Abstract
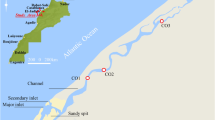
There has been an increasing interest in the consequences of the effectof discharge of effluents containing chemical elements into the marine environment.Here, we present the determination of a number of heavy metals in sedimentsfrom the Ribble Estuary in the north-west of England. Sediment cores wereobtained from the Ribble estuary and the cores were subdivided into 5 cm segmentswhich were then freeze dried. Part of the material so obtained was then usedto produce samples with particles of a given size range, since uptake of heavymetals by sediments is very particle-size dependent. Selected samples werethen reactor irradiated for instrumental neutron activation analysis. Theaims of this present study are to establish depth and longitudinal distributionsof heavy metals at selected site locations and to investigate the criticalsediment parameters that influence the uptake and retention of such contaminants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. N. Luoma,R. Dagovitz,E. Axtmann, Sci. Total Environ., 97/98 (1990) 685.
V. T. Bowen,H. D. Livingston, in: Proc. Intern. Symp. on the Impacts of Radionuclide Releases into the Marine Environment, IAEA, Vienna, 1981, p. 33.
U. Forstner,W. Salomons, Environ. Technol. Lett., 1 (1980) 494.
G. E. Gordon,K. Randle,G. G. Goles,J. B. Corliss,M. H. Beeson,S. Oxley, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 32 (1968) 369.
J. C. Laul,D. R. Case,M. Wechter,F. Schmid-Bleek,M. E. Lipschutz, J. Radioanal. Chem., 4 (1970) 241.
R. H. Filby,W. A. Haller,K. R. Shah, J. Radioanal. Chem., 5 (1970) 227.
J. R. Delater,I. D. Abercrombie, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 9 (1970) 327.
E. Cortes, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 84 (1984) 157.
K. Randle, Chem. Geol., 13 (1974) 237.
A. Ando,H. Kurasawa,T. Ohmori,E. Takeda, Geochim. J., 8 (1974) 175.
Y. Hamajima,M. Koba,K. Endo,H. Nakahara, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 89 (1985) 315.
L. T. Thorne,G. Nickless, Sci. Total Environ., 19 (1981) 207.
B. S. Krumgalz,G. Fainshtein,A. Cohen, Sci. Total Environ., 116 (1992) 15.
P. J. Kershaw, R. J. Pentreath, D. S. Woodhead, G. J. Hunt, MAAF; ISSN 0142–2499; No. 32, Lowestoft, UK, 1992.
G. W. Bryan,W. J. Langston, Environ. Pollut., 76 (1992) 89.
R. G. V. Hancock,W. C. Mayhaney, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 168 (1993) 83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Randle, K., Al-Jundi, J. Instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) of estuarine sediments. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 249, 361–367 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013210402494
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013210402494