Abstract
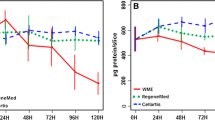
We tested the effects of low 20% O2) and high (70% O2) oxygen tension on the morphological and biochemical integrity of human liver slices incubated for up to 72 h in supplemented Williams' E medium in a dynamic rotating culture system. High oxygen tension was more effective than low oxygen tension for preserving morphological integrity in long-term culture 48–72 h). After 72 h of culture with 70% O2, the lobular pattern was well preserved, and the survival of hepatocytes approximately 80%) and other cell types was good. Immunohistochemical studies showed good preservation of the region-specific expression of CYP2E1 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes for up to 72 h of incubation in 70% O2. As compared to 20% O2, the oxidized glutathione content and reactive oxygen species production were slightly increased in 70% O2, suggesting that minimal oxidative stress occurred with the high oxygen tension. In conclusion, despite slight oxidative stress associated with high oxygen tension, 70% O2 appeared more appropriate than 20% O2 for preserving the morphological and biochemical integrity of human liver slices cultured in a dynamic organ culture system for up to 72 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altomare E, Vendemiale G, Albano O.Hepatic glutathione content in patients with alcoholic and non alcoholic liver diseases.Life Sci. 1988:43:991–8.
Azri-Meehan S, Mata HP, Gandolfi AJ, Brendel K The hepatotoxicity of chloroform in precision–cut rat liver slices.Toxicology.1992:73:239–50.
Berger SJ, Gosky D, Zborowska E, Wilson JK, Berger NA.Sensitive enzymatic cycling assay for glutathione: measurements of glutathione content and its modulation by buthionine sulfoximine 171 vivoand 171 vitroin human colon cancer.Cancer Res. 1994:54:4077–83.
Ding W-X, Shen H-M, Ong C-N.Critical role of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial permeability transition in microcystin-induced rapid apoptosis in rat hepatocytes.Hepatology.2000:32:547–55.
Drobner C, G1öckner R, Miiller D.Optimal oxygen tension conditions for viability and functioning of precision-cut liver slices.ExpToxicol Pathol. 2000:52:335–8.
Ekins S.Past, present, and future applications of precision-cut liver slices for 171 vitroxenobiotic metabolism.Drug Metab Rev. 1996:28:591–623.
Eklöw-Lastbom L, Rossi L, Thor H, Orrenius S.Effects of oxidative stress caused by hyperoxia and diquat.A study in isolated hepatocytes.Free Radic Res Commun. 1986:2:57–68.
Fariss MW.Oxygen toxicity: unique cytoprotective properties of vitamin E succinate in hepatocytes.Free Radic Biol Med. 1990:9:333–43.
Fisher R, Brendel K, Hanziik RP.Correlation of metabolism, covalent binding and toxicity for a series of bromobenzene derivatives using rat liver slices 171 vitro.Chem Biol Interact. 1993:88:191–8.
Fisher RL, Shaughnessy RP, Jenkins PM, et al.Dynamic organ culture is superior to multiwell plate culture for maintainingprecision-cut tissue slices: optimization of tissue slice cul–ture.Toxicol Methods.1995:5:99–113.
Ganthous HN, Fernando J, Gandolfi AJ, Brendel K.Biotrans-formation of halothane in guinea pig liver slices.Drug Metab Dispos. 1990:18:514–8.
Garcia-Ruiz C, Fernandez-Checa JC, Kaplowitz N.Bidirec-tional mechanism of plasma membrane transport of reduced glutathione in intact rat hepatocytes and membrane vesicles.J Biol Chem. 1992:267:22256–64.
Griffith OW.Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine.Anal Biochem. 1980:106:207–12.
Harris JW, Rahman A, Kirn BR, Guengerich FP, Collins JM.Metabolism of taxol by human hepatic microsomes and liver slices: participation of cytochrome P450 3A4 and an unknown P450 enzyme.Cancer Res. 1994:54:4026–35.
Hashemi E, Dobrota M, Till C, loannides C.Structural and functional integrity of precision-cut liver slices in xenobiotic metabolism: a comparison of the dynamic organ and multi–well plate culture procedures.Xenobiotica 1999:29:11–25.
Husain K, Sugendran K, Pant SC, Sharma VP, Vijayaraghavan R.Biochemical and pathological changes in response to hyperoxia and protection by antioxidants in rats.Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992:36:97–100.
Jungermann K, Kietzmann T.Oxygen: modulator of metabolic zonation and disease of the liver.Hepatology.2000:31:255–60.
Leeman WR, van de Gevel IA, Rutten AAJJL.Cytotoxicity of retinoic acid, menadione and aflatoxin Bl in rat liver slices using Netwell inserts as a new culture system.Toxicol In Vitro. 1995:9:291–8.
LercheLangrand C, Toutain HJ.Precision-cut liver slices: characteristics and use for in vitropharmaco-toxicology.Toxicology.2000:153:221–53.
Lomaestro BM, Malone M.Glutathione in health and disease: pharmacotherapeutic issues.Ann Pharmacother.1995:29: 1263–73.
Lupp A, Danz M, Miiller D.Morphology and cytochrome P450 isoforms expression in precision-cut rat liver slices.Toxicology.2001:161:53–66.
Martin FL, McLean AEM.Comparison of paracetamol-in-duced hepatotoxicity in the rat in vivowith progression of cell injury in vitroin rat liver slices.Drug Chem Toxicol. 1998:21:477–94.
McKinnon RA, McManus ME.Localization of cytochromes P450 in human tissues: implications for chemical toxicity.Pathology.1996:28:148–55.
Murray Gl, Burke MD.Immunohistochemistry of drug-meta-bolizing enzymes.Biochem Pharmacol.1995:50:895–903.
Musonda CA, Helsby N, Chipman JK.Effects of quercetin on drug metabolizing enzymes and oxidation of 2',7-dichloro-fluorescein in HepG2 cells.Hum Exp Toxicol. 1997:16:700–8.
Nishikawa M, Uchino J, Matsushita M, et al.Optimal oxygen tension conditions for functioning cultured hepatocytes in vitro.Artif Organs. 1996:20:169–77.
Poulsen HE, Ranek L, Andreasen PB.The hepatic glutathione content in liver diseases.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1981:41: 573–6.
Price RJ, Ball SE, Renwick AB, Barton PT, Beamand JA, Lake BG.Use of precision-cut rat liver slices for studies of xenobiotic metabolism and toxicity: comparison of the Krumdieck and Brendel tissue slicers.Xenobiotica.1998; 28:361–71.
Salyers KL, Barr J, Sipes IG.In vitrometabolism of theophylline by rat and human liver tissue.Xenobiotica.1994;24: 389–99.
Shattuck KE, Grinnell CD, Keeney SE, Noworyta K, Rassin DK.Hyperoxia and glutathione depletion in the isolated perfused rat liver.J Invest Med. 1997:45:576–83.
Siegers C-P, Bossen KH, Younes M, Mahike R, Oltmanns D.Glutathione and glutathione-Stransferasesin the normal and diseased human liver.Pharmacol Res Commun. 1982; 14:61–72.
Smith PF, Fisher RL, Shubat PJ, Gandolfi AJ, Krumdieck CL, Brendel K.In vitrocytotoxicity of allyl alcohol and bromobenzene in a novel organ culture system.Toxicol Appi Pharmacol. 1987:87:509–22.
Steams RA, Miller RR, Doss GA, et al.The metabolism of DuP 753, a nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, by rat, monkey, and human liver slices.Drug Metab Dispos. 1992:20:281–7.
Suleiman AS, Stevens JB.The effect of oxygen tension on rat hepatocytes in short-term culture.In Vitro Cell Devop Biol Animal. 1987:23:332–8.
Summer KH, Eisenburg J.Low content of hepatic reduced glutathione in patients with Wilson's disease.Biochem Med. 1985:34:107–11.
Tirmenstein MA, Nicholls-Grzemski FA, Zhang J-G, Fariss MW.Glutathione depletion and the production of reactive oxygen species in isolated hepatocyte suspensions.Chem Biol Interact. 2000:127:201–17.
Toutain HJ, Moronvalle-Halley V, Sarsat JP, Chelin C, Hoet D, Leroy D.Morphological and functional integrity of precision-cut rat liver slices in rotating organ culture and multi-well plate culture: effects of oxygen tension.Cell Biol Toxicol. 1998:14:175–90.
Tsutsumi M, Lasker JM, Shimizu M, Rosman AS, Lieber CS.The intralobular distribution ofethanol-inducible P45011EI in rat and human liver.Hepatology.1989:10:437–46.
Vendemiale G, Portincasa P, Palasciano G, Altomare E.Evidence oflipid peroxidation in patients taking neuroleptic drugs.Curr Ther Res. 1994:55:133–41.
Vickers A, Ferrero J, Fisher R, Brendel K.Xenobiotic metabolism in precision-cut dynamic organ cultured human liver slices.In Pacifici GM and Fracchia GN, eds.Advances in drug metabolism in man.Luxembourg: European Commission; 1995:681–753.
Vreugdenhil PK, Belzer FO, Southard J.H.Effect of cold storage on tissue and cellular glutathione.Cryobiology.1991:28:143–9.
Webster NR, Toothill C, Cowen PN.Tissue responses to hyperoxia.Br J Anaesth. 1987:59:760–71.
Worboys PD, Bradbury A, Houston JB.Kinetics of drug metabolism in rat liver slices.III.Relationship between metabolic clearance and slice uptake rate.Drug Metab Dispos. 1997:25:460–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, H., Sarsat, J., Lerche-Langrand, C. et al. Morphological and Biochemical Integrity of Human Liver Slices in Long-Term Culture: Effects of Oxygen Tension. Cell Biol Toxicol 18, 73–85 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015379815897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015379815897