Abstract
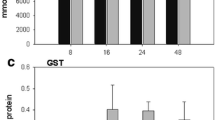
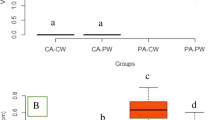
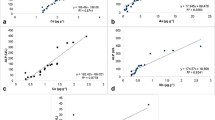
We assessed the effects on fish of lead (Pb) released to streamsby smelters located in Trail, BC (Canada), E. Helena, MT, Herculaneum, MO, and Glover, MO. Fish were collected by electrofishing from sites located downstream of smelters and from reference sites. Blood from each fish was analyzed for δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) activity and hemoglobin (Hb), and samples of blood, liver, or carcass were analyzed for Pb, zinc (Zn), or both. Fish collected downstreamof all four smelters sites had elevated Pb concentrations, decreased ALAD activity, or both relative to their respectivereference sites. At E. Helena, fish from the downstream site also had lower Hb concentrations than fish from upstream. Differences among taxa were also apparent. Consistent with previous studies, ALAD activity in catostomids (Pisces: Catostomidae-northern hog sucker, Hypentelium nigricans;river carpsucker, Carpiodes carpio; largescale sucker, Catostomus macrocheilus; and mountain sucker, C. platyrhynchus) seemed more sensitive to Pb-induced ALAD inhibition than the salmonids (Pisces: Salmonidae-rainbow trout,Oncorhynchus mykiss; brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis) or common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Some of these differences may have resulted from differential accumulation of Zn, which was not measured at all sites. We detected no ALAD activity in channel catfish (Ictaluruspunctatus) from either site on the Mississippi River at Herculaneum, MO. Our findings confirmed that Pb is releasedto aquatic ecosystems by smelters and accumulated by fish, andwe documented potentially adverse effects of Pb in fish. We recommend that Zn be measured along with Pb when ALAD activityis used as a biomarker and the collection of at least 10 fish ofa species at each site to facilitate statistical analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, W. L. and Havera, S. P.: 1985, ‘Blood lead, porphyrin, and ingested shot for detecting poisoning in waterfowl', Wildl. Soc. Bull. 13, 26–31.
Baker Jr., E. L., Hayes, C. G., Landrigan, P. J., Handke, J. L., Leger, R. T. and Housworth, W. J.: 1977, ‘A nationwide survey of heavy metal absorption in children living near primary copper, lead, and zinc smelters', Amer. J. Epidemiol. 106, 261–273.
Benes, P., Cejchanova, M. and Havlik, B.: 1985, ‘Migration and speciation of lead in a river system heavily polluted from a smelter', Water Res. 19, 1–6.
Beretic, T., Zibar-Sikic, J., Prpic-Majic, D. and Tudor, M.: 1980, ‘Some Morphological and Hematological Parameters of Abnormal Lead Absorption in Fish', in M. Branica, and K. Zdenka (eds), Lead in the Marine Environment, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 263–269.
Bortelson, G. C., Cox, S. E., Munn, M. D., Schumaker, R. J., Block, E. K., Bucy, L. R. and Cornelius S. B.: 1994, Sediment Quality Assessment of Franklin D. Roosevelt Lake and the Upstream Reach of the Columbia River, Washington, 1992, U.S. Geological Survey, Open-file Report 94-315, Tacoma, WA. 130 p.
Brigham, M. E., Goldstein, R. M. and Tornes, L. H.: 1998, Trace Elements and Organic Chemicals in Stream-Bottom Sediments and Fish Tissues, Red River of the North Basin, Minnesota, North Dakota, and South Dakota, 1992-1995. U.S. Geological Survey, Water-Resources Investigations Report 97-4043, Mounds View, MN. 32 p.
Burden, V. M., Sandheinrich, M. B. and Caldwell, C. A.: 1998, ‘Effects of lead on the growth and ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss', Environ. Pollut. 101, 285–289.
Chapman, D. C., Allert, A. L., Fairchild, J. F., May, T. W., Schmitt, C. J. and Callahan, E. V.: 2001, Toxicity and Bioavailability of Metals in the Missouri River Adjacent to a Lead Refinery, U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division, Biological Science Report USGS/BRD/BSR 2001-0004. Columbia, MO. 27 p.
Conner, E. A. and Fowler, B. A.: 1994. ‘Biochemical and immunological properties of hepatic ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus)', Aquatic Toxicol. 28, 37–52.
Crossey, M. J. and La Point, T. W.: 1988, ‘A comparison of periphyton community structural and functional responses to heavy metals', Hydrobiologia 162, 109–121.
Dieter, M. P.: 1979, ‘Blood ?-Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase (ALA-D) to Monitor Lead Contamination in Canvasback Ducks (Aythya valisineria)', in Animals as Monitors of Environmental Pollution, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pp. 177–191.
Dwyer, F. J., Schmitt, C. J., Finger, S. E. and Mehrle, P. M.: 1988, ‘Biochemical changes in longear sunfish, Lepomis megalotis, associated with lead, cadmium and zinc from mine tailings', J. Fish Biol. 33, 307–317.
Finelli, V.: 1977, ‘Lead, Zinc, and ?-Aminolevulinate Dehydratase', in S. Lee and B. Peirano (ed.), Biochemical Effects of Environmental Pollutants, Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI, p. 351–364.
Goldstein, R. M. and DeWeese, L. R.: 1999, ‘Comparison of trace element concentrations in tissue of common carp and implications for monitoring', J. Amer. Water. Res. Assoc. 35, 1133–1140.
Gonzalez, O. J., Fernandez, J. and Martin, M.: 1987, ‘Inhibition of trout (Salmo gairdneri R.) PBG-synthase by some metal ions (Mg2+, Pb2+, Zn2+)', Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 86, 163–167.
Gonzales, M. and Tejedor, M. C.: 1992, ‘delta-ALAD activity variations in red blood cells in response to lead accumulation in Rock Doves (Columba livia)', Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 49, 527–534.
Harrison, S. E. and Klaverkamp, J. F.: 1990, ‘Metal contamination in liver and muscle of northern pike (Esox lucius) and white sucker (Catostomus commersoni) and in sediments from lakes near the smelter at Flin Flon, Manitoba', Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9, 941–956.
Haux, C. and Larsson, A.: 1982, ‘Influence of inorganic lead on the biochemical blood composition in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri', Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 6, 28–34.
Haux, C., Larsson, A., Lithner, G. and Sjobeck, M-L.: 1986, ‘A field study of physiological effects on fish in lead-contaminated lakes', Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 5, 283–288.
Henny, C. L., Blus L. J., Hoffman D. J. and Grove, R. A.: 1994, ‘Lead in hawks, falcons and owls wownstream from a mining site on the coeur d'Alene river, Idaho', Environ. Monit. Assess. 29, 267–288.
Henny, C. L., Blus L. J., Hoffman D. J., Sileao, L., Audet, D. J. and Snyder, M. R.: 2000, ‘Field evaluation of lead effects on Canada geese and mallards in the Coeur d'Alene Basin, Idaho', Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 39, 97–112.
Hodson, P. V., Blunt, B. R., Spry, D. J. and Austen, K.: 1977, ‘Evaluation of erythrocyte ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity as a short-term indicator in fish of a harmful exposure to lead', J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 34, 501–508.
Hodson, P. V., Blunt, B. R., Jensen, D. and Morgan, S.: 1979, ‘Effect of fish age on predicted and observed chronic toxicity of lead to rainbow trout in lake Ontario Water', J. Great Lakes Res. 5, 84–89.
Hodson, P. V., Blunt, B. R. and Whittle, D. R.: 1984, ‘Monitoring Lead Exposure in Fish', in V. W. Cairns, P. V., Hodson, and J. O. Nriagu (eds), Contaminant Effects on Fisheries, John Wiley and Sons, New York, p. 87–981.
Holcombe, G.W., Benoit, D. A., Leonard, E. N. and McKim, J. M.: 1976, ‘Long-term effects of lead exposure on three generations of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis)', J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 33, 1731–1741.
Hopkins, B. S., Clark, D. K., Schlendar, M. and Stinson, M.: 1985, Basic Water Monitoring Program-Fish Tissue and Sediment Sampling for 1984, Washington State Department of Ecology, Publication No. 85-7, Olympia, WA, 43 p.
Hutton, M.: 1983, ‘The effects of environmental lead exposure and in vitro zinc on tissue ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase in urban pigeons', Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 74C, 441–446.
Jackson, D. R. and Watson, A. P.: 1977, ‘Disruption of nutrient pools and transport of heavy metals in a forested watershed near a lead smelter', J. Environ. Qual. 6, 331–338.
Johansson-Sjobeck, M-L. and Larsson, A.: 1979, ‘Effects of inorganic lead on delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity and hematological variables in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri', Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 8, 419–431.
Johnson, A., Norton, D. and Yake, W.: 1988, An Assessment of Metals Contamination in Lake Roosevelt, Washington State Department of Ecology, Toxics Investigations/Ground Water Monitoring Section, Water Body Olympia, WA, 71 p.
Johnson, A., Norton, D., Yake, W. and Twiss, S.: 1990, ‘Transboundary metal pollution of the Columbia River', Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 45, 703–710.
Jordan,M. J.: 1975, ‘Effects of zinc smelter emissions and fire on a chestnut-oak woodland', Ecology 56, 78–91.
Joselow, M. M.: 1980, ‘Blood Zinc and Lead Poisoning', in J.O. Nriagu (ed.), Zinc in the Environment, Part II, Health Effects, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 171–181.
Krajnovic-Ozretic, M. and Ozretic, B.: 1980, ‘The ALA-D activity test in lead-exposed grey mullet Mugil auratus', Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 3, 187–191.
Larsen, P. and Sniesko, S. F.: 1961, ‘Comparison of various methods of determination of hemoglobin in trout blood', Progr. Fish Cult. 23, 8–17.
Lowe, T. P., May, T.W., Brumbaugh, W. G. and Kane, D. A.: 1985, ‘National Contaminant Biomonitoring Program-concentrations of seven elements in freshwater fish, 1978-1981', Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 14, 363–388.
Lower, W. R. and Tsutukawa, R. K.: 1978, ‘Statistical analysis of urinary aminolevulic acid (ALAU) excretion in the white-footed mouse associated with lead smelting',’ J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 1, 551–560.
Marcus, A. H. and Schwartz, J.: 1987, ‘Dose-response curves for erythrocyte protoporphyrin vs blood lead: effects of iron status', Environ. Res. 44, 221–227.
Moore, J. N., Luoma, S. J. and Peters, D.: 1991, ‘Downstream effects of mine effluent on an intermontane riparian system', Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 48, 222–242.
Munn, M. D., Cox, S. E. and Dean, C. J.: 1995, Concentrations of Mercury and Other Trace Elements in Walleye, Smallmouth Bass, and Rainbow Trout in Franklin D. Roosevelt Lake and the Upper Columbia River, Washington, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-195, Tacoma, WA, 35 p.
Munn, M. D. and Short, T. M.: 1997, ‘Spatial heterogeneity of mercury bioaccumulation by walleye in Franklin D. Roosevelt Lake and the Upper Columbia River', Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 126, 477–487.
Mushak, P., Davis, J. M., Crocetti, A. F. and Grant, L. D.: 1989, ‘Prenatal and postnatal effects of low-level lead exposure: integrated summary of a report to the U.S. congress on childhood lead poisoning', Environ. Res. 50, 11–36.
Nakagawa, H., Nakagawa, K. and Sato, T.: 1995, ‘Evaluation of erythrocyte ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity in the blood of carp Cyprinus carpio as an indicator in fish with water lead pollution', Fish. Sci. 61, 91–95.
Nriagu, J. O.: 1978, ‘Lead in the Atmosphere', in J. O. Nriagu (ed.), The Biogeochemistry of Lead in the Environment, Part A, Ecological Cycles, Elsevier/North Holland, New York, 137–140.
Olsen, B., Caldwell, C. A., Palawski, D. U. and Malloy, J. C.: 1997, Biological Indices of Lead Exposure in Relation to Heavy Metal Residues in Sediment and Biota from Prickly Pear Creek and Lake Helena, Montana, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Montana Ecological Services Field Office, Contaminant Report No. R6/214H/97, Helena, MT, 22 p.
Pagenkopf, G. K. and Maughan, A. D.: 1984, ‘Point Source Impact of a Lead Smelter, West Central Montana', in J. O. Nriagu (ed.), Environmental Impacts of Smelters, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 75–87.
Pilgrim, W. and Hughes, R. N.: 1994, ‘Lead, cadmium, arsenic, and zinc in the ecosystem surrounding a lead smelter', Environ. Monit. Assess. 32, 1–20.
Rodrigues, A. L., Bellinaso, M. L. and Dick, T.: 1989, ‘Effects of some metal ions on blood and liver delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase of Pimelodus maculates (Pisces, Pimelodidae)', Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 94B, 65–69.
Rosin, N.: 1998, ‘Herculaneum smelter', Mining Environ. Manage. 6, 10–12.
Ryck Jr., F. M.: 1974, Water Quality of the Southeast Ozark Mining Area, Missouri Department of Conservation, Jefferson City, Aquatic Series No. 10, 28 p.
Santos, M. A. and Hall, A.: 1990, ‘Influence of inorganic lead on the biochemical blood composition of the eel, Anguilla anguilla L.', Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 20, 7–9.
Schmitt, C. J.: 1999, ‘Environmental Contaminants', in M. J. Mac, P. A. Opler, C. E. Puckett Haecker, and P. D. Doran (eds), Status and Trends of the Nation's Biological Resources. Volume 1, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA, 131–166.
Schmitt, C. J. and Caldwell, C. A.: 1997, Biochemical Indicators of Mining-Derived Contaminants in Big Creek, Iron County, Missouri, Project Completion Report to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Region 3, Ecological Services Field Office, Columbia, MO, 11 p.
Schmitt, C. J., Dwyer, F. J. and Finger, S. E.: 1984, ‘Bioavailability of Pb and Zn from mine tailings indicated by erythrocyte ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-D) activity in suckers (Pisces: Catastomidae)', Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41, 1030–1040.
Schmitt, C. J., Wildhaber, M. L., Hunn, J. B., Nash, T., Tieger, M. N. and Steadman, B. L.: 1993, ‘Biomonitoring of lead-contaminated missouri streams with an assay for erythrocyte ?-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-D) activity in fish blood', Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 464–475.
Schmitt, C. J., Zajicek, J. L., May, T. W. and Cowman, D. F.: 1999, ‘Organochlorine chemical residues and elemental contaminants in U.S. freshwater fish, 1976-1986: national contaminant biomonitoring program', Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 162, 43–104.
Serdar, D., Yake, B. and Cubbage, J.: 1994, Contaminant Trends in Lake Roosevelt,Washington State Department of Ecology, Environmental Investigations and Laboratory Services Program, Water Body No. WA-CR-9010, Publication No. 94-185, Olympia, WA, 22 p.
Settle, D. M. and Patterson, C. C.: 1980, ‘Lead in albacore: guide to lead pollution in Americans', Science (Washington, DC) 207, 1167–1176.
Smith, A. L.: 1987, Levels of Metals and Metallothionein in Fish of the Columbia River Near the International Boundary, Environment Canada, Vancouver, BC, 133 p.
Tsai, E. C-E.: 1987, ‘Analysis of ambient lead concentrations around three secondary lead smelters', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 33, 321–329.
Tyre, G. L. and Barton, R. G.: 1986, ‘Treating critical areas in the Tennessee Copper Basin', J. Soil Water Conserv. 41, 381–382.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): 1977, Heavy Metal Pollution from Spillage at Ore Smelters and Mills, Office of Research and Development, Industrial Environmental Research Laboratory, Cincinnati, OH, EPA-600/2-77-171, 109 p.
U.S. EPA: 1979, The Health and Environmental Impacts of Lead. An Assessment of Needs for Limitations, Office of Toxic Substances, Washington, DC, EPA-560/2-79-001.
Vighi, M.: 1981, ‘Lead uptake and release in an experimental trophic chain', Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 5, 177–193.
Watson, A. P.: 1975, ‘Trace Element Impact on Forest Floor Litter in the New Lead Belt Region of Southeastern Missouri', in D. H. Hemphill (ed.), Trace Substances in Environmental Health-IX, University of Missouri Press, Columbia, 227–236.
Webber, D. N., Russo, A., Seale, D. B. and Spieler, R. E.: 1991, ‘Waterborne lead affects feeding abilities and neurotransmitter levels of juvenile fathead minnow Pimephales promelas', Aquat. Toxicol. 21, 71–80.
Wigfield, D. C., Wright, S. C., Chakrabarti, C. L. and Karwowska, R.: 1986, ‘Evaluation of the relationship between chemical and biological monitoring of low-level lead poisoning', J. Appl. Toxicol. 6, 231–235.
Woodward, D. F., Brumbaugh, W. G., DeLonay, A. J., Little, E. E. and Smith, C. E.: 1994, ‘Effects on rainbow trout fry of a metals-contaminated diet of benthic invertebrates from the Clark Fork River, Montana', Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 123, 51–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitt, C.J., Caldwell, C.A., Olsen, B. et al. Inhibition of Erythrocyte δ-Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase (ALAD) Activity in Fish from Waters Affected by Lead Smelters. Environ Monit Assess 77, 99–119 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015767503629
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015767503629