Abstract
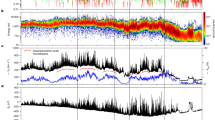
Near 1 AU the solar wind structure associated with the solar flare of 14 July 2000 (Bastille Day) consisted of a large high-speed stream of 15 July and five nearby small streams during a 10-day period. At the leading edge of the large high-speed stream, in less than 6 hours, the flow speed increased from 600 km s−1 to 1100 km s−1, the magnetic field intensity increased from 10 nT to 60 nT, and an interaction region was identified. The interaction region was bounded between the pair of a forward shock F and a reverse shock R. Additional forward shocks were also identified at the leading edge of each of the five smaller streams. This paper presents a magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) simulation using ACE plasma and magnetic field data near 1 AU as input to study the radial evolution of the Bastille Day solar wind event. The two shocks, F and R, propagated in opposite directions away from each other in the solar wind frame and interacted with neighboring shocks and streams; the spatial and temporal extent of the interaction region continued to increase with the heliocentric distance. The solar wind was restructured from a series of streams at 1 AU to a huge merged interaction region (MIR) extending over a period of 12 days at 5.5 AU. Throughout the interior of the MIR bounded by the shock pair F and R the magnetic field intensity was a few times stronger than that outside the MIR. The simulation shows how merging of shocks, collision of shocks, and formation of new shocks contributed to the evolution process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burlaga, L. F.: 1983, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 6085.
Burlaga, L. F. et al.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 3331.
Burlaga, L. F. et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Lepping, R. P. et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Smith, C.W.et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Wang, C., Richardson, J. D., and Paularena, K.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 13 007.
Wang, C. et al.: 2001, Solar Phys., this issue.
Whang, Y. C.: 1991, Space Sci. Rev. 57, 339.
Whang, Y. C.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 17 419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whang, Y., Burlaga, L., Ness, N. et al. The Bastille day Shocks and Merged Interaction Region. Sol Phys 204, 253–263 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014221210800
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014221210800