Abstract
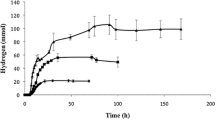
The effect of co-culturing a methanogen isolated from a paper mill waste (PMW) with cellulolytic bacteria isolated from the intestinal fluids of the silver cricket (Lepisma saccharina) on the biomethanation of filter paper strips was examined. The autoclaved filter paper strips were subjected to biomethanation in AC 21 medium inoculated with methanogen PMW in the presence and in absence of a co-culture of cellulolytic bacteria. In spite of poor initial response, methane production in the presence of the cellulolytic co-culture were found to increase gradually upto 25 days, after which a reduction in methane production was observed. Analysis of the results in terms of increased cellulose degradation in the presence of cellulolytic bacteria has been made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnara, C., Toci, R., Gandin, T.C. & Belaich, J.P. 1985 Isolation and characterization of a cellulolytic microorganism. Cellulomonas fermentus sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 35, 502–507.
Breznak, J.A. 1988 Sporomusa termitida sp. nov., a H2/CO2 utilizing acetogen isolated from termites. Archives of Microbiology 150, 282–288.
Bryant, M.P., Wolin, E.A., Wolin, M.J. & Wolfe, R.S. 1967 Methano-bacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Archives of Microbiology 59, 20–31.
Chakraborty, N., Sarkar, G.M. & Lahiri, S.C. 2000a Cellulose degrading capabilities of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from the intestinal fluids of the silver cricket. The Environmentalist 20, 9–11.
Chakraborty, N., Sarkar, G.M. & Lahiri, S.C. 2000b Effect of co-culturing of methanogens with sulphur reducing bacteria on biomethanation. The Environmentalist 20, 29–31.
Chen, M. & Wolin, M.J. 1977 Influence of CH4 production by Methanobacterium ruminantium on the fermentation of glucose and lactate by Selenomonas ruminantium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 34, 756–759.
Hungate, R.E. 1966 The Rumen and its Microbes. Academic Press Inc., New York.
Iannotti, E.L., Kafkewitz, D., Wolin, M.J. & Bryant, M.P. 1973 Glucose fermentation products of Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes causes by interspecies transfer of H2. Journal of Bacteriology 114, 1231–1240.
Khan, A.W. 1977 Anaerobic degradation of cellulose by mixed cultures. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 23, 1700–1705.
Khan, A.W. & Mes-Hartee, M. 1981 Metabolism of acetate and hydrogen by a mixed population of anaerobes capable of converting cellulose to methane. Applied Microbiology 50, 283–288.
Khan, A.W. & Trottier, T.M. 1978 Effect of sulfur-containing compounds on anaerobic degradation of cellulose to methane by mixed cultures obtained from sewage sludge. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 35, 1027–1034.
Khan, A.W., Trottier, T.M., Patel, G.B. & Martin, S.M. 1979 Nutrient requirements for the degradation of cellulose to methane by a mixed population of anaerobes. Journal of General Microbiology 112, 365–372.
Kroeker, E.J., Schulte, D.D., Sparling, A.B. & Lapp, H.M. 1979 Anaerobic treatment process stability. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation 51, 718–727.
Latham, M.J. & Wolin, M.J. 1977 Fermentation of cellulose by Ruminococcus flavefaciens in the presence and absence of Methano-bacterium ruminantium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 34, 297–301.
Miller, T.L. & Wolin, M.J. 1974 A serum bottle modification of Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Applied Microbiology 27, 985–987.
Pfeffer, J.T. & Liebman, J.C. 1976 Energy from refuse by bioconversion, fermentation and residue disposal process. Resource Recovery and Conservation 1, 295–313.
Plummer, D.T. 1988 An Introduction to Practical Biochemistry. 3rd edn (Chapter 9, p. 179). New Delhi, India: Tata McGraw-Hill publishing Co. Ltd. ISBN 0-07-099487-0.
Scheifinger, C.C., Linehan, B. & Wolin, M.J. 1975 H2 production by Selenomonas ruminantium in the presence of methanogenic bacteria. Applied Microbiology 29, 480–483.
Toerien, D.F. & Hattingh, W.H.J. 1969 Anaerobic digestion. I. The microbiology of anaerobic digestion. Water Research 3, 385–416.
Weimer, P.J. & Zeikus, J.G. 1977 Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence and presence of Methanobacterium thermautotrophicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 33, 289–297.
Winter, J. & Wolfe, R.S. 1979 Complete degradation of carbohydrate to carbon dioxide and methane by syntrophic cultures of Aceto-bacterium woodii and Methanosarcina barkeri. Archives of Microbiology 121, 97–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, N., Sarkar, G.M. & Lahiri, S.C. Biomethanation of a cellulose-based substrate in the presence and absence of a cellulolytic bacterium. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 18, 325–328 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015231209695
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015231209695