Abstract
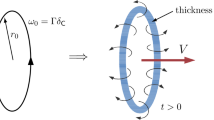
A partially invariant solution of the Euler equations is considered, where the vertical component of velocity is a function of the vertical coordinate and time, whereas the remaining components of velocity and pressure are independent of the polar angle in a cylindrical coordinate system. Using the classification of equations obtained by analysis of an overdetermined system, we consider two hyperbolic systems: the first one describes the motion of a cylindrical layer of an ideal incompressible liquid under a punch, and the second system allows obtaining solutions in a half‐cylinder with singularities at the axis of symmetry. A class of new exact solutions is obtained, which describe vortex motion of an ideal incompressible liquid, including the motion with singularities (sources of vortices) located along the axis of symmetry.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. A. Buchnev, “Lie group admitted by equations of motion of an ideal incompressible liquid," in: Dynamics of Continuous Media [in Russian] (collected scientific papers), No. 7, Novosibirsk (1971), pp. 212-214.
L. V. Ovsyannikov, “Singular vortex," J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys., 36, No. 3, 360-366 (1995).
V. V. Pukhnachov, “An integrable model of nonstationary rotationally symmetrical motion of ideal incompressible liquid," Nonlinear Dyn., 22, No. 1, 101-109 (2000).
L. V. Ovsyannikov, Group Analysis of Differential Equations, Academic Press, New York (1982).
V. K. Andreev and A. A. Rodionov, “Group classiffication and exact solutions of equations of planar and rotationally symmetric motion of an ideal liquid in Lagrangian coordinates," Differ. Uravn., 24, 1577-1586 (1988).
V. V. Pukhnachev, “New class of exact solutions of the Euler equations," Dokl. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 382, No. 6, 777-780 (2002).
L. V. Ovsyannikov, “General equations and examples,” in: Problem on Unsteady Fluid Motion with a Free Boundary [in Russian], Nauka, Novosibirsk (1967), pp. 5-75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meshcheryakova, E.Y. Exact solutions of equations of rotationally symmetric motion of an ideal incompressible liquid. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics 43, 397–405 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015366320192
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015366320192