Abstract
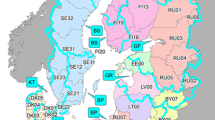
Human activities have greatly altered the nitrogen (N) cycle, accelerating the rate of N fixation in landscapes and delivery of N to water bodies. To examine relationships between anthropogenic N inputs and riverine N export, we constructed budgets describing N inputs and losses for 16 catchments, which encompass a range of climatic variability and are major drainages to the coast of the North Atlantic Ocean along a latitudinal profile from Maine to Virginia. Using data from the early 1990's, we quantified inputs of N to each catchment from atmospheric deposition, application of nitrogenous fertilizers, biological nitrogen fixation, and import of N in agricultural products (food and feed). We compared these inputs with N losses from the system in riverine export.
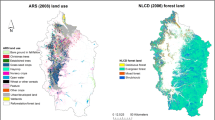
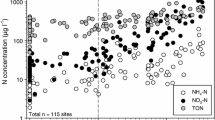
The importance of the relative sources varies widely by catchment and is related to land use. Net atmospheric deposition was the largest N source (>60%) to the forested basins of northern New England (e.g. Penobscot and Kennebec); net import of N in food was the largest source of N to the more populated regions of southern New England (e.g. Charles & Blackstone); and agricultural inputs were the dominant N sources in the Mid-Atlantic region (e.g. Schuylkill & Potomac). Over the combined area of the catchments, net atmospheric deposition was the largest single source input (31%), followed by net imports of N in food and feed (25%), fixation in agricultural lands (24%), fertilizer use (15%), and fixation in forests (5%). The combined effect of fertilizer use, fixation in crop lands, and animal feed imports makes agriculture the largest overall source of N. Riverine export of N is well correlated with N inputs, but it accounts for only a fraction (25%) of the total N inputs. This work provides an understanding of the sources of N in landscapes, and highlights how human activities impact N cycling in the northeast region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander RB, Slack JR, Ludtke AS, Fitzgerald KK & Schertz TL (1998) Data from selected U.S. Geological Survey national stream water quality monitoring networks.Water Resources Research 34(9): 2401–2405
ApSimon HM, Kruse M & Bell JNB (1987) Ammonia emissions and their role in acid deposition. Atmospheric Environment 21: 1939–1946
Barkmann J & Schwintzer CR (1999) Rapid N2 fixation in pines? Results of a Maine field study. Ecol. 79(4): 1453–1457
Battye R, Battye W, Overcash C & Fudge S (1994) Development and selection of ammonia emission factors. Final Report prepared by EC/R Incorporated for EPA Atmospheric Research and Exposure Assessment Lab, EPA Contract Number 68-D3-0034
Battaglin WA & Goolsby DA (1994) Spatial Data in Geographic Information System Format on Agricultural Chemical Use, Land Use, and Cropping Practices in the United States. USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report 94-4176 Report available online at http://water.usgs.gov/pubs/wri944176/. Data and metadata available on-line at http://water.usgs.gov/GIS/metadata/usgswrd/nit91.html
Bleken MA & Bakken LR (1997) The nitrogen cost of food production: Norwegian society. Ambio 26(3): 134–142
Boring LR & Swank WT (1984) The role of black locust (Robinia pseudo-acacia) in forest succession. J. Ecol. 72: 749–766
Bouwman AF, Lee DS, Asman WAH, Dentener FJ, Van Der Hoek KW & Olivier GJ (1997) A global high-resolution emission inventory for ammonia. Global biogeochemical cycles 11(4): 61–587
Bricker SB, Clement CG, Pirhalla DE, Orland SP & Farrow DGG (1999) National Estuarine Eutrophication Assessment: A Summary of Conditions, Historical Trends, and Future Outlook. National Ocean Service, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Springs MD
Brink GE (1990) Seasonal dry matter, nitrogen and dinitrogen fixation patterns of crimson and subterranean clovers. Crop Sci. 30: 1115–1118
Buijsman E, Maas HFM & Asman WAH (1987) Anthropogenic NH3 emissions in Europe. Atmospheric Environment 21: 1009–1022
Campbell JL, Hornbeck JW, McDowell JW, Buso DC, Shanley JB & Likens GE (2000) Dissolved organic nitrogen budgets for upland, forested ecosystems in New England. Biogeochemistry 42: 123–142
Caraco NF & Cole JJ (1999) Human impact on nitrate export: an analysis using major world rivers. Ambio 28(2): 167–170
Castro MS, Driscoll CT, Jordan TE, Reay WG, Boynton WR, Seitzinger SP, Styles RV & Cable JE (2001) Contribution of atmospheric deposition to the total nitrogen loads to thirty-four estuaries on the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of the United States. In: Valigura RA et al. (Eds) Nitrogen Loading in Coastal Water Bodies: an Atmospheric Perspective (pp 77–106). AGU
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Schimel DS, Fisher H, Howarth RW, Hedin LO, Perakis SS, Latty EF, Von Fischer JC, Elseroad A & Wasson MF (1999) Global patterns of terrestrial biological nitrogen fixation in natural systems. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 13: 623–645
Cohn TA et al. (1992) The validity of a simple statistical model for estimating fluvial constitute loads: an empirical study involving loads entering the Chesapeake Bay.Water Resour. Res. 28: 2353–2363
Currie WS, Aber JD, McDowell WH, Boone RD & Magill AH (1996) Vertical transport of dissolved organic C and N under long-term N amendments in pine and hardwood forests. Biogeochemistry 35: 471–505
Deibert EJ, Bijeriego M & Olson RA (1979) Utilization of 15N fertilizer by nodulating and non-nodulating soybean isolines. Agron. J. 71: 717–723
Dentener FJ & Crutzen PJ (1994) A three-dimensional model of the global ammonia cycle. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry 19: 331–369
EMEP (2001) Co-operative Programme for Monitoring and Evaluation of the Long-Range Transmission of Air Pollutants in Europe (EMEP), source-receptor matrices and import/export budgets for 1998. [online] URL: http://www.emep.int/index.html
Fangmeier A, Hadwiger-Fangmeier A, Van der Eerden L & Jager HJ (1994) Effects of Atmospheric Ammonia on Vegetation-A Review. Environmental Pollution
Galloway JN, Schlesinger WH, Levy H II, Michaels A & Schnoor JL (1995) Nitrogen fixation: anthropogenic enhancement-environmental response. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 9: 235–252
Garrow JS, James WPT & Ralph A (Eds) (2000) Human nutrition and dietetics 10th ed. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 900 pp
Galperin MV & MA Sofiev (1998) The long-range transport of ammonia and ammonium in the northern hemisphere. Atmospheric Environment, 32(3): 373–380
Goolsby DA, Battaglin WA, Lawrence GB, Artz RS, Aulenbach BT & Hooper RP (1999) Gulf of Mexico hypoxia assessment, Topic #3, Flux and sources of nutrient in the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River basin. Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources, Hypoxia Work Group for the Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Catchment Nutrient Task Force
Grant D & Binkley D (1987) Rates of free-living nitrogen fixation in some Piedmont forest types. Forest Sci. 33(2): 548–551
Ham GE & Caldwell AC (1978) Fertilizer placement effects on soybean seed yield, N2 fixation and 33P uptake. Agron. J. 70: 779–783
Heichel GH, Barnes DK, Vance CP & Henjum KI (1984) N2 fixation, and N and dry matter partitioning during a 4-year alfalfa stand. Crop Sci. 24: 811–815
Hendrickson QQ (1990) Asymbiotic nitrogen fixation and soil metabolism in three Ontario forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 22: 967–971
Holland EA, Dentener FJ, Braswell BH & Sulzman JM (1999) Contemporary and preindustrial global reactive nitrogen budgets. Biogeochem. 46: 7–43
Howarth RW, Billen G, Swaney D, Townsend A, Jaworski N, Lajtha K, Downing JA, Elmgren R, Caraco N, Jordan T, Berendse F, Freney J, Kudeyarov V, Murdoch P & Zhao-Liang Z (1996) Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: natural and human influences. Biogeochem. 35: 75–139
Hurd TM, Raynal DJ & Schwintzer CR (2001) Symbiotic N2 fixation of Alnus incana spp. rugosa in shrub wetlands of the Adirondack Mountains, New York, U.S.A. Oecologia 126: 94–103
Jaworski NA, Howarth RW & Hetling LJ (1997) Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen oxides onto the landscape contributes to coastal eutrophication in the Northeast United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31: 1995–2004
Johnson DW & Lindberg SE (Eds) (1991) Atmospheric deposition and forest nutrient cycling. Ecological Series 91. Springer-Verlag, NY
Jordan TE & Weller DE (1996) Human contributions to terrestrial nitrogen flux. BioScience 46: 655–664
Kittel TGF, Royle JA, Daly C, Rosenbloom NA, Gibson WP, Fisher HH, Schimel DS, Berliner LM & VEMAP2 Participants (1997) A gridded historical (1895-1993) bioclimate dataset for the conterminous United States. In: Reno NV (Ed) Proceedings of the 10th Conference on Applied Climatology, 20-24 October 1997 (pp 219–222). American Meteorological Society, Boston
Labandera C, Danso SKA, Pastorini D, Curbelo S & Martin V (1988) Nitrogen fixation in a white clover-fescue pasture using three methods of nitrogen-15 application and residual nitrogen-15 uptake. Agron. J. 80: 265–268
Lander CH & Moffitt D (1996) 1996 Nutrient Use in Cropland Agriculture (Commercial Fertilizers and Manure): Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Working Paper 14, RCAIII, NRCS, United States Department of Agriculture
Lovett GM & Lindberg SE (1993) Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of nitrogen in forests. Can. J. For. Res. 23: 1603–1616
Lovett GM & Rueth H (1999) Soil nitrogen transformations in beech and maple stands along a nitrogen deposition gradient. Ecol. Appl. 9(4): 1330–1344
Möller D & Schieferdecker (1989) Ammonia emission and deposition of NHx in the G.D.R. Atmospheric Environment 23(6): 1187–1193
MRLC (1995) Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics (MRLC) Consortium Documentation Notebook; national land cover database. [online] URL: http://www.epa.gov/mrlc/
NADP; National Atmospheric Deposition Program/National Trends Network (2000) NADP Program Office, Illinois State Water Survey, 2204 Griffith Dr., Champaign, IL 61820. [online] URL: http://nadp.sws.uiuc.edu/nadpdata
Neff JC, Holland EA, Dentener FJ, McDowell WH & Russell KM(2002) The origin, composition and rates of organic nitrogen deposition: A missing piece of the nitrogen cycle? Biochemistry 57/58: 99–136
NRC; National Research Council (2000) Clean Coastal Waters: Understanding and Reducing the Effects of Nutrient Pollution. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Ollinger SV, Aber JD, Lovett GM, Millham SE, Lathrop RG & Ellis JM (1993) A spatial model of atmospheric deposition for the northeastern U.S. Ecol. Appl. 3: 459–472
Prospero JM, Barrett K, Church T, Dentener F, Duce RA, Galloway JN, Levy H II, Moody J & Quinn P (1996) Atmospheric deposition of nutrients to the North Atlantic Basin. Biogeochemistry 35: 27–73
Puckett LJ (1995) Identifying the major sources of nutrient water pollution: a national catchment-based analysis connects nonpoint and point sources of nitrogen and phosphorus with regional land use and other factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29: 408–414
Rennie RJ, Rennie DA & Fried M (1978) Concepts of 15N usage in dinitrogen fixation. In: Isotopes in biological dinitrogen fixation (pp 107–113) International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Rice WA (1980) Seasonal patterns of nitrogen fixation and dry matter production by clovers grown in the Peace River region. Can. J. Plant Sci. 60: 847–858
Roskoski JP (1980) Nitrogen fixation in hardwood forests of the northeastern United States. Plant Soil 54: 33–44
(SCS) Soil Conservation Service (1992) Agricultural Waste Management Field Handbook, Chapter 4, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Schlesinger W & Hartley AE (1992) A global budget for atmospheric NH3. Biogeochemistry15: 191–211
Smil V (1997) Global population and the nitrogen cycle. Scientific American, July: 76–81
Smil V (1999) Nitrogen in crop production: an account of global flows. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 13(2): 647–662
Smith RA, Schwarz GE & Alexander RB (1997) Regional interpretation of water-quality monitoring data. Wat. Resour. Res. 33(12): 2781–2798
Stoddard JL (1991) Trends in Catskill stream water quality: evidence from historical data. Water Resour. Res. 27: 2855–2864
Thomas GW & Gilliam JW (1977) Agro-ecosystems in the U.S.A. AgroEcosystems 4: 182–239
Tjepkema J (1979) Nitrogen fixation in forests of central Massachusetts. Can. J. Bot. 57: 11–16
Turner RE & Rabalais NN (1991) Changes in Mississippi River water quality this century. Biosci. 41: 140–147
USDA/NASS,U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Statistics Service (1992) 1992 Census of Agriculture. [online] URL: http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/
USDA/NASS,U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Statistics Service (1997) Virginia Agricultural Statistical Bulletin, 1997. Richmond, VA: United States Department of Agriculture, 1997
U.S. Department of Commerce (1990) 1990 Census of Population: General population characteristics, United States. 1990-CP-1-1, Bureau of the Census. [online] URL: http://www.census.gov/main/www/cen1990.html
USGS, United States Geological Survey (2000) National Water Information System Data Retrieval [online] URL: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis-w/US/
Van Breemen N, Boyer EW, Goodale CL, Jaworski NA, Seitzinger S, Paustian K, Hetling L, Lajtha K, Eve M, Mayer B, Van Dam D, Howarth RW, Nadelhoffer KJ & Billen G (2002) Where did all the nitrogen go? Fate of nitrogen inputs to large watersheds in the northeastern U.S.A. Biochemistry 57/58: 267–293
Van der Hoek KW (1998) Estimating ammonia emission factors in Europe: summary of the work of the UNECE ammonia expert panel. Atmospheric Environment 32(3): 315–316
Van der Hoek KW & Bouwman AF (1999) Upscaling of nutrient budgets from agroecological niche to global scale. In: Smaling EMA, O Oenema & LO Fresco (Eds) Nutrient Disequilibria in Agroecosystems (pp 57-73) CAB International
Van Horn HH, Newton GL & Kunkle WE (1996) Ruminant nutrition from an environmental perspective: factors affecting whole-farm nutrient balance. J. Animal Sci. 74: 3082–3102
Van Horn HH (1998) Factors affecting manure quantity, quality, and use. Proceedings of the Mid-South Ruminant Nutrition Conference, Dallas-Ft. Worth, May 7-8, 1998. Texas Animal Nutrition Council, pp 9–20
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW, Schlesinger WH & Tilman DG (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and Consequences. Ecol. Appl. 7(3): 37–750
Westerman DT, Kleinkopf GE, Porter LK & Leggett GE (1981) Nitrogen sources for bean seed production. Agronomy Journal 73: 660–664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyer, E.W., Goodale, C.L., Jaworski, N.A. et al. Anthropogenic nitrogen sources and relationships to riverine nitrogen export in the northeastern U.S.A.. Biogeochemistry 57, 137–169 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015709302073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015709302073