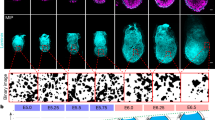
Abstract
The recently identified nidogen-2 is a matrix protein showing homology to the well-known basement membrane molecule nidogen-1. Nidogen-1 might well serve as a link between laminin-1 and collagen type IV and thus stabilise certain basement membranes in vivo and play a major role in embryogenesis. However, the exact tissue distribution of nidogen-1 and nidogen-2 during human embryogenesis is still unclear. As a first step towards the elucidation of their possible cell biological functions during human development, we compared the distribution of both nidogens during human organogenesis at the light microscope level. Nidogen-2 and nidogen-1 were found to be ubiquitous components of basement membrane zones underneath developing epithelia of most of the major organ systems. However, in the developing intestine and the pancreas anlage, only nidogen-1 was present in the epithelial basement membrane zones of all developmental stages investigated. Our data suggest that nidogen-2 and nidogen-1, as is known for mouse development, could well participate in cell biological functions during human development. These two proteins might well be able to fulfil identical functions during human organogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aumailley M, Wiedemann H, Mann K, Timpl R (1989) Binding of nidogen and the laminin–nidogen complex to basement membrane collagen type IV. Eur J Biochem 184: 241–248.
Bretschneider HJ (1980) Myocardial protection. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 28: 295–302.
Dong IJ, Chung AE (1991) The expression of the genes for entactin, laminin A, laminin B1 and laminin B2 in murine lens morphogenesis and eye development. Differentiation 48: 157–172.
Dziadek M (1995) Role of laminin–nidogen complexes in basement membrane formation during embryonic development. Experientia 51: 901–913.
Ekblom P (1993) Basement membranes in development. In: Rohrbach DH, Timpl R eds. Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Basement Membranes. New York: Academic Press, pp. 359–378.
Ekblom P, Ekblom M, Fecker L, Klein G, Zhang HY, Kadoya Y, Chu ML, Mayer U, Timpl R (1994) Role of mesenchymal nidogen for epithelial morphogenesis in vitro. Development 120: 2003–2014.
Ekblom P, Durbeej M, Ekblom M (1996) Laminin isoforms in development. In: Ekblom P, Timpl R eds. The Laminins. Reading: Harwood Academic Publisher, pp. 185–216.
Fleischmajer R, Schechter A, Bruns M, Perlish JS, MacDonald ED, Pan TC, Timpl R, Chu M-L (1995) Skin fibroblasts are the only source of nidogen during early basal lamina formation in vitro. J Invest Dermatol 105: 597–601.
Fox JW, Mayer U, Nischt R, Aumailley M, Reinhardt D, Wiedemann H, Mann K, Timpl R, Krieg T, Engel J, Chu M-L (1991) Recombinant nidogen consists of three globular domains and mediates binding of laminin to collagen type IV. EMBO J 10: 3137–3146.
Hopf M, Göhring W, Kohfeldt E, Yamada Y, Timpl R (1999) Recombinant domain IV of perlecan binds to nidogens, laminin–nidogen complex, fibronectin, fibulin-2 and heparin. Eur J Biochem 259: 917–925.
Kimura N, Toyoshima T, Kojima T, Shimane M (1998). Entactin-2: A new member of basement membrane protein with homology to entactin/nidogen. Exp Cell Res 241: 36–45.
Kleinman HK, Kibbey MC, Schaper W, Hadley MA, Dym M, Grant DS (1993) Role of basement membrane in differentiation. In: Rohrbach DH, Timpl R, eds. Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Basement Membranes. New York: Academic Press, pp. 309–323
Kohfeldt E, Sasaki T, Göhring W, Timpl R (1998) Nidogen-2: A new basement membrane protein with diverse binding properties. J Mol Biol 282: 99–109.
Martinez-Hernandez A, Amenta PS (1995) The extracellular matrix in hepatic regeneration. FASEB J 9: 1401–1410.
Mayer U, Nischt R, Pöschl E, Mann K, Fukuda K, Gerl M, Yamada Y, Timpl R (1993) A single EGF-like motif of laminin is responsible for high affinity nidogen binding. EMBO J 12: 1879–1885.
Mayer U, Timpl R (1994) Nidogen. A versatile binding protein of basement membranes. In:Yurchenco PD, Birk DE, Mecham RP, eds. Extracellular Matrix Assembly and Structure.San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 389–416.
Miosge N, Günther E, Becker-Rabbenstein V, Herken R (1993) Ultrastructural localization of laminin subunits during the onset of mesoderm formation in the mouse embryo. Anat Embryol 187: 601–605.
Miosge N, Heinemann S, Leissling A, Klenczar C, Herken R (1999a) Ultrastructural triple localization of laminin-1, nidogen-1 and collagen type IV helps to elucidate basement membrane structure in vivo. Anat Rec 254: 382–388.
Miosge N, Sasaki T, Timpl R (1999b) Angiogenesis inhibitor endostatin is a distinct component of elastic fibers in vessel walls. FASEB J 13: 1743–1750.
Miosge N, Köther F, Heinemann S, Kohfeldt E, Herken R, Timpl R (2000a) Ultrastructural colocalization of nidogen-1 and nidogen-2 with laminin-1 in murine kidney basement membranes. Histochem Cell Biol 113: 115–124.
Miosge N, Quondamatteo F, Klenczar C, Herken R (2000b) Nidogen-1: Expession and ultrastructural localization during the onset of mesoderm formation in the early mouse embryo. J Histochem Cytochem 48: 229–238.
Miosge N (2001) The ultrastructural composition of basement membranes in vivo. Histol Histopathol 16: 1239–1248.
Mollard R, Dziadek M (1998) A correlation between epithelial proliferation rates, basement membrane component localization patterns, and morphogenetic potential in the embryonic mouse lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 19: 71–82.
Murshed M, Smyth N, Miosge N, Karolat J, Krieg T, Paulsson M, Nischt R (2000) Absence of nidogen-1 does not affect murine basement membrane formation. J Mol Cell Biol 20: 7007–7012.
O'Rahilly R, Müller F (1996) Human Embryology & Teratology, New York: Wiley-Liss.
Quondamatteo F, Scherf C, Miosge N, Herken R (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of laminin, nidogen and type IV collagen during the embryonic and fetal development of the human liver. Histochem Cell Biol 111: 39–47. 530 N. Miosge et al.
Sasaki T, Göhring W, Miosge N, Abrams WR, Rosenbloom J, Timpl R (1999) Tropoelastin binding to fibulins, nidogen-2 and other extracellular matrix proteins. FEBS Lett 460: 280–284.
Streuli C (1996) Basement membrane as a differentiation and survival factor. In: Ekblom P, Timpl R, eds. The Laminins. Reading: Harwood Publisher, pp. 217–233.
Thomas T, Dziadek M (1993) Genes coding for basement membrane glycoproteins laminin, nidogen, and collagen type IV are differentially expressed in the nervous system and by epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells of the mouse embryo. Exp Cell Res 208: 54–67.
Thomas T, Dziadek M (1994) Expression of collagen α1(IV), laminin and nidogen genes in the embryonic mouse lung: Implications for branching morphogenesis. Mech Dev 45: 193–201.
Timpl R (1996) Macromolecular organization of basement membranes. Curr Op Cell Biol 8: 618–624.
Timpl R, Brown JC (1996) Supramolecular assembly of basement membranes. BioEssays 18: 123–132.
Warburton MJ, Monaghan P, Ferns SA, Rudland PS, Perusinghe N, Chung AE (1984) Distribution of entactin in the basement membrane of the rat mammary gland. Evidence for a non-epithelial origin. Exp Cell Res 152: 240–254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miosge, N., Holzhausen, S., Zelent, C. et al. Nidogen-1 and Nidogen-2 are Found in Basement Membranes During Human Embryonic Development. Histochem J 33, 523–530 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014995523521
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014995523521