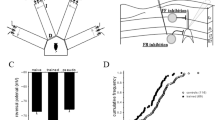
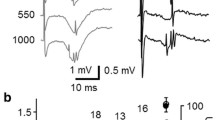
Abstract
Using the model of long-term posttetanic potentiation (LTP) in slices of the olfactory cortex of rat brain, we have tested a hypothesis according to which activation of nerve cells results in a release of neuromodulatory factors into extracellular space; these factors, diffusing over significant distances, are capable of synchronously modifying the initial reactivity of neuronal populations. Using the technique of bioassay, i.e., transfer of perfusate from the tetanized donor slice to the recipient slice, in combination with pharmacological and neurochemical techniques, we found that in response to excitation, the cells of olfactory cortex slices secrete peptides. This observation confirms the above hypothesis. The spectrum of released peptides changes depending on the degree of cell excitation and, in addition, is frequency-dependent. It has been demonstrated that the key target of these peptides are N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors. We propose that two peptide pools are involved in the initial and late phases of LTP. The possible significance of peptide cell regulation in mechanisms of neuronal plasticity is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Agnati, L.F., Zole, M., Stromberg, I., and Fuxe, K., Intercellular Communication in the Brain: Wiring Versus Volume Transmission, J. Neurosci., 1995, vol. 69, no. 3, pp. 711-726.
Affinity Chromatography Principles and Methods, Pharmacia Fine Chemicals., 70, 1979.
Bartfai, T., Iverfeldt, K., Fisone, G., Serfozo, P., Regulation of the Release of Coexisting Neurotransmitters, Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 1988, vol. 28, pp. 285-310.
Bashir, Z.I. and Collingridge, G.L., Synaptic Plasticity: Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus, Current Opinion in Neurobiol., 1992, vol. 2, pp. 328-335.
Bliss, T.V.P. and Collingridge, G.L., A Synaptic Model of Memory: Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus, Nature, 1993, vol. 361, no. 6407, pp. 31-39.
Bloche, A. and Thoenen, H., Characterization of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Release from Hippocampal Neurons: Evidence for a Constitutive and an Unconventional Sodium-Dependent Regulated Pathway, Eur. J. Neurosci., 1995, vol. 7, pp. 1220-1228.
Castren, E., Pitkanen, M., Sirvio, J., et al., The Induction of LTP Increases BDNF and NGF mRNA but Decreases NT-3 mRNA in the Dentate Gyrus, Neuroreport, 1993, vol. 4, pp. 895-898.
Charriaut-Marlangue, C., Aniksztejn, L., Roisin, M.P., and Ben-Ari, Y., Release of Proteins During Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus of Anesthetized Rat, Neurosci. Lett., 1988, vol. 91, nos. 1-3, pp. 308-314.
Collins, G.G.S., Pharmacological Evidence that NMDA Receptors Contribute to Mono-and Di-Synaptic Potentials in Slices of Mouse Olfactory Cortex, Neuropharmacology, 1991, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 547-555.
Collins, G.G.S., The Characteristics and Pharmacology of Olfactory Cortical LTP Induced by Theta-Burst High Frequency Stimulation and 1S, 3R-ACPD, Neuropharmacology, 1994, vol. 33, pp. 87-95.
Cropper, E.C., Price, D., Tenenbaum, R., et al., Release of Peptide Cotransmitters from a Cholinergic Motor Neuron Under Physiological Conditions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1990, vol. 87, pp. 933-937.
Deadwyler, S.A., Dunwidde, T., and Lynch, G., A Critical Level of Protein Synthesis Is Required for Long-Term Potentiation, Synapse, 1987, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 90-95.
Duffy, C., Teyler, T.J., and Shashoua, V.E., Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampal Slice: Evidence for Stimulated Secretion of Newly Synthesized Proteins, Science, 1981, vol. 212, no. 4499, pp. 1148-1151.
Engert, F. and Bonhoeffer, T., Synapse Specificity of Long-Term Potentiation Breaks Down at Short Distances, Nature, 1997, vol. 388, pp. 279-284.
Fazeli, M.S., Corbet, J., Dunn, M.J., et al., Changes in Protein Synthesis Accompanying Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus in vivo, J. Neurosci., 1993, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 1346-1353.
Fazeli, M.S., Errington, M.L., Dolphin, A.C., and Bliss, T.V.P., Increased Efflux of Haemoglobin-Like Protein and an 80 kDa Protease into Push-Pull Perfusates Following the Induction of Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus, Brain Res., 1990, vol. 521, nos. 1-2, pp. 247-253.
Fazeli, M.S., Errington, M.L., Dolphin, A.C., and Bliss, T.V.P., Long-Term Potentiation in the Dentate Gyrus of Anesthetized Rat Is Accompanied by an Increase in Protein Efflux into Push-Pull Cannula Perfusates, Brain Res., 1988, vol. 473, no. 1, pp. 51-59.
Figurov, A., Pozzo-Miller, L.D., Olafsson, P., et al., Regulation of Synaptic Responses to High-Frequency Stimulation and LTP by Neurotrophins in the Hippocampus, Nature, 1996, vol. 381, pp. 706-709.
Fitzsimonds, R.M. and Poo, M.M., Retrograde Signaling in the Development and Modification of Synapses, Physiol. Rev., 1998, vol. 78, no. 1, pp. 143-170.
Frey, U., Krug, M., Reymann, K.G., and Matthies, H., Anisomycin, an Inhibitor of Protein Synthesis, Blocks Late Phases of LTP Phenomena in the Hippocampal CA1 Region in vitro, Brain Res., 1988, vol. 452, nos. 1-2, pp. 57-65.
Frey, U., Frey, S., Schollmeier, F., and Krug, M., Influence of Actinomycin D, a RNA-Synthesis Inhibitor, on Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Hippocampal Neurons in vivo and in vitro, J. Physiol., 1995, vol. 490, pp. 703-711.
Gubler, E.V. and Genkin, A.A., Primenenie kriteriev neparametricheskoi statistiki dlya otsenki razlichii dvukh grupp nablyudenii v medikobiologicheskikh issledovaniyakh (The Use of the Criteria of Nonparametric Statistics to Estimate Differences between Two Observation Groups in Medical-Biological Studies), Leningrad: Meditsina, 1969.
Gustafsson, B. and Wigstrom, H., Physiological Mechanisms Underlying Long-Term Potentiation, Trends Neurosci., 1988, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 156-162.
Hesse, G.W., Hofstein, R., and Shashoua, V.E., Protein Release from Hippocampus in vitro, Brain Res., 1984, vol. 305, no. 1, pp. 61-66.
Hoffman, W.H. and Haberly, L.B., Bursting Induces Persistent All-or-None EPSPs by an NMDA-Dependent Process in Piriform Cortex, J. Neurosci., 1989, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 206-215.
Jung, M.W., Larson, J., and Lynch, G., Long-Term Potentiation of Monosynaptic EPSPs in Rat Piriform in vitro, Synapse, 1990a, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 279-283.
Jung, M.W., Larson, J., and Lynch, G., Role of NMDA and Non-NMDA Receptors in Synaptic Transmission in Rat Piriform Cortex, Exp. Brain Res., 1990b, vol. 82, no. 5, pp. 451-455.
Kanter, E.D. and Haberly, L.B., NMDA-Dependent Induction of Long-Term Potentiation in Afferent and Association Fiber Systems of Piriform Cortex in vitro, Brain Res., 1990, vol. 525, no. 1, pp. 175-179.
Kapur, A. and Haberly, L.B., Duration of NMDA-Dependent Synaptic Potentiation in Piriform Cortex in vivo Is Increased After Epileptiform Bursting, J. Neurophysiol., 1998, vol. 80, no. 4, pp. 1623-1629.
Korte, M., Kang, H., Bonhoeffer, T., and Schuman, E., A Role of BDNF in the Late-Phase of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation, Neuropharmacology, 1998, vol. 37, nos. 4-5, pp. 553-560.
Krug, M., Lossner, B., and Ott, T., Anisomycin Blocks the Late Phase of Long-Term Potentiation in Dentate Gyrus of Freely Moving Rats, Brain Res. Bull., 1984, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 39-42.
Kupfermann, I., Functional Studies of Cotransmission, Physiol. Rev., 1991, vol. 71, no. 3, pp. 683-732.
Leninger, A., Principles of Biochemistry, New York: Worth, 1982. Translated under the title Osnovy biokhimii, Moscow: Mir, 1985.
Margolis, F.L., Carnosine, Trends Neurosci., 1978, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 42-44.
Mokrushin, A.A. and Emel'yanov, N.A., Posttetanic and Frequency-Dependent Potentiation in Slices of the Rat Brain Olfactory Cortex, Fiziol. Zh., 1990, vol. 76, no. 4, pp. 425-429.
Mokrushin, A.A. and Emelyanov, N.A., Effects of Melanostatine (MIF-1) on Focal Potentials in Slices of Rat Brain Cortex, Neuropeptides, 1991, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 87-94.
Mokrushin, A.A. and Tokarev, A.V., Endogenous Regulators of Long-Term Potentiation and Depression in Slices of the Rat Brain Olfactory Cortex, Fiziol. Zh., 1995, vol. 81, no. 8, pp. 39-44.
Mokrushin, A.A. and Plekhanov, A.Y., Analysis of Perfusates Collected from Surviving Rat Brain Olfactory Cortex Slices, in Neurochemistry, New York: Plenum, 1997, pp. 519-521.
Mokrushin, A.A., Peptide-Dependent Mechanisms of Neuronal Plasticity in the Olfactory Cortex, Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg, 1997.
Mokrushin, A.A. and Samoilov, M.O., Peptide-Dependent Mechanisms of Long-Term Posttetanic Potentiation (Facts and Hypothesis), Usp. Fiziol. Nauk, 1999, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 3-28.
Musyashchikova, S.S. and Mokrushin, A.A., Studies on Reactive Depression According to V.N. Chernigovskii, Izv. Akad. Nauk. Ser. Biol., 1988, no. 3, pp. 374-383.
Nguyen, P.V., Abel, T., and Kandel, E.R., Requirement for a Critical Period of Transcription for a Late Phase of LTP, Science, 1994, vol. 265, no. 5175, pp. 1104-1107.
Ojika, K., Tsugu, Y., Mitake, S, et al., NMDA Receptor Activation Enhances the Release of a Cholinergic Differentiation Peptide (HCNP) from Hippocampal Neurons in vitro, Develop. Brain Res., 1998, vol. 106, nos. 1-2, pp. 173-180.
Otani, S. and Abraham, W.C., Inhibition of Protein Synthesis in the Dentate Gyrus, but Not the Entorhinal Cortex, Blocks Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation in Rats, Neurosci. Lett., 1989, vol. 106, nos. 1-3, pp. 175-180.
Otani, S., Marshall, C., and Tate, W., Maintenance of Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Dentate Gyrus Required Protein Synthesis but Not Messenger RNA Synthesis Immediately Posttetanization, J. Neurosci., 1989, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 519-526.
Otani, S., Roisin-Lallemand, M.P., and Ben-Ari, Y., Enhancement of Extracellular Protein Concentrations During Long-Term Potentiation in the Rat Hippocampal Slice, J. Neurosci., 1992, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 265-272.
Patterson, S.L., Grover, L.M., Schwartzkroin, P.A., and Bothwell, M., Neurotrophin Expression in Rat Hippocampal Slices: A Stimulus Paradigm Inducing LTP in CA1 Evokes Increases in BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs, Neuron, 1992, vol. 9, pp. 1081-1088.
Raize, T.E. and Mokrushin, A.A., Effect of the Factors Released from Brain Cortex Donor Slices after Tetanic Stimulation on the Activity of Phosphoinositide Regulatory System in the Recipient Brain Cortex Slices, Satellite Simposia of the XXXIII Intern. Congress of Physiol. Sci. Molecular and Genetic Bases of Adaptive Behavior, Koltushi, 1997, p. 44.
Reis, D.J., Yang, X.C., and Milner, T.A., Agmatine Containing Axon Terminals in Rat Hippocampus Form Synapses on Pyramidal Cells, Neurosci. Lett., 1998, vol. 250, no. 3, pp. 185-188.
Rochel, S. and Margolis, F.L., Carnosine Release from the Olfactory Bulb Synaptosomes Is Calcium Dependent and Depolarization Stimulated, J. Neurochem., 1982, vol. 38, pp. 1505-1514.
Sastry, B.R., Chirwa, S.S., May, P.B.Y., et al., Are Nerve Growth Factors Involved in Long-Term Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus and Spatial Memory? in Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus, Hass, H. and Heidelberg, B.G., Eds., 1988a, pp. 102-105.
Sastry, B.R., Chirwa, S.S., May, P.B.Y., and Maretic, H., Substances Released During Tetanic Stimulation of Rabbit Neocortex Induce Neurite Growth in PC-12 Cells and Long-Term Potentiation in Guinea-Pig Hippocampus, Neurosci. Lett., 1988b, vol. 91, nos. 1-3, pp. 101-105.
Schuman, E.M. and Madison, D.V., Locally Distributed Synaptic Potentiation in the Hippocampus, Science, 1994, vol. 263, pp. 532-536.
Shashoua, V.E., Hesse, G.W., and Moore, B.W., Proteins of the Brain Extracellular Fluid: Evidence for Release of S100 Protein, J. Neurochem., 1984, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 1536-1541.
Song, D.K., Park, W.K., Bae, J.H., et al., Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Rapidly Potentiates Synaptic Transmission through NMDA but Suppresses It through Non-NMDA Receptors in Rat Hippocampal Neurons, Brain Res., 1998, vol. 799, no. 1, pp. 177-180.
Stanton, P.K. and Sarvey, J.M., Blockade of Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Hippocampal CA1 Region by Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis, J. Neurosci., 1984, vol. 4, no. 12, pp. 3080-3088.
Thieles, E., Weisz, D.J., and Berger, T.W., In vivo Modulation of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Potentiation by the Glycine Modulatory Site, Neuroscience, 1992, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 501-509.
Tseng, G.F. and Haberly, L.B., Characterization of Synaptically Mediated Fast and Slow Inhibitory Processes in Piriform Cortex in an in vitro Slice Preparation, J. Neurophysiol., 1988, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 1352-1376.
Uenishi, N., Shors, T.J., Finch, C.E., et al., Increased Synthesis of Two Polypeptides in Area CA1 of the Hippocampus in Response to Repetitive Electrical Stimulation, Brain Res., 1991, vol. 567, no. 2, pp. 248-252.
Whim, M.D. and Lloyd, P.E., Frequency-Dependent Release of Peptide Cotransmitters from Identified Cholinergic Motor Neurons in Aplysia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1989, vol. 86, pp. 9034-9038.
Xie, Z., Morishita, W., Kam, T., et al., Studies on Substances That Induce Long-Term Potentiation in Guinea-Pig Hippocampal Slices, J. Neurosci., 1991, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 11-20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokrushin, A.A. The Role of Endogenous Peptides in the Development of Long-Term Posttetanic Potentiation. Biology Bulletin 29, 62–74 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013246019876
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013246019876