Abstract
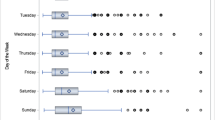
In this paper multilevel analysis is used to study individual choices of time allocation to maintenance, subsistence, leisure, and travel time exploiting the nested data hierarchy of households, persons, and occasions of measurement. The multilevel models in this paper examine the joint and multivariate correlation structure of four dependent variables in a cross-sectional and longitudinal way. In this way, observed and unobserved heterogeneity are estimated using random effects at the household, person, and temporal levels. In addition, random coefficients associated with explanatory variables are also estimated and correlated with these random effects. Using the wide spectrum of options offered by multilevel models to account for individual and group heterogeneity, complex interdependencies among individuals within their households, within themselves over time, and within themselves but across different indicators of behavior, are analyzed. Findings in this analysis include large variance contribution by each level considered, clear evidence of non-linear dynamic behavior in time-allocation, different trajectories of change in time allocation for each of the four dependent variables used, and lack of symmetry in change over time characterized by different trajectories in the longitudinal evolution of each dependent variable. In addition, the multivariate correlation structure among the four dependent variables is different at each of the three levels of analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat C (2000) A multi-level cross-classified model for discrete response variables. Transportation Research 34B: 567–582.
Bryk AS & Raudenbush SW (1992) Hierarchical Linear Models. Newberry Park: Sage.
Goldstein H (1995) Multilevel Statistical Models. London and New York: Edward Arnold.
Goulias KG (1999a) Multilevel random effects analysis of modal use constraints and perceptions on public transportation using data from Germany. In: Sacharov LJ (ed) Urban Transport V, Urban Transport and the Environment for the 21st Century (pp 181–190). Southampton: WIT Press.
Goulias KG (1999b) Longitudinal analysis of activity and travel pattern dynamics using Generalized Mixed Markov Latent Class Models. Transportation Research 33B(8): 535–557.
Goulias KG & Ma J (1996) Analysis of longitudinal data from the Puget Sound transportation panel. Task B: Integration of PSTP databases and PSTP codebook. Final Report. # 9619. The Pennsylvania Transportation Institute, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA.
Golob TF & McNally MG (1997) A model of activity participation and travel interactions between household heads. Transportation Research 31B: 177–194.
Greene WH (1997) Econometric Analysis, Third Edition. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Longford NT (1993) Random Coefficient Models. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Ma J & Goulias KG (1997) An analysis of activity and travel patterns in the Puget Sound Transportation Panel. In: Ettema DF & Timmermans HJP (eds) Activity-Based Approaches to Travel Analysis (pp 189–207) The Netherlands: Pergamon.
Ma J & Goulias KG (1998) Forecasting Home Departure Time, Daily Time Budget, Activity Duration, and Travel Time Using Panel Data. Preprint 98-00392 TRB CD-ROM. Paper presented at the 77th Annual Transportation Research Board Meeting, January 11-15, Washington DC.
Murakami E & Watterson WT (1990) Developing a household travel panel survey for the Puget Sound Region. Transportation Research Record 1285. 40–48.
Murakami E & Ulberg C (1997) The Puget Sound transportation panel. In: Golob TF, Kitamura R & Long L. Panels for Transportation Planning Methods and Applications (pp 159–192) Boston: Kluwer.
Pas EI (1999) Time in travel choice modeling: from relative obscurity to center stage. In: Garling T, Laitila T & Westin K (eds) Theoretical Foundations of Travel Choice Modeling. Pergamon, Amsterdam.
Searle SR, Casella G & McCulloch CE (1992) Variance Components. New York: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulias, K.G. Multilevel analysis of daily time use and time allocation to activity types accounting for complex covariance structures using correlated random effects. Transportation 29, 31–48 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012973004152
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012973004152