Abstract
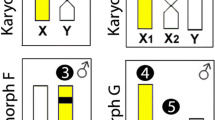
We describe SC complements and results from comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) on mitotic and meiotic chromosomes of the zebrafish Danio rerio, the platyfish Xiphophorus maculatus and the guppy Poecilia reticulata. The three fish species represent basic steps of sex chromosome differentiation: (1) the zebrafish with an all-autosome karyotype; (2) the platyfish with genetically defined sex chromosomes but no differentiation between X and Y visible in the SC or with CGH in meiotic and mitotic chromosomes; (3) the guppy with genetically and cytogenetically differentiated sex chromosomes. The acrocentric Y chromosomes of the guppy consists of a proximal homologous and a distal differential segment. The proximal segment pairs in early pachytene with the respective X chromosome segment. The differential segment is unpaired in early pachytene but synapses later in an ‘adjustment’ or ‘equalization’ process. The segment includes a postulated sex determining region and a conspicuous variable heterochromatic region whose structure depends on the particular Y chromosome line. CGH differentiates a large block of predominantly male-specific repetitive DNA and a block of common repetitive DNA in that region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albini S, Jones G, Wallace B (1984) A method for preparing two-dimensional surface-spreads of synaptonemal complexes from plant meiocytes for light and electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res 152: 280–285.
Almeida-Toledo LF, Foresti F, Daniel MFZ, Toledo-Filho SA (2000) Sex chromosome evolution in fish: the formation of the neo-Y-chromosome in Eigenmannia (Gymnotiformes). Chromosoma 109: 197–200.
Amores A, Postlethwait JH (1999) Banded chromosomes and the Zebrafish karyotype. Meth in Cell Biol 60: 323–338.
Anders A, Anders F, Förster W, Klinke K, Rase S (1969) XX-, XY, YY-Weibchen und XX-, XY-, YY-Männchen bei Platypoccilus maculatus (Pocciliidae). Zool Anz Suppl 33: 333–339.
Baroiller J-F, Guiguien Y, Fostier A (1999) Endocrine and environmental aspects of sex differentiation in fish. Cell Mol Life Sci 55: 910–931.
Blin N, Stafford DW (1976) A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucl Acids Res 3: 2303–2308.
Carrasco LAP, Penman DJ, Bromage N (1999) Evidence for the presence of sex chromosomes in Nile Tilapia (Orcochromis niloticus) from synaptonemal complex analysis of XX, XY and YY genotypes. Aquaculture 173: 207–218.
Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D, Hnilicka J, Yu A, Guttman DS (1997) Lack of degeneration of loci on the neo-Y chromosome of Drosophila americana americana. Genetics 145: 989–1002.
Conover DO, Kynard BE (1981) Environmental sex determination: Interaction of temperature and genotype in a fish. Science 213: 577–579.
Daga R, Thode G, Amores A (1996) Chromosome complement, C-banding, Ag-NOR and replication banding in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Chromosome Res 4: 29–32.
Dzwillo M (1959) Genetische Untersuchungen an domestizierten Stämmen von Lebistes reticulatus (Peters). Mitt Hamburg Zool Mus Inst 57: 143–186.
Dzwillo M (1962) Über die künstliche Erzeugung funktioneller Männchen weiblichen Genotyps bei Lebistes reticulatus. Biologisches Zentralblatt 81: 575–584.
Ecker M, Fritz A, Westerfield M (1992) Identification of two families of satellite-like repetitive DNA sequences from the zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Genomics 13: 1169–1173.
Foerster W, Anders F (1977) Zytogenetischer Vergleich der Karyotypen verschiedener Rassen und Arten lebendgebärender Zahnkarpfen der Gattung Xiphophorus. Zool Anz 198: 167–177.
Gordon M (1954) Two opposing sex-determining mechanisms, one XX-XY, the other WY-YY, in different natural populations of the platyfish Xiphophorus maculatus. Proc 9th Int Congr Genetics (Suppl to Caryologia 6) 2: 960–964.
Gornung E, Gabrielli I, Cataudella S, Sola L (1997) CMA3-banding pattern and fluorescence in situ hybridization with 18S rRNA genes in zebrafish chromosomes. Chromosome Res 5: 40–46.
Grossman A, Short R, Cain G (1981) Karyotype evolution and sex chromosome differentiation in Schistosomes (Trematoda, Schistosomatidae). Chromosoma 84: 413–430
Kallman KD (1984) A new look at sex determination in poeciliid fishes. In: Turner BJ (ed) Evolutionary Genetics of Fishes. New York, Plenum Press, pp 95–171.
Kirpičnikov VS (1987) Genetische Grundlagen der Fischzüchtung. Berlin: VEB Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag.
Kosswig C (1964) Polygenic sex determination. Experientia 20: 190–199.
Lapierre JM, Cacheux V, Da Silva F et al. (1998) Comparative genome hybridization: technical development and cytogenetic aspects for routine use in clinical laboratories. Annal Génétique 41: 56–62.
Morescalchi A (1992) Chromosomes, sex determination and environment in teleosteans. In: Dallai R (ed) Sex Origin and Evolution. Modena: UZI, pp 137–149.
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1981) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. II. Synaptic adjustment in a tandem duplication. Chromosoma 81: 519–535
Nakayama I, Foresti F, Tewari R, Schartl M, Chourront D (1994) Sex chromosome polymorphism and heterogametic males revealed by two cloned probes in the ZW/ZZ fish Leporinus elongatus. Chromosoma 103: 31–39.
Nanda I, Feichtinger W, Schmid M, Schröder J, Zischler H, Epplen J (1990) Simple repetitive sequences are associated with differentiation of the sex chromosomes in the guppy fish. J Mol Evol 30: 456–462.
Nanda I, Schartl M, Epplen J, Feichtinger W, Schmid M (1993) Primitive sex chromosomes in poeciliid fishes harbor simple repetitive DNA sequences. J Exp Zool 265: 301–308.
Nanda I, Volff J-N, Weis S et al. (2000) Amplification of a long terminal repeat-like element on the Y chromosome of the platyfish, Xiphophorus maculatus. Chromosoma 109: 173–180.
Pelegri F, Schulte-Merker S (1999) A gynogenesis-based screen for maternal-effect genes in the zebrafish. Meth Cell Biology 60: 1–20.
Pijnacker L, Ferwerda M (1995) Zebrafish chromosome banding. Genome 38: 1052–1055.
Solari AJ (1992) Equalization of Z and W axes in chicken and quail oocytes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 59: 52–56.
Stebbins G (1971) Chromosomal Evolution in Higher Plants. Arnold, London.
Steinemann M, Steinemann S, Lottspeich F (1993) How Y chromosomes become genetically inert. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5737–5741.
Traut W (1994) Sex determination in the fly Megaselia scalaris, a model system for primary steps of sex chromosome evolution. Genetics 136: 1097–1104.
Traut W, Willhoeft U (1990) A jumping sex determining factor in the fly Megaselia scalaris. Chromosoma 99: 407–412.
White M (1973) Animal Cytology and Evolution, 3rd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Winge O (1934) The experimental alteration of sex chromosomes into autosomes and vice versa, as illustrated by Lebistes. CR Trav Lab Carlsberg Ser Physiol 21: 1–49.
Yamamoto T (1958) Artificial induction of functional sex-reversal in genotypic females of the Medaka (Oryzias latipes). J Exp Zool 137: 227–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traut, W., Winking, H. Meiotic chromosomes and stages of sex chromosome evolution in fish: zebrafish, platyfish and guppy. Chromosome Res 9, 659–672 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012956324417
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012956324417