Abstract
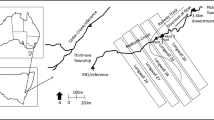
Leachate emanating from a coal-storage area at an electricutility plant in Northwest Indiana (U.S.A.) is impacting groundwater quality. This assessment is based on results of along-term groundwater monitoring program conducted at Purdue University's Wade Utility Plant where a monthly average of 32,000metric tons of both high- and low-sulfur coal are stored. Groundwater from both a perched and major aquifer (the WabashValley Aquifer) as well as surface water from a large retentionpond were sampled monthly for 34 consecutive months. Such a long-term, continuous sampling scheme proved beneficial in identifying seasonal trends and anomalies within the chemistryof ground- and surface waters. Data show elevated concentrationsof sulfate and hardness in the perched zones and the WabashValley Aquifer (WVA). Lead in the WVA has also been reported ata concentration greater than the state maximum contaminant level, while several metals (Be, Cd, Cu, Pb, Ni, Se, and Zn) containedwithin retention-pond sediments have the highest concentrationsin aquatic sediments ever reported within the State of Indiana.Due to the buffering capacity of carbonate minerals in underlyingunconsolidated deposits, the acidic pH of coal-pile leachate is raised to values typical for groundwater in carbonate terrain common in Northwest Indiana. Further ameliorating the input of acid percolation is the dilution capabilities of both the WVA and the recharge pond. Hence, sites without such advantages would exhibit a greater degree of groundwater contamination than what is observed at Purdue's coal-storage facility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. A., Bertsch, P. M., Feldman, S. B. and Zelazny, L. W.: 1991, ‘Interactions of acidic metal-rich coal pile runoff with a subsoil’, Env. Sci. Technol. 25, 2038–2046.
Anderson, W. C. and Youngstrom, M. P.: 1976, ‘Coal pile leachate-quantity and quality characteristics’, Journal of Sanitary Engineering, Division of the American Society of Civil Engineering, 102(EE6), p. 1239–1253.
Bjelke, W.: 1960, ‘Recharge capacity of the Purdue Gravel Pit’, M.S. Thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Purdue University, 150 pp.
Bright, G. R.: 1986, ‘Background levels of potential toxicants in Indiana stream and lake Sediments’, Indiana Department of Environmental Management.
Brookman, G. T., Binder, J. J. and Wade III, J. A.: 1977, ‘Measurement and modeling of storm water runoff from coal storage piles and the impact on receiving waters’, in Proc. 3rd Symp. on Coal Preparation NCA/BCR Coal Fon. and Expo IV, Washington, D.C., 18–20 Oct. 1977, p. 214–242.
Carlson, C. A.: 1990, ‘Subsurface leachate migration from a reject coal pile in South Carolina’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 53, p. 345–366.
Cox, D. B., Chu, T. Y. J. and Ruane, R. J.: 1977, ‘Quality and treatment of coal-pile runoff’, in Proc. 3rd Symp. On Coal Preparation NCA/BCR Coal Conf. and Expo IV, Washington, D.C., 18–20 Oct. 1977, p 252–277.
Energy Information Administration: 1998, Electric Power Annual, 1997'. DOE/EIA-0348(97), July 14, 1998.
Everett, L. G.: 1985, Groundwater Monitoring Handbook for Coal and Oil Shale Development, Elsevier, New York, 305 pp.
Franson, M. A. H. (ed.): 1980, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 15th edition, 1134 pp.
Fritz, S. J., Bryan, J. D., Harvey, F. E. and Leap, D. I.: 1994, ‘A geochemical and isotopic approach to delineate landfill leachates in a RCRA study’, Ground Water 32(4), 743–750.
Harvey, F. E.: 1990, ‘A hydrogeochemical investigation of the aquifer system near West Lafayette, Indiana’, M.S. Thesis, Dept. of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, Purdue University. 319 pp.
Leap, D. I., Fritz, S. J. Bryan, J. D. Clabaugh, B. D. Henderson, M. E. Lee, K. K. Roberts, R. L. and Smith, W. R.: 1990, ‘Final report of the results of a RCRA facilities investigation of solid waste management units on the Horticulture Research Farm and the Thomas Farm, Purdue University, Tippecanoe County, Indiana’, Water Resources Research Center, Tech. Report 61, 107 pp.
Morrison, D. V., Gemmecke, D. L., Hudson, S. A., Baxter, D. M. and Nethercutt, T.A.: 1997, ‘Water works annual report’, Purdue University, West Lafayette Campus.
Morrison, D. V., Gemmecke, D. L., Hudson, S. A., Baxter, D. M. and Nethercutt, T. A.: 1998, ‘Water works annual report’, Purdue University, West Lafayette Campus.
Ontario Environmental: 1991, ‘Evaluation of environmental and regulatory issues associated with Purdue University's south campus gravel pit pond: Report of Findings’, 38 pp.
STORET, U.S. EPA on-line database, <http://www.epa.gov/OWOW/STORET/index.html>.
Wachter, R. A. and Blackwood, T. R.: 1978, ‘Source assessment: water pollutants from coal storage areas’, EPA-600-2-78-004M. Industrial Environ. Res. Lab., Off. of Res. and Dev., U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio.
Wangen, L. E. and Jones, M. M.: 1984, ‘The attenuation of chemical elements in acidic leachates from coal mineral wastes by soils’, Environmental Geology and Water Science 6, p. 161–170.
Weinreb, G.: 1987, ‘A hydrogeological investigation of thermal contamination within the Wabash Valley Outwash Aquifer, West Lafayette, Indiana’, M.S. Thesis, Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, Purdue University, 170 pp.
Zelmanowitz, S., Boyle, W. C., Armstrong, D. E. and Park, J. K.: 1995, ‘Ability of subsoils to buffer extremely acidic simulated coal-pile leachates’, Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 121, no. 11, p. 816–823.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cook, A.M., Fritz, S.J. Environmental Impacts of Acid Leachate Derived from Coal-Storage Piles upon Groundwater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 135, 371–388 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014750225629
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014750225629