Abstract
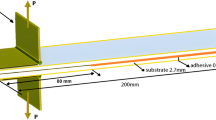
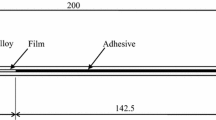
This paper investigates the roles of external loads and specimen geometry on crack path selection in adhesively bonded joints. First, the effect of mixed mode fracture on crack path selection is studied. Using epoxy as an adhesive and aluminum as the adherends, double cantilever beam (DCB) specimens with various T-stress levels are prepared and tested under mixed mode fracture loading. Post-failure analyses on the failure surfaces using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) suggest that the failure tends to be more interfacial as the mode II fracture component in the loading increases. This fracture mode dependence of the locus of failure demonstrates that the locus of failure is closely related to the direction of crack propagation in adhesive bonds. Through analyzing the crack trajectories in failed specimens, the effect of mixed mode fracture on the directional stability of cracks is also investigated. The results indicate that the direction of the crack propagation is mostly stabilized when more than 3% of mode II fracture component is present at the crack tip regardless of the T-stress levels in the specimens for the material system studied. Second, using a high-speed camera to monitor the fracture sequence in both quasi-static and low-speed impact tests, the effect of debond rate on the locus of failure and directional stability of cracks is investigated. Post-failure analyses including XPS, Auger electron spectroscopic depth profile, and scanning electron microscopy indicate that as the crack propagation rate increases, the failure tends to be more cohesive and the cracks tend to be directionally unstable. Last, as indicated by the finite element analyses results, the T-stresses, and therefore the directional stability of cracks in adhesive bonds, are closely related to the thickness of the adhesive layer and also the thickness of adherend. This specimen geometry dependence of crack path selection is studied analytically and is verified experimentally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABAQUS (1998). Version 5.8, Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorenson, Inc.
Akisanya, A.R. and Fleck, N.A. (1992a). Analysis of a wavy crack in sandwich specimens. International Journal of Fracture 55, 29–45.
Akisanya, A.R. and Fleck, N.A. (1992b). Brittle fracture of adhesive joints. International Journal of Fracture 58, 93–114.
Beer, F.P. and Johnston, E.R., Jr. (1992). Mechanics of Materials, second edition. McGraw-Hill, Inc.
Blackman, B.R.K., Dear, J.P., Kinloch, A.J. and Osiyemi, S. (1991). The calculation of adhesive fracture energies from double-cantilever beam test specimens. Journal of Materials Science Letters 10, 253–256.
Blackman, B.R.K., Dear, J.P., Kinloch, A.J., Macgillivray, H., Wang, Y., Williams, J.G. and Yayla, P. (1995). The failure of fibre composites and adhesively bonded fibre composites under high rates of test, part I mode I loading – experimental studies. Journal of Materials Science 30, 5885–5900.
Blackman, B.R.K., Kinloch, A.J., Wang, Y. and Williams, J.G. (1996). The failure of fibre composites and adhesively bonded fibre composites under high rates of test, part II mode I loading – dynamic effects. Journal of Materials Science 31, 4451–4466.
Blackman, B.R.K., Dear, J.P., Kinloch, A.J., Macgillivray, H. Wang, Y., Williams, J.G. and Yayla, P. (1996). The failure of fibre composites and adhesively bonded fibre composites under high rates of test, part III mixedmode I/II and mode II loadings. Journal of Materials Science 31, 4467–4477.
Broek, D. Elementary engineering fracture mechanics. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers (1982).
Chai, H. (1984). The characterization of mode I delamination failure in non-woven, multidirectional laminates. Composites 14, 277–290.
Chai, H. (1986). On the correlation between the mode I fracture of adhesive joints and laminated composites. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 24, 413–431.
Chai, H. (1987). A note on crack trajectory in an elastic strip bounded by rigid substrates. International Journal of Fracture 32, 211–213.
Chao, Y.J. and Liu, S. (1997). On the failure of cracks under mixed-mode loads. International Journal of Fracture 87, 201–223.
Chao Y. J., Liu, S. and Broviak, B. (1999). Brittle fracture: constraint effect and crack curving under mode I conditions (to be published).
Chen, B. and Dillard, D.A. (2001a). Numerical analysis of the directionally unstable crack propagation in adhesively bonded joints. International Journal of Solids and Structures (in press).
Chen, B. and Dillard, D.A. (2001b). The effect of the T-stress on the crack path selection in adhesively bonded joints. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives (in press).
Chen, B. and Dillard, D.A. (2001c). Crack path selection in adhesively bonded joints: the role of material properties. Journal of Adhesion (in press).
Cotterell, B. and Rice, J.R. (1980). Slightly curved or kinked cracks. International Journal of Fracture 16, 155–169.
Daghyani, H.R., Ye, L., and Mai, Y.M. (1996). Effect of thermal residual stress on the crack path in adhesively bonded joints. Journal of Materials Science 31, 2523–2529.
Dillard, D.A., Park, T.G., Zhang, H., and Chen, B. (1999). Measurement of residual stresses and thermal expansion in adhesive bonds. Proceedings of 22nd Annual Meeting of the Adhesion Society, 336–338.
Dillard, D.A., Chen, B., Chang, T., and Lai, Y.H. (1999). Analysis of the notched coating adhesion test. Journal of Adhesion 69, 99–120.
Ergodan, V.F. and Sih, G.C. (1963). On crack extension in plates under plane loading and transverse shear. Transaction of ASME, Journal of Basic Engineering 85, 519–527.
Fleck, N.A., Hutchinson, J.W., and Suo, Z. (1991). Crack path selection in a brittle adhesive layer. International Journal of Solids and Structures 27, 1683–1703.
Geubelle P.H., and Knauss, W.G. (1994). Crack propagation at and near bimaterial interfaces: linear analysis. Journal of Applied Mechanics 61, 560–566.
Goldstein, R.V. and Salganik, R.L. (1974). Brittle fracture of solids with arbitrary cracks. International Journal of Fracture 10, 507–523.
Hutchinson, J.W. and Suo, Z. (1992). Mixed mode cracking in layered materials. Advances in Applied Mechanics 29, 63–191.
Liechti, K.M. and Liang, Y.M. (1995). Toughening mechanisms in mixed-mode Interfacial fracture. International Journal of Solids and Structures 32, 957–978.
Liechti, K.M. and Freda, T. (1989). On the use of laminated beams for the determination of pure mixed-mode fracture properties of structural adhesives, Journal of Adhesion 28, 145–169.
Liechti, K.M. and Hanson, E.C. (1988). Nonlinear effects in mixed-mode interfacial delaminations. International Journal of Fracture 36, 199–217.
Lin, C., and Liechti, K.M. (1986). Similarity concepts in the fatigue fracture of adhesively bonded joints. Journal of Adhesion 24, 101–121.
Palaniswamy, K. and Knauss, W.G. (1978). On the problem of crack extension in brittle solids under general loading. In S. Nemat-Nasser (editor), Mechanics Today, Vol. 4. Pergamon Press, London, pp. 87–148.
Parvatareddy, H., Dillard, J.G., McGrath, J.E., and Dillard, D.A. (1998). Environmental aging of the Ti-6Al-4V/FM-5 polyimide adhesive bonded system: implications of physical and chemical aging on durability. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 12, 615–637.
Parvatareddy, H. and Dillard D.A. (1999). Effect of mode mixity on the fracture toughness of Ti-6Al-4V/FM-5 adhesive joints. International Journal of Fracture 96, 215–228.
Ravi-Chandar, K. and Knauss, W.G. (1984a). An investigation into dynamic fracture. I – Crack initiation and arrest. International Journal of Fracture 25, 247–262.
Ravi-Chandar, K. and Knauss, W.G. (1984b). An investigation into dynamic fracture. II – Microstructural aspects. International Journal of Fracture 26, 65–80.
Ravi-Chandar, K. and Knauss, W.G. (1984c). An investigation into dynamic fracture. III – On steady-state crack propagation and branching. International Journal of Fracture 26, 141–154.
Ravi-Chandar, K. and Knauss, W.G. (1984d). An investigation into dynamic fracture. IV – On the interaction of stress wave with propagating cracks. International Journal of Fracture 26, 189–200.
Sundararaman, V. and Davidson, B.D. (1997). An unsymmetric double cantilever beam test for interfacial fracture toughness determination. International Journal Solids and Structures 34, 799–817.
Suo, Z. and Hutchinson, J.W. (1990). Interface crack between two elastic layers, International Journal of Fracture 43, 1–18.
Swadener, J.G. and Liechti, K.M. (1998). A symmetric shielding mechanisms in the mixed-mode fracture of a glass/epoxy interface. Journal of Applied Mechanics 65, 25–29.
Swadener, J.G., Liechti, K.M., and de Lozanne, A.L. (1999). Intrinsic toughness and adhesion mechanisms of glass/epoxy interface. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 47, 223–258.
Thouless, M.D. (1990). Fracture of a model interface under mixed-mode loading. Acta. Metall. Mater 38, 1135–1140.
Vrana, M.A., Dillard, J.G., Ward, T.C., Rakestraw, M.D., and Dillard, D.A. (1995). The influence of curing agent content on the mechanical and adhesive properties of Dicyandiamide cured epoxy systems. Journal of Adhesion 55, 31–42.
Williams, M.L. (1957). On the stress distribution at the base of a stationary crack. Journal of Applied Mechanics 24, 109–114.
Xiao, F., Hui, C.Y., and Kramer, E.J. (1993). Analysis of a mixed mode fracture specimen: the asymmetric double cantilever beam. Journal of Materials Science 28, 5620–5629.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Dillard, D.A., Dillard, J.G. et al. Crack path selection in adhesively bonded joints: the roles of external loads and speciment geometry. International Journal of Fracture 114, 167–190 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015020919823
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015020919823