Abstract
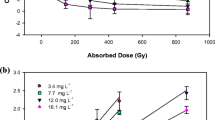
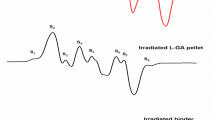
To evaluate the effects of a neutron activation radiolabeling technique on an enteric-coated multiparticulate formulation of erythromycin, test quantities were produced under industrial pilot scale conditions. The pellets contained the stable isotope erbium oxide (Er-170), which was later converted by neutron activation into the short-lived gamma ray-emitting radionuclide, erbium-171. In vitro studies indicated that the dissolution profile, acid resistance, and enteric-coated surface of the pellets were minimally affected by the irradiation procedure. Antimicrobial potency was also unaffected, as determined by microbiological assay. Neutron activation thus appears to simplify the radiolabeling of complex pharmaceutical dosage forms for in vivo study by external gamma scintigraphy.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. L. Casey, R. M. Beihn, G. A. Digenis, and M. S. Shambhu. J. Pharm. Sci. 65:1412–1413, (1976).
P. B. Daly, S. S. Davis, M. Frier, J. G. Hardy, J. W. Kennedy, and C. G. Wilson. Int. J. Pharm. 10:17–24 (1982).
E. Hunter, J. T. Fell, R. T. Calvert, and H. Sharm. Int. J. Pharm. 4:175–183 (1980).
M. Jay, R. M. Beihn, G. A. Digenis, F. H. Deland, L. Cald-well, and A. R. Mlodozeniec. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 37:266–268 (1985).
M. Jay, G. A. Digenis, T. S. Foster, and D. R. Antonow. Digest. Dis. Sci. 31:139–144 (1986).
A. Parr, M. Jay, G. A. Digenis, and R. M. Beihn. J. Pharm. Sci. 74:590–591 (1985).
A. Parr, R. M. Beihn, and M. Jay. Int. J. Pharm. 32:251–256 (1986).
D. P. Hutcheson, D. H. Gray, B. Venugopol, and T.D. Luckey. Environ. Qual. Safety 1:74–80 (1975).
D. W. Bruce, B. E. Hietrink, and K. P. Dubois. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 5:750–759 (1963).
D. P. Hutcheson, B. Venugopal, D. H. Gray, and T. Luckey. J. Nutri. 109:702–707 (1979).
F. J. Baker and M. R. Breach. Medical Microbiological Techniques, Butterworths, Woburn, Mass., 1980, pp. 345–346.
K. Tsuji, P. D. Rahn, and K. A. Steindler. J. Pharm. Sci. 72:23–26 (1983).
E. Kivan and E. Rodriguez. Macromol. Sci. Phys. 7:209–224 (1973).
G. Newkome and C. Marston. J. Org. Chem. 50:4161–4163 (1985).
A. Parr and M. Jay. Pharm. Res. 4:524–526 (1987).
A. Parr, R. M. Beihn, R. M. Franz, G. J. Szpuner, and M. Jay. Pharm. Res. 4:486–489 (1987).
G. P. Jacbos. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 35:1023–1027 (1984).
G. P. Jacobs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 6:547–568 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parr, A.F., Digenis, G.A., Sandefer, E.P. et al. Manufacture and Properties of Erythromycin Beads Containing Neutron-Activated Erbium-171. Pharm Res 7, 264–269 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015826229323
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015826229323