and Arsenic Compounds. IARC Monograph on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Overall Evaluations of Carcinogenicity. IARC, 1987, pp 100–106
Hopenhayn-Rich C, Biggs ML, Fuchs A, Bergoglio R, Tello EE, Nicolli H, Smith AH: Bladder cancer mortality associated with arsenic in drinking water in Argentina. Epidemiology 7: 117–124, 1996
Smith AH, Goycolea M, Haque R, Biggs ML: Marked increase in bladder and lung cancer mortality in a region of Northern Chile due to arsenic in drinking water. Am J Epidemiol 147: 660–669, 1998
Viren J, Silvers A: Nonlinearity in the lung cancer dose-response for airborne arsenic: Apparent confounding by year of hire in evaluating lung cancer risks from arsenic exposure in Tacoma smelter workers. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 30: 117–129, 1999
Schwartz RA: Arsenic and the skin. Int J Dermatol 36: 241–250, 1997
Engel RR, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Receveur O, Smith AH: Vascular effects of chronic arsenic exposure: A review. Epidemiol Rev 16: 184–209, 1994
Tseng CH, Chong CK, Chen CJ, Tai TY: Dose-response relationship between peripheral vascular disease and ingested inorganic arsenic among residents in blackfoot disease endemic villages in Taiwan. Atherosclerosis 120: 125–133, 1996
Simeonova PP, Luster MI: Mechanisms of arsenic carcinogenicity: Genetic or epigenetic mechanisms? J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19: 281–286, 2000
Kitchin KT: Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172: 249–261, 2001
Lee TC, Tanaka N, Lamb PW, Gilmer TM, Barrett JC: Induction of gene amplification by arsenic. Science 241: 79–81, 1988
Lerda D: Sister-chromatid exchange (SCE) among individuals chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Mutat Res 312: 111–120, 1994
Li JH, Rossman TG: Inhibition of DNA ligase activity by arsenite: A possible mechanism of its comutagenesis. Mol Toxicol 2: 1–9, 1989
Cavigelli M, Li WW, Lin A, Su B, Yoshioka K, Karin M: The tumor promoter arsenite stimulates AP-1 activity by inhibiting a JNK phosphatase. Embo J 15: 6269–6279, 1996
Burleson FG, Simeonova PP, Germolec DR, Luster MI: Dermatotoxic chemical stimulate of c-jun and c-fos transcription and AP-1 DNA binding in human keratinocytes. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 93: 131–148, 1996
Kachinskas DJ, Qin Q, Phillips MA, Rice RH: Arsenate suppression of human keratinocyte programming. Mutat Res 386: 253–261, 1997
Germolec DR, Spalding J, Yu HS, Chen GS, Simeonova PP, Humble MC, Bruccoleri A, Boorman GA, Foley JF, Yoshida T, Luster MI: Arsenic enhancement of skin neoplasia by chronic stimulation of growth factors. Am J Pathol 153: 1775–1785, 1998
Klimecki WT, Borchers AH, Egbert RE, Nagle RB, Carter DE, Bowden GT: Effects of acute and chronic arsenic exposure of human-derived keratinocytes in an in vitro human skin equivalent system: A novel model of human arsenicism. Toxicol In Vitro 11: 89–98, 1997
Brown JL, Kitchin KT: Arsenite, but not cadmium, induces ornithine decarboxylase and heme oxygenase activity in rat liver: Relevance to arsenic carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 98: 227–231, 1996
Trouba KJ, Glanzer JG, Vorce RL: Wild-type and Ras-transformed fibroblasts display differential mitogenic responses to transient sodium arsenite exposure. Toxicol Sci 50: 72–81, 1999
Simeonova PP, Wang S, Toriuma W, Kommineni V, Matheson J, Unimye N, Kayama F, Harki D, Ding M, Vallyathan V, Luster MI: Arsenic mediates cell proliferation and gene expression in the bladder epithelium: Association with AP-1 transactivation. Cancer Res 60: 3445–3453, 2000
Arnold LL, Cano M, St John M, Eldan M, van Gemert M, Cohen SM: Effects of dietary dimethylarsinic acid on the urine and urothelium of rats. Carcinogenesis 20: 2171–2179, 1999
Huang C, Bode AM, Chen NY, Ma WY, Li J, Nomura M, Dong Z: Transactivation of AP-1 in AP-1-luciferase reporter transgenic mice by arsenite and arsenate. Anticancer Res 21: 261–267, 2001
Angel P, Karin M: The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cellproliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1072: 129–157, 1991
Tiniakos DG, Mellon K, Anderson JJ, Robinson MC, Neal DE, Horne CH: c-jun oncogene expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Br J Urol 74: 757–761, 1994
Skopelitou A, Hadjiyannakis M, Dimopoulos D, Kamina S, Krikoni O, Alexopoulou V, Rigas C, Agnantis NJ: p53 and c-jun expression in urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma: Correlation with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) histological grade and clinical stage. Eur Urol 31: 464–471, 1997
Rossman TG, Uddin AN, Burns FJ, Bosland MC: Arsenite is a cocarcinogen with solar ultraviolet radiation for mouse skin: An animal model for arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 176: 64–71, 2001
Yamamoto S, Konishi Y, Matsuda T, Murial T, Shibata MA, Matsui-Yuasa I, Otani S, Kuroda K, Endo G, Fukushima S: Cancer induction by an organic arsenic compound, Dimethylarsince acid (Cacodylic acid), in F344/DuCrj rats after pretreatment with five carcinogens. Cancer Res 55: 1271–1276, 1995
Su B, Karin M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Immunol 8: 402–411, 1996
Treisman R: Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 205–215, 1996
Karin M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades as regulators of stress responses. Ann NY Acad Sci 851: 139–146, 1998
Cavigelli M, Li WW, Lin A, Su B, Yoshioka K, Karin M: The tumor promoter arsenite stimulates AP-1 activity by inhibiting a JNK phosphatase. Embo J 15: 6269–6279, 1996
Liu Y, Guyton KZ, Gorospe M, Xu Q, Lee JC, Holbrook NJ: Differential activation of ERK, JNK/SAPK and P38/CSBP/RK map kinase family members during the cellular response to arsenite. Free Rad Biol Med 21: 771–781, 1996
Chen W, Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ, Liu Y: Tumor promoter arsenite activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through a signaling pathway mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor and Shc. Mol Cell Biol 18: 5178–5188, 1998
Huang C, Ma WY, Li J, Goranson A, Dong Z: Requirement of Erk, but not JNK, for arsenite-induced cell transformation. J Biol Chem 274: 14595–14601, 1999
Simeonova PP, Wang S, Hulderman T, Luster MI: c-Src-dependent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by arsenic: Role in carcinogenesis. J Biol Chem 26: 26, 2001
Thogersen VB, Jorgensen PE, Sorensen BS, Bross P, Orntoft T, Wolf H, Nexo E: Expression of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor in human bladder cancer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 59: 267–277, 1999
Chen WS, Lazar CS, Poenie M, Tsien RY, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG: Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. Nature 328: 820–823, 1987
Carpenter G: Employment of the epidermal growth factor receptor in growth factor-independent signaling pathways. J Cell Biol 146: 697–702, 1999
Bjorge JD, Jakymiw A, Fujita DJ: Selected glimpses into the activation and function of Src kinase. Oncogene 19: 5620–5635, 2000
Akhand AA, Pu M, Senga T, Kato M, Suzuki H, Miyata T, Hamaguchi M, Nakashima I: Nitric oxide controls src kinase activity through a sulfhydryl group modification-mediated Tyr-527-independent and Tyr-416-linked mechanism. J Biol Chem 274: 25821–25826, 1999
Lopez S, Miyashita Y, Simons SS Jr: Structurally based, selective interaction of arsenite with steroid receptors. J Biol Chem 265: 16039–16042, 1990
Griendling KK, Sorescu D, Lassegue B, Ushio-Fukai M: Modulation of protein kinase activity and gene expression by reactive oxygen species and their role in vascular physiology and pathophysiology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 2175–2183, 2000
Chen K, Vita JA, Berk BC, Keaney JF Jr: c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation by hydrogen peroxide in endothelial cells involves SRC-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. J Biol Chem 276: 16045–16050, 2001
Vacaresse N, Lajoie-Mazenc I, Auge N, Suc I, Frisach MF, Salvayre R, Negre-Salvayre A: Activation of epithelial growth factor receptor pathway by unsaturated fatty acids. Circ Res 85: 892–899, 1999
Tice DA, Biscardi JS, Nickles AL, Parsons SJ: Mechanism of biological synergy between cellular Src and epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1415–1420, 1999
Biscardi JS, Maa MC, Tice DA, Cox ME, Leu TH, Parsons SJ: c-Srcmediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J Biol Chem 274: 8335–8343, 1999
Maa MC, Leu TH, McCarley DJ, Schatzman RC, Parsons SJ: Potentiation of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated oncogenesis by c-Src: Implications for the etiology of multiple human cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 6981–6985, 1995
Irby RB, Yeatman TJ: Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene 19: 5636–5642, 2000
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E: Integrin signaling. Science 285: 1028–1032, 1999
Weed SA, Parsons JT: Cortactin: Coupling membrane dynamics to cortical actin assembly. Oncogene 20: 6418–6434, 2001
Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Paxton WG, Schieffer E, Bernstein KE: Electroporation of pp60c-src antibodies inhibits the angiotensin II activation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 270: 15734–15738, 1995
Sayeski PP, Ali MS, Hawks K, Frank SJ, Bernstein KE: The angiotensin II-dependent association of Jak2 and c-Src requires the N-terminus of Jak2 and the SH2 domain of c-Src. Circ Res 84: 1332–1338, 1999
Abe J, Takahashi M, Ishida M, Lee JD, Berk BC: c-Src is required for oxidative stress-mediated activation of big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1. J Biol Chem 272: 20389–20394, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simeonova, P.P., Luster, M.I. Arsenic carcinogenicity: Relevance of c-Src activation. Mol Cell Biochem 234, 277–282 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015971118012
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015971118012