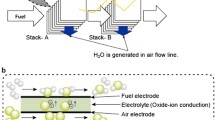
Abstract
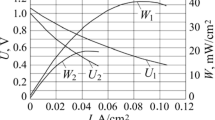
The effects of activation, ohmic and concentration polarization on the overall polarization in solid oxide fuel cells are presented. A complete analysis was conducted based on thermodynamic principles for the calculation of cell voltage. Treating the fuel cell as a control volume, the irreversibility term in a steady flow thermodynamic system was related to the overall polarization. The entropy production was calculated and related to the lost work of the fuel cell, while the heat loss from the cell was determined from the entropy balance. To generalize the cell voltage–current density expression, the Butler–Volmer model was used in the calculation of activation polarization and both ordinary and Knudsen diffusions were considered in the calculation of concentration polarization. The overall cell resistance was deduced from the generalized cell voltage–current density expression. The concentration resistance at the anode can be minimized by humidifying the hydrogen with an appropriate amount of water, depending on the thickness of the anode used. Comparison of polarization effects on the cell performance between the electrolyte-supported and anode-supported cells showed that the latter would give a better cell performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.A. Liese and R.S. Gemmen, ASME Paper 99-GT-360 (1999).
S.E. Veyo and W.L. Lundberg, ASME Paper 99-GT-356 (1999).
D.J. White, ASME Paper 99-GT-419 (1999).
P.F. van den Oosterkamp, A.A. Goorse and L.J.M.J. Blomen, J. Power Sources 41 (1993) 239–252.
P. Costamagna, P. Costa and V. Antonucci, Electrochim. Acta 43 (1998) 375.
S.H. Chanand Z.T. Xia, J. Electrochem.Soc. 148 (2001) A388–A394.
S.H. Chan, K.A. Khor and Z.T. Xia, J. Power Sources 93 (2001) 130.
J.H. Hirschenhofer, D.B. Stauffer, R.R. Engleman and M.G. Klett, 'Fuel Cell Handbook', 4th edn., Department of Energy, USA (1998).
J.W. Kim, A.V. Virkar, K.Z. Fung, K. Mehta and S.C. Singhal, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 (1999) 69.
K. Huang, B. Tichy and J.B. Goodenough, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81 (1998) 2581.
R. Maric, S. Ohara, T. Fukui, H. Yoshida, M. Nishimura, T. Inagaki and K. Miura, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 (1999) 2006.
T. Ishihara, M. Honda, T. Shibayama, H. Minami, H. Nishiguchi and Y. Takita, J. Electrochem. Soc. 145 (1998) 3177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, S., Xia, Z. Polarization effects in electrolyte/electrode-supported solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 32, 339–347 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015593326549
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015593326549