Abstract
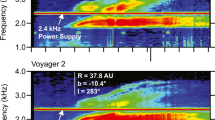
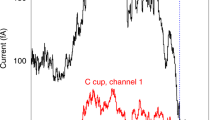
A transient flow system containing several streams and shocks associated with the Bastille Day 2000 solar event was observed by the WIND and ACE spacecraft at 1 AU. Voyager 2 (V2) at 63 AU observed this flow system after it moved through the interplanetary medium and into the distant heliosphere, where the interstellar pickup protons strongly influence the MHD structures and flow dynamics. We discuss the Voyager 2 magnetic and plasma observations of this event. Increases in the magnetic field strength B, density N, temperature T and speed V were observed at the front of a stream at V2, consistent with presence of a shock related to the Bastille Day shock at 1 AU. However, the jumps occurred in a 16.9-hour data gap, so that the shock was not observed directly, and the properties of the candidate shock cannot be determined precisely. The candidate shock was followed by a merged interaction region (MIR) that moved past V2 for at least 10 days. The first part of this MIR contains a structure that might be a magnetic cloud. Just ahead of the shock there was an abrupt increase in density associated with a decrease in temperature such that the solar wind thermal pressure was constant across it. Just behind the shock there was an abrupt decrease in density associated with a net increase in magnetic field strength. This appears to be a pressure balanced structure in which the interstellar pickup protons make a significant contribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axford, W. I.: 1972, in C. P. Sonett, P. J. Coleman, Jr., and J. M. Wilcox (eds.), 'The Interaction of the Solar Wind with the Interstellar Medium', Solar Wind, NASA Spec. Publ. SP-308, p. 609.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1975, Space Sci. Rev. 17, 372.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7217.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1995, Interplanetary Magnetohydrodynamics, Oxford University Press, New York.
Burlaga, L. F. and Behannon, K. W.: 1982, Solar Phys. 81, 181.
Burlaga, L. F., McDonald, F. B., and Ness, N. F.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 1.
Burlaga, L. F., McDonald, F. B., and Schwenn, R.: 1986, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 13331.
Burlaga, L. F., Schwenn, R., and Rosenbauer, H.: 1983, Geophys. Res. Lett. 10, 413.
Burlaga, L. F., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., and Schwenn R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673.
Burlaga, L. F., McDonald, F. B., Ness, N. F., Schwenn, R., Lazarus, A. J., and Mariani, F.: 1984, J. Geophys. Res. 89, 6579.
Burlaga, L. F., McDonald, F. B., Goldstein, M. L., and Lazarus, A. J.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 12127.
Burlaga, L. F., Ness, N. F., Belcher, J. W., and Whang, Y. C.: 1996, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 15523.
Holzer, T. E.: 1972, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 5407.
Lepping, R. P., Jones, J. A., and Burlaga, L. F.: 1990, J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957.
Lepping, R. P. et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Osherovich, V. A.: 1998, in T. Chang and J. R. Jasperse (eds.), Physics of Space Plasmas 15, 265.
Osherovich, V. A., Fainberg, J., and Stone, R. G.: 1999, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 401.
Pauls, H. L. and Zank, G. P.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 19779.
Rice, W. K. M. and Zank, G. P.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12563.
Smith, C.W.et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Wang, C., Richardson, J. D., and Gosling, J. T.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 2429.
Wang, C., Richardson, J. D., and Burlaga, L. F.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Wang, C., Richardson, J. D., and Paularena, K.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res., in press.
Whang, Y. C.: 1991, Space Sci. Rev. 57, 339.
Whang, Y. C. and Burlaga, L. F.: 1986, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 3341.
Whang, Y. C. and Burlaga, L. F.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 6721.
Whang, Y. C., Burlaga, L. F., and Ness, N. F.: 1995, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 17015.
Whang, Y. C., Burlaga, L. F., and Ness, N. F.: 1996, Space. Sci. Rev. 78, 393.
Whang, Y. C., Lu, J. Y., and Burlaga, L. F.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 19787.
Whang, Y. C., Burlaga, L. F., Ness, N. F., and Smith, C. W.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Zank, G. P.: 1999, Space Sci. Rev. 89, 413.
Zank, G. P. and Pauls, H. L.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 7037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burlaga, L., Ness, N., Richardson, J. et al. The Bastille day Shock and Merged Interaction Region at 63 au: Voyager 2 Observations. Sol Phys 204, 399–411 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014269926730
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014269926730