Abstract
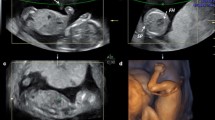
Objective: When the fetal spine is in anterior position, it shadows the fetal heart, resulting in the difficult visualization using two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound. The purpose of this study was to compare the basic cardiac views of normal fetuses between 2D and 3D ultrasound to demonstrate whether 3D ultrasound improved the visualization of these views in fetuses in anterior spine positions. In addition, inter- and intra-observation reliabilities of basic cardiac views using 3D ultrasound were evaluated for their clinical applicability. Methods: Using a multiplanar technique, integrated 3D ultrasound was used to display the four-chamber view, aortic outflow tract and pulmonary outflow tract in fetuses in anterior spine positions for 23 uncomplicated singleton pregnant women. The imaging visualizations of these views for the 23 fetuses in 3D ultrasound were compared with those in 2D ultrasound using the McNemar test. We also evaluated the inter- and intra-observation differences of each basic cardiac view in 3D ultrasound using the κ statistic and McNemar test, respectively. Results: Only in the pulmonary outflow tract, 3D ultrasound had significantly better visualization than the 2D ultrasound in the fetuses in anterior spine positions (p < 0.05). There was good inter-observation reliability and no intra-observation differences for the technique were observed. Conclusions: Among the basic cardiac views in fetuses in anterior spine positions, 3D ultrasound improved the visualization of pulmonary outflow and provided reliable alternate technique for clinical use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuo HC, Chang FM, Wu CH, Yao BL, Liu CH. The primary application of three-dimensional ultrasonography in obstetrics. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992; 166: 880–886.
Mueller GM, Weiner CP, Yankowitz J. Three-dimensional ultrasound in the evaluation of fetal head and spine anomalies. Obstet Gynecol 1996; 88: 372–378.
Steiner H, Staudach A, Spitzer D, Schaffer H. Three-dimensional ultrasound in obstetrics and gynaecology: technique, possibilities and limitations. Hum Reprod 1994; 9: 1773–1778.
Pretorius DH, House M, Nelson TR, Hollenbach KA. Evaluation of normal and abnormal lips in fetuses: comparison between three-and two-dimensional sonography. AJR 1995; 165: 1233–1237.
Sklansky MS, Nelson TR, Pretorius DH. Three-dimensional fetal echocardiography: gated versus nongated techniques. J Ultrasound Med 1998; 17: 451–457.
Nelson TR, Pretorius DH, Sklansky MS, Hagen-Ansert S. Three-dimesional echocardiographic evaluation of fetal heart anatomy and function: acquisition, analysis, and display. J Ultrasound Med 1996; 15: 1–9.
Chang FM, Hsu KF, Ko HC, et al. Fetal heart volume assessment by three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997; 9: 42–48.
Sklansky MS, Nelson TR, Pretorius DH. Usefulness of gated three-dimensional fetal echocardiography to reconstruct and display structures not visualized with two-dimensional imaging. Am J Cardio 1997; 80: 665–668.
Levental M, Pretorius DH, Sklansky MS, Budorick NE, Nelson TR, Lou K. Three-dimensional ultrasonography of normal fetal heart: comparison with twodimensional imaging. J Ultrasound Med 1998; 17: 341–348.
Achiron R, Glaser J, Gelernter I, Hegesh J, Yagel S. Extended fetal echocardiographic examination for detecting cardiac malformations in low risk pregnancies. Br Med J 1992; 304: 671–674.
Bromley B, Estroff JA, Sanders SP, et al. Fetal echocardiography: accuracy and limitations in a population at high and low risk for heart defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992; 166: 1473–1481.
Kirk JS, Riggs TW, Comstock CH, Lee W, Yang SS, Weinhouse E. Prenatal screening for cardiac anomalies: the value of routine addition of the aortic root to the four-chamber view. Obstet Gynecol 1994; 84: 427–431.
DeVore GR. The aortic and pulmonary outflow tract screening examination in the human fetus. J Ultrasound Med 1992; 11: 345–348.
Drose JA. Scanning: indications and technique. In: Drose JA editor. Fetal Echocardiography. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1998; 15–57.
Meyer-Wittkopf M, Cook A, McLennan A, Summers P, Sharland GK, Maxwell DJ. Evaluation of three-dimensional ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of congenital heart anomalies in fetal cardiac specimens. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996; 8: 303–308.
Riccabona M, Pretorius DH, Nelson TR, Johnson D, Budorick NE. Three-dimensional ultrasound: display modalities in obstetrics. J Clin Ultrasound 1997; 25: 157–167.
Deng J, Gardener JE, Rodeck CH, Lees WR. Fetal echocardiography in three and four dimensions. Ultrasound Med Biol 1996; 22: 979–986.
Zosmer N, Jurkovic D, Jauniaux E, Gruboeck K, Lees C, Campbell S. Selection and identification of standard cardiac views from three-dimensional volume scans of the fetal thorax. J Ultrasound Med 1996; 15: 25–32.
Copel JA, Morotti R, Hobbins JC, Kleinman CS. The antenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease using fetal echocardiography: is color flow mapping necessary? Obstet Gynecol 1991; 78: 1–8.
Sharland GK, Chita SK, Allan LD. The use of colour Doppler in fetal echocardiography. Int J Cardiol 1990; 28: 229–236.
Chiba Y, Kanzaki T, Kobayashi H, Murakami M, Yutani C. Evaluation of fetal structural heart disease using color flow mapping. Ultrasound Med Biol 1990; 16: 221–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, PH., Chen, GD. & Lin, LY. Imaging comparison of basic cardiac views between two- and three-dimensional ultrasound in normal fetuses in anterior spine positions. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 18, 17–23 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014392309528
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014392309528