Abstract
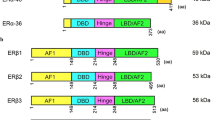
Estrogen receptor alpha (ER-α) is an important regulator of growth and differentiation in the mammary gland and the female reproductive tract. It is also involved in the development of malignant tumors. The human ER-β is highly homologous to the extensively studied human ER-α. It binds to the endogenous 17β-estradiol with similar affinity as ER-α and the transcriptional activity through the consensus ERE can be stimulated. Five ER-β isoforms were cloned and characterized. They diverge at a common position within the predicted helix 10 of the ligand-binding domain of the human ER-β, with nucleotide sequences consistent with different exon usage. These isoforms of human ER-β show differential expression in tissues and in tumor cell lines. Furthermore, they are predicted to form DNA-binding heterodimers when coexpressed. Expression of some of the ER-β isoforms in human breast tissue, breast cancer, and breast cancer cell lines were reported by several groups. However, there is no complete analysis of the gene expression pattern of all ER-β isoforms in breast cancer so far. In this study, we examined the mRNA expression of each of the ER-β isoforms in 30 tumors from breast cancer patients and 21 breast cell lines. In conclusion, expression of ER-β1, ER-β2, and ER-β5 were observed in different cell lines as well as in the tumors, ER-β4 isoform was expressed in all samples, and ER-β3 isoform was not detected in any of the samples examined. There were no associations of the expression of all ER-β isoforms with the invasiveness of the cell lines as well as with clinical parameters of the tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA: Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 5925–5930, 1996
Tremblay GB, Tremblay A, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Labrie F, Giguere V: Cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional analysis of the murine estrogen receptor beta. Mol Endocrinol 11: 353–365, 1997
Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R: ER beta: identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett 392: 49–53, 1996
Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton JC, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, van der Burg B, Gustafsson JA: Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology 139: 4252–4263, 1998
Moore JT, McKee DD, Slentz-Kesler K, Moore LB, Jones SA, Horne EL, Su JL, Kliewer SA, Lehmann JM, Willson TM: Cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor beta isoforms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247: 75–78, 1998
Dotzlaw H, Leygue E, Watson PH, Murphy LC: Estrogen receptor-beta messenger RNA expression in human breast tumor biopsies: relationship to steroid receptor status and regulation by progestins. Cancer Res 59: 529–532, 1999
Fuqua SA, Schiff R, Parra I, Friedrichs WE, Su JL, McKee DD, Slentz-Kesler K, Moore LB, Willson TM, Moore JT: Expression of wild-type estrogen receptor beta and variant isoforms in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 59: 5425–5428, 1999
Leygue E, Dotzlaw H, Watson PH, Murphy LC: Expression of estrogen receptor beta1, beta2, and beta5 messenger RNAs in human breast tissue. Cancer Res 59: 1175–1179, 1999
Speirs V, Malone C, Walton DS, Kerin MJ, Atkin SL: Increased expression of estrogen receptor beta mRNA in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer patients. Cancer Res 59: 5421–5424, 1999
Kury FD, Schneeberger C, Sliutz G, Kubista E, Salzer H, Medl M, Leodolter S, Swoboda H, Zeillinger R, Spona J: Determination of HER-2/neu amplification and expression in tumor tissue and cultured cells using a simple, phenol free method for nucleic acid isolation. Oncogene 5: 1403–1408, 1990
Tong D, Czerwenka K, Sedlak J, Schneeberger C, Schiebel I, Concin N, Leodolter S, Zeillinger R: Association of in vitro invasiveness and gene expression of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, pS2 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 56: 91–97, 1999
Speirs V, Parkes AT, Kerin MJ, Walton DS, Carleton PJ, Fox JN, Atkin SL: Coexpression of estrogen receptor α and β: poor prognostic factors in human breast cancer? Cancer Res 59: 525–528, 1999
Järvinen TAH, Pelto-Huikko M, Holli K, Isola J: Estrogen receptor α is coexpressed with ERβ and PR and are associated with nodal status, grade, and proliferation rate in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 156: 29–35, 2000
Iwao K, Miyoshi Y, Egawa C, Ikeda N, Noguchi S: Quantitative analysis of estrogen receptor-β mRNA and its variants in human breast cancers. Int J Cancer 88: 733–736, 2000
Cowley SM, Hoare S, Mosselman S, Parker MG: Estrogen receptors alpha and beta form heterodimers on DNA. J Biol Chem 272: 19858–19862, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, D., Schuster, E., Seifert, M. et al. Expression of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in human breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71, 249–255 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014465916473
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014465916473