Abstract
Modern high-speed mechanisms often experience undesirable vibrations,which may render a required accuracy unattainable or, even worse, leadto a failure of the whole process. Instead of suppressing the vibrationby a stiffer design, active control methods may greatly improve thesystem performance and lead the way to a reduction of the mechanism'sweight.
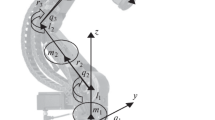
We investigate a four-bar-linkage mechanism and show that byintroducing an additional degree of freedom for a controlled actuatorand providing a suitable control strategy, the dynamically inducedinaccuracies can be substantially reduced and new reference paths bedescribed. The modeling of the four-bar-linkage mechanism as a hybridmultibody system and the modeling of the complete system including theactuator is briefly explained. From the combined feedforward–feedbackoptimal control approach presented in [11], a time-varying outputcontrol law is derived that leads to a very good system performancefor both a regulating and a tracking problem. The experimental resultsshow the effectiveness of the applied control strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellmann, R., Dynamic Programming, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 1957.
Bormann, J., 'Optimierung der Dynamik mechanischer Ñbersetzungsgetriebe durch geregelte Stelleingriffe', Ph.D. Thesis, University of Essen, Fortschr.-Ber. VDI-Reihe 11, Nr. 249, Düsseldorf, 1997.
Föllinger, O.: Regelungstechnik, Hüthig Buch Verlag, Heidelberg, 1992.
Franklin, G.F., Powell, J.D. and Workmann, M.L., Digital Control of Dynamic Systems, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1990.
Golub, G. and Van Loan, C., Matrix Computations, John Hopkins Press, Baltimore, MD, 1989.
Hinrichs, N., 'Reibungsschwingungen mit Selbst-und Fremderregung: Experiment, Modellierung und Berechnung', Ph.D. Thesis, VDI-Fortschritt-Berichte Reihe 11, Nr. 240, Düsseldorf, 1997.
Liao, C.Y. and Sung, C.K.: 'An elastodynamic analysis and control of flexible linkages using piezoceramic sensors and actuators', ASME, J. Mech. Design 115, 1993, 658-665.
Oliver, J.H., Wysocki, D.A. and Thompson, B.S., 'The synthesis of flexible linkages by balancing the tracer point quasi-static deflections using microprocessors and advanced materials technology', Mech. Mach. Theory 20(2), 1985, 103-104.
Scheideler, E., Dynamik von aktiven Getriebemechanismen, VDI-Fortschrittberichte, Reihe 11, Nr. 221, Düsseldorf, 1995.
Shefer, M., 'Discrete optimal tracking with prescribed disturbances', J. Guidance 2(4), 1988, 371-372.
von Stein, H. and Ulbrich, H., 'Optimal control of a flexible mechanism using a combined feedforward-feedback strategy', in Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Motion and Vibration Control, Zürich, Switzerland, August 25-28, G. Schweitzer, R. Siegwart and P. Cattin (eds), Institute of Robotics, ETH-Zürich, 1998, Vol. 2, 399-404.
Sung, C.K. and Chen, Y.C.: 'Vibration control of the elastostatic responce of high-speed-flexible mechanism', J. Vibration Acoust. 113, 1991, 14-21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulbrich, H., von Stein, H. A Combined Feedforward–Feedback Control Strategy for Improving the Dynamics of a Flexible Mechanism. Multibody System Dynamics 7, 229–248 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014448907708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014448907708