Abstract
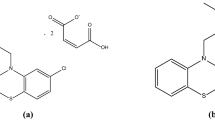
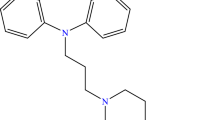
The stability–pH profile of the γ-aminobutyric acid prodrug, Progabide, was found to be bell shaped, with maximum stability occurring at pH 6 to 7 with a t 1/2 of 126 min. Of its metabolic derivatives, the deamidated product PGA degraded in a similar fashion to Progabide, whereas the hydrolytic degradation product SL79.182 was, as expected, a stable compound. Progabide behaved as a typical weak base, with its solubility increasing with a decrease in pH. SL79.182 behaved as a typical phenolic weak acid, with its solubility increasing with an increase in pH. Both compounds displayed low intrinsic solubilities of 14.5 × 10−5 M for Progabide and 33.4 × 10−6 M for SL79.182. An increase in temperature resulted in an increase in the solubility but a decrease in the stability of Progabide. The data obtained indicate that the gastric pH and gastric emptying rate will have a profound effect on the oral bioavailability of Progabide.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. A. Sinkula. In E. B. Roche (ed.), Design of Biopharmaceutical Properties Through Prodrugs and Analogs, American Pharmeutical Association, Washington, D.C., 1977, pp. 1–17.
G. Bartholini, B. Scatton, B. Zivkovic, and K. G. Lloyd. In P. Krogsgaard-Larsen, J. Scheel-Krager, and H. Kofod (eds.), GABA-Neurotransmitters, Munksgaard, Copenhagen, 1979, pp. 326–339.
J. P. Kaplan, B. M. Raizon, M. Desarmenien, P. Feltz, P. M. Headley, P. Worms, K. G. Lloyd, and G. Bartholini. J. Med. Chem. 23:702–704 (1980).
N. F. Farraj, S. S. Davis, G. D. Parr, and H. N. E. Stevens. Pharm. Res. 4:28–32 (1987).
N. F. Farraj, S. S. Davis, G. D. Parr, and H. N. E. Stevens. Submitted for publication (1987).
R. M. C. Dawson, D. C. Elliott, W. H. Elliott, and K. M. Jones. Data for Biochemical Research, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1986, pp. 417–448.
B. Maupas, S. Letellier, M. B. Fleury, and B. Mompon. Analysis 12:122–128 (1984).
D. G. Pope. Drug Cosmet. Ind. 127:48–66, 110–116 (1980).
B. Ferrandes, A. Durand, P. Padovani, J. T. Burke, D. Garrigou, J. Fraisse-Andre, P. Hermann, and J. Allen. In G. Bartholini, L. Bossi, K. G. Lloyd, and P. L. Morselli (eds.), Epilepsy and GABA Receptor Agonists, L.E.R.S. Monograph Series, Vol. 3, Raven Press, New York, 1985, pp. 217–230.
N. F. Farraj, S. S. Davis, G. D. Parr, and H. N. E. Stevens. Int. J. Pharm., in press (1988).
S. Miyazaki, H. Inoue, T. Nadai, T. Arita, and M. Nakano. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27, 1441:1447 (1979).
Z. T. Chowhan. J. Pharm. Sci. 67:1257–1260 (1978).
H. A. Krebs and J. C. Speakman. J. Chem. Soc. 593–595 (1945).
S. Niazi. Textbook of Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, 1979.
B. E. Ballard. J. Pharm. Sci. 63:1345–1358 (1974).
M. A. Lauffer. Entropy Driven Processes in Biology, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1975.
K. Embil and G. Torosian. J. Pharm. Sci. 71:191–193 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farraj, N.F., Davis, S.S., Parr, G.D. et al. The Stability and Solubility of Progabide and Its Related Metabolic Derivatives. Pharm Res 5, 226–231 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015941729400
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015941729400