Abstract
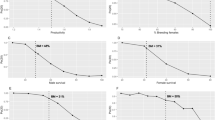
The Przewalski's gazelle, Procapra przewalskii, is now isolated in four local populations on the east and northwest shores of Qinghai Lake. We have been being conducting field surveys in the Qinghai Lake region since 1994. Based on the information we gathered from those surveys, we carried out a Population Viability Analysis (PVA) on the Przewalski's gazelle. We discovered that the Przewalski's gazelle would be extinct within 200 years if no management measures were taken. Since the local population size of the gazelle is small, the most effective measures are to control the wolf density and to reduce the impact of climatic catastrophes. In order to increase the population of the gazelle, we should also take measures to increase primary production of the grassland, to establish a habitat corridor, and to increase the rate of migration of individuals among different local populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bailey, J.A., Principles of Wildlife Management, New York: Wiley, 1984.
Ballou, J., Demographic Processes in Small and Fragmented Population, Florida Key Deer Population Viability Assessment. Population Viability Analysis Workshop, Florida, USA, 1990, pp. 30-39.
Foose, T.J. and Ballou, J.D., Population Management: Theory and Practice, Int. Zoo Yearbook, 1988, no. 27, pp. 26-41.
Goodman, D., The Demography of Chance Extinction, in Viable Population for Conservation, Soule, M. E., Ed., New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1987, pp. 35-58.
Haig, S.M., Ballou, J.D., and Derrickson, S.R., Management Options for Preserving Genetic Diversity: Reintroduction of Guam Rails to the Wild, Conservation Biology, 1990, vol. 4, pp. 290-300.
Haig, S., Belthoff, J. R., and Allen D. H., Population Viability Analysis for a Small Population of Red-Cockaded Wood-peckers and an Evaluation of Enhancement Strategies, Conserv. Biol., 1993, vol. 7, pp. 289-301.
Jiang, Z., Feng, Z., and Wang, Z., Przewalski's Gazelle in China, Conserv. Biol., 1996, no. 13, pp. 324-325.
Jiang, Z. and Li, D., Antelopes of China, Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci., 1998, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 458-461.
Jiang, Z., Li, D., and Wang, Z., Population Declines of Przewalski's Gazelle around Qinghai Lake, China, Oryx, 2000, no. 34, pp. 129-135.
Lacy, R.C., VORTEX: A Computer Simulation Model for Population Viability Analysis, Wildl. Res., 1993, no. 20, pp. 45-65.
Lande, R., Genetics and Demography in Biological Conservation, Science, 1988, vol. 241, pp. 1455-1460.
Lei, R., Jiang, Z., and Liu, B., Group Pattern and Social Seg-regation in Przewalski's Gazelle (Procapra przewalskii) around Qinghai Lake, China, J. Zool. (London), 2001 (in press).
Li, D., Jiang, Z., and Wang, Z., Habitat Characteristics and Activity Habit of Procapra przewalskii, Acta Theriol. Sinica, 1999, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 17-24.
Lindenmayer, D.B., Lacy, R.C., Thomas, V.C., and Clark, T., Predictions of the Impacts of Changes in Population Size and Environmental Variability on Leadbeater's Possum, Gymnobelideus leadbeateri McCoy (Marsupialia: Petauridae), Using Population Viability Analysis: An Application of the Computer VORTEX, Wildl. Res., 1993, no. 20, pp. 67-86.
Ralls, K. and Ballou, D., Effects of Inbreeding on Infant Mortality in Captive Primates, International Journal of Primatology, 1982, vol. 3, pp. 491-505.
Ralls, K., Brugger, K., and Ballou, J.D., Inbreeding and Juve-nile Mortality in Small Populations of Ungulates, Science, 1979, vol. 206, pp. 1101-1103.
Seal, U.S. and Lacy, R.C., Florida Panther (Felis concolor coryi): Viability Analysis and Species Survival Plan, Captive breeding Specialist Group, Species Survival Commission of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gainesville, Florida, USA. 1989.
Song, Y.L., Population Viability Analysis for Two Isolated Population of Haianan Eld's Deer, Conserv. Biol., 1996, no. 10, pp. 1467-1472.
Wayne, R.K., Lehman, N., Girman, D., Gogan, P.J.P., Gilbert, D.A., Hansen, K., Peterson, R.O., Seal, U.S., Eisen-hawer, A., Mech, L.D., and Krumenaker R.J., Conservation Genetics of the Endangered Isle Royale Gray Wolf, Conservation Biology, 1991, no. 5, pp. 41-51.
Wei, F. and Hu, J., Population Viability Primary Analysis of Giant Panda, Symposia of Chengdu International Giant Panda Workshop, Zhang Anju and He Guangxi, Eds., Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technique Press, 1994, pp. 116-122.
Zhang, X., Wang, D., and Wang, K., VORTEX Model and Its Application in Lipotes vexillifer Population Management, Chin. Biodiv., 1994, no. 2, pp. 133-139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Jiang, Z. Population Viability Analysis for the Przewalski's Gazelle. Russian Journal of Ecology 33, 115–120 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014404925410
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014404925410