Abstract
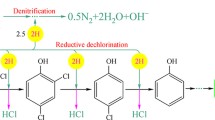
Microorganisms collected from sediments of Ho-Tsin River in southern Taiwan were used in this study. The ability to dechlorinate hexachlorobenzene (HCB) was induced by enrichmentincubation in yeast extract amended culture and acclimation withHCB. Addition of lactate or replacement of yeast extract by lactate did not enhance the dechlorination ability. With strong electron capturing capability, denitrifying bacteria resulted incomplete inhibition of dechlorination in the mixed culturecontained nitrate. In the culture amended with sulfate, sulfate reducing bateria shared electrons and nutrient with HCB-dechlorinating consortium but grabbed more electrons when treated with vancomycin. Results from multi-factors tests indicate that the influences of factors on dechlorination werecomplicated. Dechlorinating microbes, electron suppliers, sulfatereducing bacteria and denitrifying bacteria, all possibly caused a great effect on dechlorination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association: 1976a, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 14th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, pp. 427–429.
American Public Health Association: 1976b, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 15th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, pp. 436–440.
Chang, B. V., Zheng, J. X. and Yuan, S. Y.: 1996, 'Effects of alternative electron donors, acceptors and inhibitors on pentachlorophenol dechlorination', Chemosphere 33, 313–320.
Chang, B. V., Chen, I. M., Yuan, S. Y. and Wang, Y. S.: 1997, 'Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene by an anaerobic mixed culture', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 25–32.
Chang, B. V., Chiang, C. W. and Yuan, S. Y.: 1999, 'Microbial dechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in anaerobic sewage sludge', J. Environ. Sci. Health. (B) 34, 491–507.
Chen, I. M., Chang, F. C. and Wang, Y. S.: 1997, 'Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene and polychlorinated biphenyls in anaerobic sediments from tropical rivers with enrichment', in Proc. 17th Symposium on Chlorinated Dioxins and Related Compounds 33, Indianapolis, Indiana, U.S.A., August 25–29 1997, pp. 189–192.
Chen, I. M., Chang, F. C., Chang, B. V. and Wang, Y. S.: 2000, 'Specificity of microbial activities in the reductive dechlorination of chlorinated benzenes', Water Environ. Res. 72, 1–5.
Chen, I. M., Chang, F. C. and Wang, Y. S.: 2001, 'Correlation of gas chromatographic properties of chlorobenzenes and polychlorinated biphenyls with the occurrence of reductive dechlorination by untamed microorganisms', Chemosphere (in press).
Distefano, T. D., Gossett, J. M. and Zinder, S. H.: 1992, 'Hydrogen as an electron donor for de-chlorination of tetrachloroethene by anaerobic mixed culture', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 3622–3629.
Fathepure, B. Z., Tiedje, J. M. and Boyd, S. A.: 1988, 'Reductive dechlorination of hexachloroben-zene to tri-and di-chlorobenzenes in anaerobic sewage sludge', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 327–330.
Häggblom, M. M., Rivera, M. D. and Young, L. Y.: 1993, 'Influence of alternative electron acceptors on the anaerobic biodegradability of chlorinated phenols and benzoic acids', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 1162–1167.
Holliger, C., Schraa, G., Stams, A. J. M. and Zehnder, A. J. B.: 1992, 'Environment and properties of an anaerobic mixed culture reductively dechlorinating 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene to 1,3-dichlorobenzene', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 1636–1644.
Jain, M. K., Zeikus, J. G. and Bhatnagar, L.: 1991, 'Methanogens', in P. N. Levett (ed.), Anaerobic Microbiology, Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York, pp. 223–245.
MacFarlane, G. T. and Gibson, G. R.: 1991, 'Sulfate Reducing Bacteria', in P. N. Levett (ed.), Anaerobic Microbiology, Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York, pp. 201–222.
Nowak, J., Kirsch, N. H., Hegemann, W. and Stan, H.-J.: 1996, 'Total reductive dechlorination of chlorobenzenes to benzene by a methanogenic mixed culture enriched from Saale river sediment', Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 700–709.
Pavlostathis, S. G. and Zhuang, P.: 1993, 'Reductive dechlorination of chloroalkenes in microcosms developed with a field contaminated soil', Chemosphere 27, 585–595.
Ramanand, K., Balba, M. T. and Duffy, J.: 1993, 'Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated benzenes and toluenes under methanogenic condition', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 3266–3272.
Rosenbrock, P., Martens, R., Buscot, F. and Munch, J. C.: 1997, 'Initiation of [36Cl]hexachlorobenzene dechlorination in three different soils under artificially induced anaerobic conditions', Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 115–120.
Wang, Y. S., Subba-Rao, R. V. and Alexander, M.: 1984, 'Effect of substrate concentration and or-ganic and inorganic compounds on the occurrence and rate of mineralization and cometabolism', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46, 1195–1200.
Wang, Y. S., Madsen, E. L. and Alexander, M.: 1985, 'Microbial degradation by mineralization or cometabolism determined by chemical concentration and environment', J. Agric. Food. Chem. 33, 495–499.
Widdel, F.: 1988a, 'Microbiology and Ecology of Sulfate-and Sulfur-Reducing Bacteria', in A. J. B. Zehnder (ed.), Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms, Wiley Interscience Publication, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 477–481.
Widdel, F.: 1988b, 'Biochemistry of Methane Production', in A. J. B. Zehnder (ed.), Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms, Wiley Interscience Publication, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 710–714.
Zehnder, A. J. B. and Wuhrmann, K.: 1976, 'Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes', Science 194, 1165–1166.
Zhuang, P. and Pavlostathis, S. G.: 1995, 'Effect of temperature, pH and eletron donor on the microbial dechlorination of chloroalkenes', Chemosphere 31, 3537–3548.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, IM., Chang, BV., Yuan, SY. et al. Reductive Dechlorination of Hexachlorobenzene under Various Additions. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 139, 61–74 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015861217112
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015861217112