Abstract
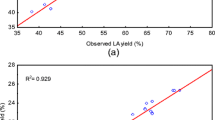
Immobilized lipase from Rhizomucor miehei (Lipozyme IM-20) was employed in the esterification of isovaleric acid and isoamyl alcohol to synthesize isoamyl isovalerate in n-heptane. Response surface methodology (RSM) based on a five-level, five-variable central composite rotatable design (CCRD) was used to evaluate the effects of important variables: enzyme concentration (20–40% w/w of acid), acid concentration (0.2–1.0 M), incubation period (24–120 h), alcohol concentration (0.25–1.25 M) and temperature (30–70 °C) on the esterification yield of isoamyl isovalerate. Extent of conversion was found to be excellent at all acid and alcohol concentrations employed in the range of 0.2–1.25 M, even at low enzyme concentration (20% w/w). The optimum conditions arrived at are as follows: 35% (w/w) enzyme concentration, 1.0 M acid concentration, 1.25 M alcohol concentration and 120 h incubation period, at 35 °C. Under these conditions, the predicted value was 680 mM ester matched very well with an experimental value of 678 mM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burdock, G.A. 1995 Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients. pp. 380. vol. 2, 3rd edn. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC press, ISBN 0-84932711-3.
Cochran, W.G. & Cox, G.M. 1992 Experimental Designs. 2nd edn. pp. 335–375. New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-54567-8.
Langrand, G., Rondot, N., Triantaphylides, C. & Baratti, J. 1990 Short chain flavor esters synthesis by microbial lipases. Biotechnology Letters 12, 581–586.
Montgomery, D.C. 1991 Response surface method and design In Design and Analysis of Experiments, 3rd edn. Chp. 16. ed. Montgomery, D.C. pp. 521–568. New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-52994-X.
Nishio, T., Chikano, T. & Kaminura, M. 1987 Terpene alcohol ester synthesis by polyethylene glycol-modified lipase in benzene. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 52, 1203–1208.
Prapulla, S.G., Jacob, Z., Nagin, C., Rajalakshmi, R. & Karanth, N.G. 1992 Maximization of lipid production by Rhodotorula gracilis CFR-1 using response surface methodology. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 40, 965–970.
Shieh, C.J., Akoh, C.C. & Koehler, P.E. 1995 Four factor response surface optimization of enzymatic modification of triolein to structured lipids. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society 72, 619–623.
Welsh, F.W., Murray, W.D. & Williams, R.E. 1989 Microbiological and enzymatic production of flavor and fragrance chemicals. CRC Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 9, 105–169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdary, G., Divakar, S. & Prapulla, S. Modelling on isoamyl isovalerate synthesis from Rhizomucor miehei lipasein organic media: optimization studies. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 18, 179–185 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014914911918
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014914911918