Abstract
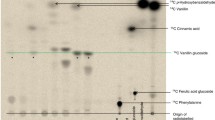
After feeding with vanillin,Vanilla planifolia Andrews cell culture was able to produce the highest amount of glucovanillin compared to Ilex dumosaReissek and Catharanthus roseus (L.) G.Don cell cultures. The optimum yield of glucovanillin was obtained from V. planifolia cells fed with 6.6 mM vanillin and harvested after 12 h. The yield was 3.28 mM glucovanillin (49.7%). This glucoside was stored mainly in the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deus-Neumann B & Zenk MH (1986) Accumulation of alkaloids in plant vacuoles does not involve an ion-trap mechanism. Planta 167: 44–53
Gamborg OL, Miller RA & Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 50: 151–158
Hallard D, Van der Heijden R, Verpoorte R, Cardoso MIL, Pasquali G, Memelink J & Hoge JHC (1997) Suspension cultured transgenic cells of Nicotiana tabacum expressing tryptophan decarboxylase and strictosidine synthase cDNAs from Catharanthus roseus produce strictosidine upon secologanin feeding. Plant Cell Rep 17: 50–54
Kometani T, Tanimoto H, Nishimura T & Okasa S (1993) Glucosylation of vanillin by cultured plant cells. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 57(8): 1290–1293
Kraemer KH, Schenkel EP & Verpoorte R (1999) Glucosylation of ethanol in Ilex paraguariensis cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 509–513
Leong G, Uzio R & Derbesy M (1989) Synthesis, identification, and determination of glucosides present in green vanilla beans (Vanilla fragrans Andrews). Flav. Fragr. J. 4: 163–167
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Sommer J, Schroeder C & Stöckigt J (1997) In vivo formation of vanillin glucoside. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 50: 119–123
Tabata M, Umetani Y, Ooya M & Tanaka S (1988) Glucosylation of phenolic compounds by plant cell cultures. Phytochemistry 27: 809–513
Winterhalter P & Skouroumounis GK (1997) Glycoconjugated aroma compounds: Occurence, role and biotechnological transformation. In: Scheper T (ed) Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, Vol 55 (pp 73–105). Springer Verlag, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuana, Dignum, M. & Verpoorte, R. Glucosylation of exogenous vanillin by plant cell cultures. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 69, 177–182 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015224425075
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015224425075