Abstract
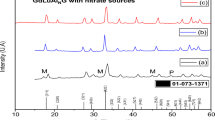
In this work, SiO2 samples with silver, prepared using the sol-gel method, were analyzed after being thermally treated in air in the range of 100 to 800°C. The sol-gel starting solutions were prepared by mixing tetra-ethyl-orthosilicate (TEOS), water and ethanol. Samples with 4 different H2O/TEOS molar ratios (3.3, 5, 7.5 and 11.7 respectively) and with different nominal Ag concentrations were prepared (1, 2 and 4%vol. of Ag). It was found that upon annealing, different silver spices were formed, such as Ag2 +, Ag+, Ag°, and metallic silver aggregates. The identification of these spices was carried out by means of X-ray diffraction, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR), optical emission and optical absorption. It was also found that the specific type of silver spices observed depends on the structure of the SiO2 matrix and on the annealing temperatures. It was found that samples prepared from precursor solutions with a low H2O/TEOS ratio have a more open structure, and therefore silver diffuses faster and forms agglomerates at lower temperatures. Samples prepared from solutions with larger H2O/TEOS ratios have a more dense structure, which allows the formation of atomic or molecular spices in addition to silver particles. A systematic study of this system was carried out using EPR on samples prepared from solutions having different H2O/TEOS molar ratios, various Ag concentrations and subjected to different thermal treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nogami, in Sol-Gel Optics: Processing and Applications, edited by L.C. Klein (Kluwer Academic, Hingham, M.A. 1994), p. 329.
M.A. Villegas, Bol. Soc. Esp. Cerám. Vidrio 33, 181 (1994).
C.R. Bamford, Color Generation and Control in Glasses (Elservier Science, Amsterdam; Oxford, NewYork, 1977), p. 48.
S.D. Stookey, G.H. Beall, and J.E. Pierson, J. Appl. Phys. 49, 5114 (1978).
C.J. Brinker and G.W. Scherer, in Sol-Gel Science, The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing (Academic Press, 1990).
E. Borsella, E. Cattaruzza, G. De Marchi, F. Gonella, G. Mattei, P. Mazzoldi, A. Quaranta, G. Battaglin, and R. Polloni, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 245, 122 (1999).
M.A. García, S.E. Paje, J. Llopis, M.A. Villegas, and J.M. Fernández Navarro, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 32, 975 (1999).
Shaw-Kwen Ma and Juh Tzeng Lue, Solid State Comm. 97, 979 (1996).
J.M. Yañez-Limón, J.F. Pérez-Robles, J. González-Hernández, R. Zamorano-Ulloa, and D. Ramírez-Rosales, Thin Solid Films 373, 184 (2000).
J.M. Yañez-Limón, J.F. Pérez-Robles, J. González-Hernández, Y.V. Vorobiev, J.A. Romano, F.C.G. Gandra, and E.C. Da Silva, J. Sol-Gel Science and Technology 18, 207 (2000).
J.F. Pérez-Robles, F.J. García Rodríguez, J.M. Yañez-Limón, F.J. Espinoza-Beltran, Y.V. Vorovieb, and J. González-Hernández, J. Physics and Chemistry of Solids 60, 1729 (1999).
J.C. Phillips, Phys. Rev. B 33, 4443 (1986).
M.G. Garnica-Romo, J. González-Hernández, M.A. Hernández-Landaverde, Y. Vorobiev, F. Ruiz, and J.R. Martínez, J. Mat. Research 16, 2007 (2001).
R. Martínez-Mendoza, F. Ruiz, Y.V. Vorobiev, F. Pérez-Robles, and J. González-Hernández, J. Chem. Phys. 109, 751 (1998).
R.A. Zhitnikov and D.P. Peregud, Sov. Phys. Solid State 17, 1080 (1975).
Yu.N. Alenko, R.A. Zhitnikov, V.K. Krasikov, and D.P. Peregud, Sov. Phys. Solid State 18, 902 (1976).
N.I. Mel'nikov, D.P. Peregood, and R.A. Zhitnikov, J. Non-Crystalline Sol. 16, 195 (1974).
A.V. Dmtryuk, G.O. Karapetyan, and O.A. Yashcharzhinskaya, Sov. Phys. Solid State 27, 1066 (1998).
G. Swarnabala and M.V. Rajusekharan, Inorg. Chem. 28, 662, (1989).
S.E. Paje, J. Llopis, M.A. Villegas, and J.M. Fernández Navarro, Appl. Phys. A. 63, 431 (1996).
N.N. Vil'Chinskaya, A.V. Dmitryuk, E.G: Ignat'ev, G.T. Petrovskii, and Savvina, Sov. Phys. Solid State 26, 497 (1984).
S.E. Paje, J. Llopis, M.A. Villegas, M.A. García, and J.M. Fernández Navarro, Appl. Phys. A. 67, 429 (1998).
A. Meijerink, M.M.E. Van Heek, and G. Blasse, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 54, 901 (1993).
B. Riegel, I. Hartmann, N. Kiefer, J. Grob, and J. Fricke, J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 211, 294 (1997).
C.J. Brinker, K.D. Keeter, D.N. Schaeter, and C.S. Ashley, J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 48, 47(1982).
H.C. Van der Hulst, in Light Scattering by Small Particles (Chapman, New York, 1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnica-Romo, M., Limón, J.Y., González-Hernández, J. et al. Structure and Electron Spin Resonance of Annealed Sol-Gel Glasses Containing Ag. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 24, 105–112 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015283522804
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015283522804