Abstract
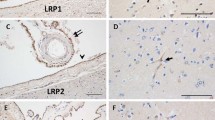
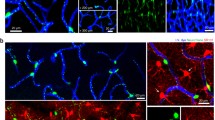
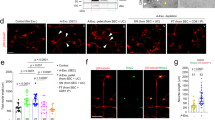
Apolipoprotein D, a lipocalin transporter of small hydrophobic molecules including sterols, steroid hormones and arachidonic acid, is a widely expressed protein in peripheral and neural tissues. It has been shown to be upregulated in the context of neural injury, and with neuronal degeneration and regeneration. Here we have used light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry with immunogold labeling to delineate the pattern of expression of apoD in the human brain. Our results confirm previous observations that apoD is a predominantly glial protein in the nervous system. In addition we have found that apoD is present in the cytosol and outer membrane of the nuclear envelope of glial cells in the neuropil. The labeled glial cells were putatively identified as a population of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Immunoreactivity was also associated with the cytosol of perivascular cells, and lysosomes of pericytes, in the walls of blood vessels. These observations suggest a potential role for glial cells and apoD, in the transport of sterols and small hydrophobic molecules to, or from, blood vessels in the cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, CY., Ong, WY., Sundaram, R.K. et al. Immunocytochemical localization of apolipoprotein D in oligodendrocyte precursor-like cells, perivascular cells, and pericytes in the human cerebral cortex. J Neurocytol 30, 209–218 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012797623620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012797623620