Abstract
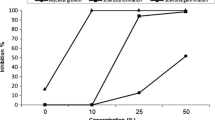
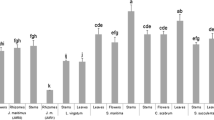
Scopoletin (7-hydroxy-6-methoxy coumarin) which inhibited the conidial germinationof Corynespora cassiicola was isolated from the uninfected mature leaves ofHevea brasiliensis. Scopoletin was not detected in uninfected immature rubber leaves. The immature leaves produced scopoletin after being infected with C. cassiicola. The concentration of scopoletin in infected leaves was higher than in uninfected mature leaves. Scopoletin also inhibited the conidial germination of other fungal pathogens of H. brasiliensis. However, no correlation was observed between scopoletin accumulation and clonal resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breton F, Sanier C, D'Auzac J. Scopoletin production and degradation in relation to resistance of Hevea brasiliensis to Corynespora cassiicola. Journal of Plant Physiology 1997; 151: 595–602.
Brown AE, Soepena H. Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum acutatum and C. gloeosporioides on leaves of Hevea. Mycological Research 1994; 98: 264–256.
Budavari S, O'Neil MJ, Smith A, Heckelman PE, Kinneary JF. The Merck Index, 12th ed., Merck & Co., Inc., NJ, 1996.
Dravill AG, Albershem P. Phytoalexins and their elicitors. A defense against microbial infection in plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology 1984; 35: 242–275.
Garcia D, Sanior C, Machoix JJ, Auzac J. Accumulation of scopoletin in Hevea brasiliensis infected by Microcyclus ulei (P. Henn.) V. ARX and eva1uation of its fungitoxicity for three leaf pathogens of rubber tree. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 1995; 47: 4, 213–223.
Giesemann A, Bichland B, Lieberei R. Identification of scopoletin a phytoalexin of the rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis. Journal of Phylopathology 1986; 117: 373–376.
Smith CJ. Accumulation of Phytoalexins: Defense mechanism and stimulus response system. New Phytologist 1996; 132: 145.
Tar AM, Low FC. Phytoalexin production by Hevea brasiliensis in response to infection by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and its effect on other fungi. Proceedings of the International Rubber Conference 1975; 217–226.
Tip-pyang S, Veerachato C, Phuwapraisirisan P, Sathanasaowapak A. Antibacterial compounds from “Arfeillea arborescens” ACGC Chemical Research Communication 1999; 9: 15–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, W.P.K., Deraniyagala, S.A., Wijesundera, R.L.C. et al. Isolation of scopoletin from leaves of Hevea brasiliensis and the effect of scopoletin on pathogens of H. brasiliensis . Mycopathologia 153, 199–202 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014910132595
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014910132595