Abstract
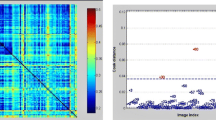
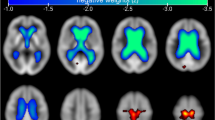
Brain tissue samples, obtained from the Alzheimer Disease Brain Bank,Institute of Psychiatry, London, were taken from both left and right hemispheresof three regions of the cerebrum, namely the frontal, parietal and occipitallobes for both Alzheimer and 'normal' subjects. Trace elementconcentrations in the frontal lobe were determined for twenty six Alzheimer(15 male, 11 female) and twenty six 'normal' (8 male, 18 female)brain tissue samples. In the parietal lobe ten Alzheimer (2 male, 8 female)and ten 'normal' (8 male, 2 female) samples were taken along withten Alzheimer (4 male, 6 female) and ten 'normal' (6 male, 4 female)from the occipital lobe. For the frontal lobe trace element concentrationswere determined using proton induced X-ray emission (PIXE) analysis whilein parietal and occipital regions instrumental neutron activation analysis(INAA) was used. Additionally eighteen Alzheimer (9 male, 9 female) and eighteenage matched 'normal' (8 male, 10 female) living subjects wereexamined using positron emission tomography (PET) in order to determine regionalcerebral metabolic rates of glucose (rCMRGlu). The rCMRGlu of 36 regions ofthe brain was investigated including frontal, occipital and parietal lobesas in the trace element study. Hierarchical cluster analysis was applied tothe trace element and glucose metabolism data to discover which variablesin the resulting dendrograms displayed the most significant separation betweenAlzheimer and 'normal' subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Stedman,N. M. Spyrou, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 217 (1997) 163.
J. D. Stedman,N. M. Spyrou, Nutrition, 11 (1995) No. 5, 542.
D. A. Cutts,N. M. Spyrou,R. P. Maguire,J. D. Stedman,K. L. Leenders, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 244 (2000) 179.
W. D. Ehmann,W. R. Markesbery, Neurotoxicology, 7 (1986) 197.
G. McKhann,D. Drachman,M. Folstein,R. Katzman,D. Price,E. M. Stadlan, Neurology, 34 (1994) 939.
C. G. Rhodes,R. J. S. Wise,J. M. Gibbs,R. S. J. Frackowiak,J. Hatazawa,A. J. Palmer,D. G. T. Thomas,T. Jones, Ann. Neurol., 14 (1983) 614.
J. Talairach,P. Tournoux, Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain, Thieme, Stuttgart, 1988.
D. Wishart, Clustan Graphics Primer: A Guide to Cluster Analysis, Clustan Ltd., Edinburgh, 1999.
M. Ebadi,P. L. Iversen,R. Hao,D. R. Cerutis, Neurochem. Int., 27 (1995) 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cutts, D., Spyrou, N., Maguire, R. et al. Hierarchical clustering of Alzheimer and “normal” brains using elemental concentrations and glucose metabolism determined by PIXE, INAA and PET. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 249, 455–460 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013203611580
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013203611580