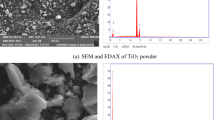
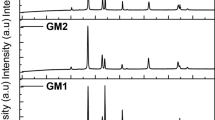
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite (HA) reinforced high density polyethylene (HDPE) was invented as a biomaterial for skeletal applications. In this investigation, tribological properties (e.g. wear rate and coefficient of friction) of unfilled HDPE and HA/HDPE composites were evaluated against the duplex stainless steel in dry and lubricated conditions, with distilled water or aqueous solutions of proteins (egg albumen or glucose) being lubricants. Wear tests were conducted in a custom-built test rig for HDPE and HA/HDPE containing up to 40 vol % of HA. It was found that HA/HDPE composites had lower coefficients of friction than unfilled HDPE under certain conditions. HA/HDPE also exhibited less severe fatigue failure marks than HDPE. The degradation and fatigue failure of HDPE due to the presence of proteins were severe for low speed wear testing (100 rpm) as compared to high speed wear testing (200 rpm). This was due possibly to the high shear rate at the contact which could remove any degraded film instantaneously at high sliding speed, while with a low sliding speed the build-up of a degraded layer of protein could occur. The degraded protein layer would stay at the contact for a longer time and mechanical activation would induce adverse reactions, weakening the surface layer of HDPE. Both egg albumen and glucose were found to be corrosive to steel and adversely reactive for HDPE and HA/HDPE composites. The wear modes observed were similar to that of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Specimens tested with egg albumen also displayed higher wear rates, which was again attributed to corrosion accelerated wear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Charnley, “Low Friction Anthroplasty of the Hip: Theory and Practice” (Springer, New York, 1979).
G. K. Mckee and J. Watson-Farrar, J. Bone Joint Surg. 48B (1966) 245-259.
W. Bonfield, M. Wang and K. E. Tanner, Acta Mater. 46 (1998) 2509-2518.
Z. Lu and H. Mckellop, Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. 211H (1997) 101-108.
B. M. Wroblewski, ibid. 211H (1997) 109-118.
W. Bonfield, M. D. Grynpas, A. E. Tully, J. Bowman and J. Abram, Biomaterials 2 (1981) 185-186.
W. Bonfield, Bioceramics 11 (1998) 37-40.
M. Wang, C. Berry, M. Braden and W. Bonfield, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 9 (1998) 621-624.
M. Wang, R. Joseph and W. Bonfield, Biomaterials 19 (1998) 2357-2366.
M. Wang, S. Deb, K. E. Tanner and W. Bonfield, in “Proceedings of the Seventh European Conference on Composite Materials” (London, UK, 1996), vol 2, pp. 455-460.
M. Wang, I. M. Ward and W. Bonfield, in “Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Composite Materials” (Gold Coast, Australia, 1997), vol.1, pp. 488-495.
F. J. Guild and W. Bonfield, Biomaterials 14 (1993) 985-993.
J. Suwanprateeb, K. E. Tanner, S. Turner and W. Bonfield, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 8 (1997) 469-472.
J. Huang, M. Wang, S. Best, K. E. Tanner and W. Bonfield, Bioceramics 11 (1998) 165-168.
J. Huang, L. Di Silvio, M. Wang, K. E. Tanner and W. Bonfield, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 8 (1997) 775-779.
L. Di Silvio, M. Dalby and W. Bonfield, ibid. 9 (1998) 845-848.
W. Bonfield and Z. B. Luklinska, in “The Bone-Biomaterials Interface”, edited by J. E. Davies (University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Canada, 1991) pp. 89-93.
R. N. Downs, S. Vardy, K. E. Tanner and W. Bonfield, Bioceramics 4 (1991) 239-246.
M. Wang, D. Porter and W. Bonfield, Br. Ceram. Trans. 93 (1994) 91-95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Chandrasekaran, M. & Bonfield, W. Friction and wear of hydroxyapatite reinforced high density polyethylene against the stainless steel counterface. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 13, 607–611 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015139213211
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015139213211