Abstract
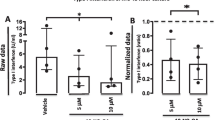
Administration of gammalinolenic acid (GLA), an unsaturated fatty acid, reduces joint inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Addition of GLA in vitro suppresses release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) from human monocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). LPS-induced IL-1β release is followed by IL-1-induced IL-1β release, an amplification process termed “autoinduction.” We show here, using IL-1α stimulation to simulate autoinduction, that administration of GLA to healthy volunteers and to patients with inflammatory arthritis reduces LPS-induced IL-1β secretion mainly by reducing autoinduction of IL-1β. GLA reduces LPS-induced pro-IL-1β mRNA modestly and IL-1α-induced pro-IL-1β gene expression markedly. In addition to reducing amplification of IL-1β, GLA increases the amount of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) secreted from stimulated cells, thereby facilitating an increase in the secreted IL-1Ra/IL-1β ratio. IL-1β is important to host defense, but the amplification mechanism may be excessive in genetically predisposed individuals. Thus, reduction of IL-1β autoinduction may be protective in some patients with endotoxic shock and with diseases characterized by chronic inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Fantone, JC, Kunkel SL, Zurier RB: Effects of prostaglandins on in vivo immune and inflammatory reactions. In Prostaglandins and Immunology, JS Goodwin (ed). Boston, Martinus Nijhoff Publishing, 1985, pp 123–146
Baker DG, Krakauer KA, Tate G, Laposata M, Zurier RB: Suppression of human synovial proliferation by dihomo-_linolenic acid. Arthritis Rheum 32:1273–1281, 1989
DeLuca P, Zurier RB: Marine and botanical lipids as immunomodulatory and therapeutic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 21:759–777, 1995
Zurier RB: Gammalinolenic acid treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. In Medicinal Fatty Acids in Inflammation, JM Kremer (ed). Basal, Birkhäuser Verlag, 1998, pp 29–44
Santoli D. Zurier RB: Prostaglandin E (PGE) precursor fatty acids inhibit human IL-2 production by PGE-independent mechanism. J Immunol 143:1303–1309, 1989
Santoli D, Phillips PD, Colt TL, Zurier RB: Suppression of interleukin 2-dependent human T cell growth by E-series prostaglandins (PGE) and their precursor fatty acids: evidence for a PGE-independent mechanism of inhibition by the fatty acids. J Clin Invest 85:424–432, 1990
DeMarco DM, Santoli D, Zurier RB: Effects of fatty acids on proliferation and activation of human synovial compartment lymphocytes. J Leuk Biol 56:612–618, 1994
Leventhal LG, Boyce EG, Zurier RB: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with gammalinolenic acid. Ann Intern Med 119:867–873, 1993
Zurier RB, Rossetti RG, Jacobson EW, DeMarco DM, Liu NY, Temming JE, White BM, Laposata L: Gammalinolenic acid treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, placebocontrolled trial. Arthritis Rheum 39:1808–1817, 1996
DeLuca P, Rossetti RG, Alavian C, Karim P, Zurier RB: Effects of gammalinolenic acid on interleukin-1? and tumor necrosis-? secretion by stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes: Studies in vitro and in vivo. J Investig Med 47:246–250, 1999
Arend WP, Dayer JM: Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor ? in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:151–160, 1995
Dinarello CA, Wolff SM: The role of interleukin-1 in disease. N Engl J Med 323:106–113, 1993
Dinarello CA: Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87:2095–2147, 1996
Ruschen S, Tellberry W, Warnatz H: Kinetics of cytokine secretion by mononuclear cells of the blood from rheumatoid arthritis patients are different from those of healthy controls. Clin Exp Immunol 89:32–37, 1992
Firestein GS, Boyle DL, YY C, Paine MM, Whisenand TD, Zvaifler NJ, Arend WP: Synovial interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1 balance in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37:644–652, 1994
Dinarello CA, Ikejima TI, Warner SJ, Orencole SF, Lonnemann G, Cannon JG, Libby P: Interleukin-1 induces interleukin-1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin-1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol 139:1902–1910, 1987
Amano Y, Lee SW, Alison AC: Inhibition by glucocorticoids of the formation of interleukin-1?, interleukin-?, and interleukin-6: Mediation by decreased mRNA stability. Molec Pharmacol 43: 176–182, 1993
Furse RR, Rossetti RG, Zurier RB: Gammalinolenic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid with antiinflammatory properties, blocks amplification of IL-1? production by human monocytes. J Immunol 167:490–496, 2001
Rothman D, Allen H, Herzog L, Pilapil A, Seiler CM, Zurier RB: Effects of unsaturated fatty acids on interleukin-1?production by human monocytes. Cytokine 9:1008–1012, 1997
Kato T, Imatani T, Miura T, Minaguchi K, Saitoh E, Okudah K: Cytokine-inducing activity of family 2 cystatins. Biol Chem 381:1143–1147, 2000
Endres S, Ghorbani R, Kelley VE, Georgilis K, Lonnemann G, vander Meer JW, Cannon JG, Rogers TS, Klempner MS, Weber PC, Dinarello CA: The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med 320:265–271, 1989
Endres S, Meydani SN, Ghorbani R, Schindler R, Dinarello CA: Dietary supplementation with n-3 fatty acids suppresses interleukin-2 production and mononuclear cell proliferation. J Leukocyte Biol 54:599,603, 1993
Szewczenko-Pawlikowski M, Kozak W: Accumulation of unsaturated lipids in monocytes during early phase pyrogen tolerance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1484:183–194, 2000
Granowitz EV, Clark BD, Vannier E, Callahan MV, Dinarello CA: Effect of interleukin-1 blockade on cytokine synthesis: I. IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits IL-1 induced cytokine synthesis and blocks the binding of IL-1 to its type II receptor on human monocytes. Blood 79:2356–2363, 1992
Granowitz EV, Poutsiaka DD, Dinarello CA: Effect of interleukin-1 (IL-1) blockade on cytokine synthesis: II. IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine synthesis by human monocytes. Blood 79:2364‐, 1992
Murphy K, Haudek SB, Thompson M, Giroir GP: Molecular biology of septic shock. New Horizons 6:181–193, 1998
Arend WP: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Adv Immunol 54: 167–1993
Eisenberg SP, Evans RJ, Arend WP, Verderber E, Brewer MT, Hannum CH, Thompson RC: Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Nature 343:341–1990
Rubartelli A, Sitia R: Secretion of mammalian proteins that lack a signal sequence. In Unusual Secretory Pathways: From Bacteria to Man, A Kuchler, A Rubartelli, BI Holland (eds). Austin, RG Landes, 1997, pp 87–104
Singer II, Scott S, Hall JL, Limjuco G, Chin J, Schmidt JA: Interleukin-1?is localized in the cytoplasmic ground substance but is largely absent from the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane of stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med 167:389–407, 1988
Cerretti DP, Kozlosky CJ, Mosley B, Nelson N, Van Ness K, Greenstreet TA, March CJ, Kronheim SR, Druck T, Cannizzaro LA, Huebner K, Black RA: Molecular cloning of the interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 256:97–100, 1992
Andrei C, Dazzi C, Lotti L, Torrisi MR, Chimini G, Rubartelli A: The secretory route of the leaderless protein interleukin-1β involves exocytosis of endolysosome-related vesicles. Molec Biol Cell 10:1463–1475, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furse, R.K., Rossetti, R.G., Seiler, C.M. et al. Oral Administration of Gammalinolenic Acid, an Unsaturated Fatty Acid with Anti-inflammatory Properties, Modulates Interleukin-1β Production by Human Monocytes. J Clin Immunol 22, 83–91 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014479702575
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014479702575