Abstract
Purpose. The objective was to design and prepare water insoluble lipoparticulates (ISLPs) for efficient gene delivery to lung tissue.
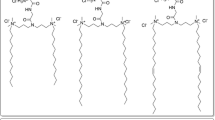
Methods. Nona{(ethylenimine)-co-[(2-aminoethyl)-N-choleseteryl-oxycarbonyl-ethylenimine]} (NEACE-T) was synthesized in both its free-base and chloride salt-forms using linear polyethylenimine (PEI, Mw 423) as a headgroup and cholesteryl chloroformate as a hydrophobic lipid anchor resulting in a T-shaped lipononamer. Semitele- chelic Nα-cholesteryloxycarbonyl nona(ethylenimine) (st-NCNEI-L) was synthesized similarly resulting in a linear lipononamer. As confirmed by 1H-NMR, the site of conjugation was either a primary amine resulting in a linear configuration (st-NCNEI-L) or a secondary amine resulting in a T-shaped configuration (NEACE-T). ISLPs were prepared by combining NEACE-T or st-NCNEI-L with a colipid, 2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) at 1/1, 1/2, and 2/1 molar ratios and the lipoparticulates were hydrated and filtered. ISLP/p2CMVmIL-12 complexes were characterized for particle size, zeta potential, surface morphology, cytotoxicity, and in vitro transfection efficiency.
Results. Transgene expression was dependent on the site of cholesterol conjugation, lipononamer:colipid molar ratio, and ISLP/p2CMVmIL-12 charge ratios. ISLP/p2CMVmIL-12 complexes were nontoxic to murine colon adenocarcinoma (CT-26) cells at 9/1 (±) or lower, had a mean particle size of 330-400 nm while the ζ potential varied from 36-39 mV. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed the surface morphology to be that of an oblate spheroid with a size comparable to that determined by dynamic light scattering. ISLP/p2CMVmIL-12 complexes prepared using free-base NEACE-T:DOPE (1/2) at charge ratios of 3/1 and 5/1 (±) provided the highest levels of transgene expression, 18 times more than the levels provided by the salt-form. Secreted levels of mIL-12 p70 were 75 times higher for ISLP/p2CMVmIL-12 complexes than naked p2CMVmIL-12 and nearly 4 times higher than PEI 25 kDa/p2CMVmIL-12 complexes.
Conclusions. The transfection efficiency of the ISLPs was dependent on the site of cholesterol conjugation, amount of colipid, and charge ratio. The highest levels of transgene expression were provided by NEACE-T:DOPE (1/2)/p2CMVmIL-12 at a 3/1 (±) charge ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
X. Gao and L. Huang. A novel cationic liposome reagent for efficient transfection of mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 179:280–285 (1991).
E. R. Lee, J. Marshall, C. S. Siegel, C. Jiang, N. S. Yew, M. R. Nichols, J. B. Nietupski, R. J. Ziegler, M. B. Lane, K. X. Wang, N. C. Wan, R. K. Scheule, D. J. Harris, A. E. Smith, and S. H. Cheng. Detailed analysis of structures and formulations of cationic lipids for efficient gene transfer to the lung. Hum. Gene Ther. 7:1701–1717 (1996).
P. L. Felgner, T. R. Gadek, M. Holm, R. Roman, H. W. Chan, M. Wenz, J. P. Northrop, G. M. Ringold, and M. Danielsen. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:7413–7417 (1987).
G. Byk, C. Dubertret, V. Escriou, M. Frederic, G. Jaslin, R. Rangara, B. Pitard, J. Crouzet, P. Wils, B. Schwartz, and D. Scherman. Synthesis, activity, and structure-activity relationship studies of novel cationic lipids for DNA transfer. J. Med. Chem. 41: 229–235 (1998).
Y. Yamazaki, M. Nango, M. Matsuura, Y. Hasegawa, M. Hasegawa, and N. Oku. Polycation liposomes, a novel nonviral gene transfer system, constructed from cetylated polyethylenimine. Gene Ther. 7:1148–1155 (2000).
J. S. Choi, E. J. Lee, H. S. Jang, and J. S. Park. New cationic liposomes for gene transfer into mammalian cells with high efficiency and low toxicity. Bioconjug. Chem. 12:108–113 (2001).
X. Zhou and L. Huang. DNA transfection mediated by cationic liposomes containing lipopolylysine: characterization and mechanism of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1189:195–203 (1994).
J. Marshall, J. B. Nietupski, E. R. Lee, C. S. Siegel, P. W. Rafter, S. A. Rudginsky, C. D. Chang, S. J. Eastman, D. J. Harris, R. K. Scheule, and S. H. Cheng. Cationic lipid structure and formulation considerations for optimal gene transfection of the lung. J. Drug Target. 7:453–469 (2000).
M. C. Filion and N. C. Phillips. Major limitations in the use of cationic liposomes for DNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 162:159–170 (1998).
B. Abdallah, A. Hassan, C. Benoist, D. Goula, J. P. Behr, and B. A. Demeneix. A powerful nonviral vector for in vivo gene transfer into the adult mammalian brain: polyethylenimine. Hum. Gene Ther. 7:1947–1954 (1996).
W. T. Godbey, K. K. Wu, and A. G. Mikos. Size matters: Molecular weight affects the efficiency of poly(ethylenimine) as a gene delivery vehicle. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 45:268–275 (1999).
A. J. Geall, R. J. Taylor, M. E. Earll, M. A. W. Eaton, and I. S. Blagbrough. Synthesis of cholesteryl polyamine carbamates: pKa studies and condensation of calf thymus DNA. Bioconjug. Chem. 11:314–326 (2000).
N. Oudrhiri, J. P. Vigneron, M. Peuchmaur, T. Leclerc, J. M. Lehn, and P. Lehn. Gene transfer by guanidinium-cholesterol cationic lipids into airway epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:1651–1656 (1997).
B. D. Freimark, H. P. Blezinger, V. J. Florack, J. L. Nordstrom, S. D. Long, D. S. Deshpande, S. Nochumson, and K. L. Petrak. Cationic lipids enhance cytokine and cell influx levels in the lung following administration of plasmid: cationic lipid complexes. J. Immunol. 160:4580–4586 (1998).
Y. Liu, D. Liggitt, W. Zhong, G. Tu, K. Gaensler, and R. Debs. Cationic liposome-mediated intravenous gene delivery. J. Biol. Chem. 270:24864–24870 (1995).
H. Farhood, R. Bottega, R. M. Epand, and L. Huang. Effect of cationic cholesterol derivatives on gene transfer and protein kinase C activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1111:239–246 (1992).
M. Whitmore, S. Li, and L. Huang. LPD lipopolyplex initiates a potent cytokine response and inhibits tumor growth. Gene Ther. 6:1867–1875 (1999).
N. S. Templeton, D. D. Lasic, P. M. Frederik, H. H. Strey, D. D. Roberts, and G. N. Pavlakis. Improved DNA:liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 15:647–652 (1997).
R. I. Mahato, M. Lee, S. Han, A. Maheshwari, and S. W. Kim. Intratumoral delivery of p2CMVmIL-12 using water-soluble lipopolymers. Mol. Ther. 4:130–138 (2001).
H. Schreier, L. Gagne, T. Bock, G. W. Erdos, P. Druzgala, J. T. Conary, and B. W. Muller. Physicochemical properties and in vitro toxicity of cationic liposome cDNA complexes. Pharm. Acta Helv. 72:215–223 (1997).
R. I. Mahato, K. Kawabata, T. Nomura, Y. Takakura, and M. Hashida. Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic characteristics of plasmid DNA/cationic liposome complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 84: 1267–1271 (1995).
A. Maheshwari, R. I. Mahato, J. McGregor, S. Han, W. E. Samlowski, J. S. Park, and S. W. Kim. Soluble biodegradable polymer-based cytokine gene delivery for cancer treatment. Mol. Ther. 2:121–130 (2000).
J. S. Kim, A. Maruyama, T. Akaike, and S. W. Kim. Terplex DNA delivery system as a gene carrier. Pharm. Res. 15:116–121 (1998).
C. S. Tannenbaum, N. Wicker, D. Armstrong, R. Tubbs, J. Finke, R. M. Bukowski, and T. A. Hamilton. Cytokine and chemokine expression in tumors of mice receiving systemic therapy with IL-12. J. Immunol. 156:693–699 (1996).
J. Zabner, A. J. Fasbender, T. Moninger, K. A. Poellinger, and M. J. Welsh. Cellular and molecular barriers to gene transfer by a cationic lipid. J. Biol. Chem. 270:18997–19007 (1995).
R. I. Mahato, K. Anwer, F. Tagliaferri, C. Meaney, P. Leonard, M. S. Wadhwa, M. Logan, M. French, and A. Rolland. Biodistribution and gene expression of lipid/plasmid complexes after systemic administration. Hum. Gene Ther. 9:2083–2099 (1998).
Y. Xu and F. C. Szoka, Jr. Mechanism of DNA release from cationic liposome/DNA complexes used in cell transfection. Biochemistry 35:5616–5623 (1996).
A. R. Klemm, D. Young, and J. B. Lloyd. Effects of polyethyleneimine on endocytosis and lysosome stability. Biochem. Pharmacol. 56:41–46 (1998).
S.-O. Han, R. I. Mahato, and S. W. Kim. Water-Soluble Lipopolymer for Gene Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 12:337–345 (2001).
D. D. Lasic and Y. Barenholz. From Gene Delivery and Diagnostics to Ecology, Handbook of Nonmedical Applications of Liposomes. Vol. 4, CRC Press, LLC, Boca Raton, Florida (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furgeson, D.Y., Cohen, R.N., Mahato, R.I. et al. Novel Water Insoluble Lipoparticulates for Gene Delivery. Pharm Res 19, 382–390 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015166806366
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015166806366