Abstract
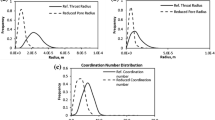
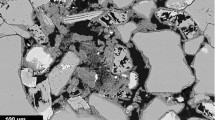
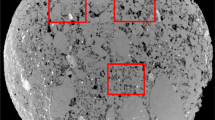
We generate the network model equivalents of four samples of Fontainebleau sandstone obtained from the analysis of microtomographic images. We present the measured distributions of flow-relevant geometric and topological properties of the pore space. We generate via bond dilution from a regular lattice, stochastic network models with identical geometric (pore-size, throat-size) and topological (coordination number distribution) properties. We then simulate the two-phase flow properties directly on the network model and the stochastic equivalent for each sample. The simulations on the stochastic networks are found to provide a poor representation of the results on the direct network equivalents. We find that the description of the network topology is particularly crucial in accurately predicting the residual phase saturations. We also find it necessary to introduce into the stochastic network geometry both extended pore-pore correlations and local pore-throat correlations to obtain good agreement with flow properties on the rock-equivalent network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakke, S. and Oren P.: 1997, 3-D pore-scale modelling of sandstones and flow simulations in the Pore Networks,SPE J. 2, 136–149.
Blunt, M., King, M. and Scher, H.: 1992, Simulation and theory of two-phase flow in porous media, Phys. Rev. A 46 7680–7699.
Blunt, M., King, M. J. and Zhou, D.: 1994, What determines residual oil saturation in three-phase flow, In: SPE/DOE 9th Symp. on Improved Oil Recovery.
Doyen, P.: 1988, Permeability, conductivity and pore geometry of sandstone, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7729–7740.
Dullien, F.: 1992, Porous Media: Fluid Transport and Pore Structure; NY: Academic.
Dunsmuir, J. H., Ferguson, S. R. and D'Amico, K. L.: 1991, Design and operation of an imaging x-ray detector for microtomography, IOP conf. Series 121, 257–261.
Flannery, B. P., Deckman, H. W., Roberge, W. G. and D'Amico, K. L.: 1987, Three-dimensional x-ray microtomography, Science 237 1439–1444.
Galam, S. and Mauger, A.: 1994. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 5526–5531.
Galam, S. and Mauger, A.: 1996, Universal formulas for percolation thresholds, Phys.Rev.E 53, 2177–2180.
Heiba, A. and Sahimi M.: 1982, Scriven, L. & Davis, H., Percolation theory of two-phase relative permeability, SPE Paper 10015.
Heiba, A.: 1983, Effect of Wettability on 2-phase relative permeabs & Capill. presence, SEP Paper 12172.
Heiba, A., Sahimi, M., Scriven, L. and Davis, H.: 1992, Percolation theory of two-phase relative permeability, SPE Reserv. Engng bd7, 123–132.
Hewett, T.: 1986, Fractal distributions of reservior heterogeneity and their influence of fluid transport, Technical Report, SPE Paper 15836.
Hilfer, R.: 1996, Transport and relaxation phenomena in porous media, Adv. Chem. Phys. XCII, 299–424.
Ioannidis, M. A. and Chatzis, I.: 1993, A mixed percolation model of capillary hysteresis and entrapment in mercury porosimetry, Chem. Eng. Sci. 48, 951.
Ioannidis, M. A., Kwiecien, M. J., Chatzis I., MacDonald, I. F. and Dullien, F. A. L.: 1997, Comprehensive pore structure characterization using 3-D computer reconstruction and stochastic modelling, Technical report, SPE Paper 38713.
Kamath, J., Xu, B. and Yortsos, Y. C.: 1998, Use of pore network models to interpret laboratory experiments on vugular rocks, J. Petroleum Sci. Engng. 20, 109–120.
Knackstedt, M. A., Marrink, S. J., Sheppard, A. P., Pinczewski W. V. and Sahimi, M.: 1999, Invasion percolation on correlated and elongated lattices: Implications to the interpretation of phase saturations in rock cores, Transport in Porous Media 44, 465–485.
Knackstedt, M. A., Sahimi, M. and Sheppard, A. P.: 2000a, Invasion percolation with long-range correlations: First-order phase transition and nonuniversal scaling properties, Phys. Rev. E. 61, 4920.
Knackstedt, M. A., Sheppard, A. P. and Pinczeswki, W. V.: 1998, Simulation of mercury porosi-metry on correlated grids: Evidence for extended correlated heterogeneity at the pore scale in rocks, Phys.Rev.E.RapidCommun. 58, R6923–R6926.
Knackstedt, M. A., Sheppard, A. P. and Sahimi, M.: 2000b, Pore network modelling of two-phase flow in porous rocks: The effect of correlated heterogeneity Adv. Water Resour. Volume 24, pp. 257–277 (2001).
Koplik, J., Lin, C. and Vermette, M.: 1984, Conductivity and permeability from microgeometry, J. Appl. Phys. 56, 3127–3132.
Larson, R., Scriven, L. E. and Davis, H. T.: 1977, Percolation theory of residual phase in porous media, Nature 268, 409–413.
Larson, R., Scriven, L. E. and Davis, H. T.: 1991, Percolation theory of two-phase flow in porous media, Chem. Eng. Sci. 36, 57–73.
Lee, T. C., Kashyap, R. L. and Chu, C.-N.: 1994, Building skeleton models via 3-D medial surface/axis thinning algorithms, CVGIP: Grophic. Models Image Process. 56, 462–478.
Lin, C. and Cohen M. H.: 1982, Quantitative methods for microgeometric modelling, J. Appl. Phys. 53, 4152–4165.
Lindquist, B., Lee, S. M. and Coker D.: 1996, Medial axis analysis of void structure in three-dimensional tomographic images of porous media, J. Geophys. Res. 101B, 8297–3210.
Lindquist, B. and Venkatarangan, A.: 1999, Investigation 3-D geometry of porous media from high resolution images, Phys. Chem. Earth 24, 87.
Lindquist, W. B., Venkatarangan, A., Dunsmuir, J. and Wong, T. F.: 2000, Pore and throat-size distributions measured from synchrotron x-ray tomographic images of Fontainbleau sandstones, J. Geophys. Res. 105B, 21508.
McDougall and Sorbie: 1993, The predictions of waterflood performance in mixed wet systems from pae-scale modelling & simulation, SPE Paper 25271.
O'Keefe, M.: 1999a, Coordination sequences for lattices, preprint.
O'Keefe, M.: 1999b, On the calculation, use and properties of coordination sequence, preprint.
O'Keefe, M. and Hydes B. G.: 1996, Crystal Structures I: Patterns and symmetry. Washington D.C.: Mineralogical Society of America.
Oren, P., Bakke, S. and Arntzen, O. J.: 1998, Extending predictive capabilities of network models, SPE J. 3, 324–336.
Oren, P., Billiotte, J. and Pinczewski, W.: 1992, Mobilisation of waterflood residual oil by gas injection of water-wet conditions, SPE Formation Evaluation 7, 70–78.
Oren, P., Billiotte, J. and Pinczewski, W.: 1994, Pore scale network modelling of waterflood residual oil recovery by immiscible gas flooding, In: SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Houston, USA.
Oren, P. and Pinczewski, W.: 1991, The effect of film flow in the mobilization of waterflood residual oil by gas flooding, In: 6th European IOR-Symposium, Houston, USA.
Oren, P. and Pinczewski, W.: 1994, Effect of wettability and spreading on recovery of waterflood residual oil by immiscible gasflooding, SPE Form. Eval. 8, 149–156.
Paterson, L., Painter S., Knacksstedt, M. and Pinczewski, W. V.: 1996, Pattern of fluid flow in naturally heterogeneous rocks, Physica A 233, 619–628.
Paterson, L., Painter, S., Zhang, X. and Pinczewski, W. V.: 1997, Simulating residual saturation and relative permeability of heterogeneous formations, SPE 36523.
Pereira, G., Pinczewski, W., Chan, D., Peterson, L. and Oren, P.: 1996, Pore-scale network model for drainage dominated three-phase flow in porous media, Transport in Porous Media 24, 167–201.
Sahimi, M.: 1993, Flow, dispersion, and displacement processes in porous media and fractured rocks: From continuum models to fractals, percolation, cellular automata and simulated annealing, Rev. Mod. Physics 65, 1393–1534.
Sahimi, M.: 1994, Applications of Percolation Theory, (Ist edn.) Taylor and Francis, London.
Sheppard, A. P. and Sok R. M.: 2000, Fast algorithm for trapping and searching in invasion percolation, Transport in Porous Media p. submitted.
Spanne, P., Thovert J., Jacquin, J., Lindquist, W. B., Jones, K. and Coker, D.: 1994, Syncho-tron computed microtomography of porous media: topology and transports Phys. Rev. Lett 73, 2001–2004.
Stauffer, D. and Aharony A.: (1994), Introduction to Percolation Theory, (2nd edn.) Taylor and Francis, London.
Studing, P. N. and Ziff, R. M.: 1999, Site percolation thresholds for Archimedean latticed, Phys. Rev. E 60, 275–283.
Thovert, J.-F., Salles, J. and Adler, P.: 1993, Computerised characterization of the geometry of real porous media: their description, analysis and interpretation, J. Microscopy 170, 65–79.
Wilkinson, D. and Willemsen, J.: 1983, Invasion percolation: a new form of percolation theory, J. Phys. A: Math, Gen. 16, 3365–3376.
Xu, B., Kamath, J., Yortsos, Y. C. and Lee, S. H.: 1999, Use of pore network models to simulate laboratory corefloods in a heterogeneous carbonate sample, SPE J 4, 179–186.
Zhao, H. Q. and MacDonald, I. F.: 1993, An unbiased and efficient producedure for 3-D connectivity measurement as applied to porous media, J. Microscopy 172, 157–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sok, R.M., Knackstedt, M.A., Sheppard, A.P. et al. Direct and Stochastic Generation of Network Models from Tomographic Images; Effect of Topology on Residual Saturations. Transport in Porous Media 46, 345–371 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015034924371
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015034924371