Abstract
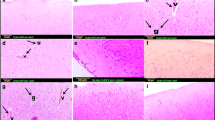
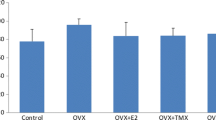
A number of studies have shown that 17β-estradiol has neuroprotective properties. In this study the neuroprotective effect of 17β-estradiol against quinolinic-acid-induced neuronal damage was investigated. Ovariectomized rats were separated into three groups of five animals each. Rats received daily subcutaneous injections of either olive oil or 17β-estradiol in olive oil for 7 days prior to and following a single intrahippocampal injection of 1 μmol quinolinic acid in 2 μL phosphate-buffered saline. The brains were removed and the hippocampi either sectioned and stained for microscopic examination or used in glutamate receptor saturation binding studies. Glutamate receptor displacement binding studies were also performed using concentrations of 0.05 nM–5 μM 17β-estradiol or quinolinic acid. The results show that 17β-estradiol protects hippocampal neurons from quinolinic-acid-induced neurodegeneration by competing with quinolinic acid to bind to the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. This would result in a decrease in intracellular free-calcium influx and resultant neuronal swelling.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bender, D.A. (1983). Biochemistry of tryptophan in health and disease. [Review]. Mol. Aspects Med. 6:101–197.
Cooper, J.R., Bloom, F.E., and Roth, R.H. (1996). The Biochemical Basis of Neuropharmacology, 7th edn., Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 183, 471.
Daya, S. (1982). The Influence of Sex Steroids on Pineal Enzymes, MSc thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown 6140, South Africa, pp. 74.
Foy, M.R., Xu, J., Xie, X., Brinton, R.D., Thompson, R.F., and Berger, T.W. (1999). 17β-Estradiol enhances NMDA receptor-mediated EPSP's and long-term potentiation. J. Neurophysiol. 81:925–929.
Gazzaley, A.H., Weiland, N.G., McEwen, B.S., and Morrison, J.H. (1996). Differential regulation of NMDAR1 mRNA and protein by estradiol in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 16:6830–6838.
Gould, E., Woolley, C.S., Frankfurt, M., and McEwen, B.S. (1990). Gonadal steroids regulate dendritic spine density in hippocampal pyrimidal cells in adulthood. J. Neurosci. 10:1286–1291.
König, J.F.R. and Klippel, R.A. (1963). The Rat Brain, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland, pp. 108–114.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265.
McEwen, B.S. (1998). Multiple ovarian hormone effects on brain structure and function. J. Gender Spec. Med. 1:33–41.
Moroni, F., Lombard, G., Moneti, G., and Aldinio, C. (1984). The excitotoxin quinolinic acid is present in the brain of several mammals and its cortical content increases during the aging process. Neurosci. Lett. 47:51.
Morse, J.K., DeKosky, S.T., and Scheff, S.W. (1992). Neurotrophic effects of steroids on lesion-induced growth in the hippocampus. Exp. Neurol. 118:47–52.
Santamaria, A. and Rios, C. (1993). MK-801, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, blocks quinolinic acid-induced lipid peroxidation in rat corpus striatum. Neurosci. Lett. 159:51–54.
Santamaria, A., Rios, C., Perez, P., Flores, A., Galvan-Arzate, S., Sorio-Rico, L., and Solis, F. (1996). Quinolinic acid neurotoxicity: In vivo increased copper and manganese content in rat corpus striatum after quinolinate intrastriatal injection. Toxicol. Lett. 87:113–119.
Schwarcz, R., Brush, G.S., Foster, A.C., and French, E.D. (1984). Seizure activity and lesions after intrahippocampal quinolinic acid injection. Exp. Neurol. 84:1–17.
Schwarcz, R., Whetsell, W.O., and Mangano, R.M. (1983). Quinolinic acid: An endogenous metabolite that produces axon-sparing lesions in rat brain. Science 219:316–318.
Singer, C.A., Rogers, K.L., Strickland, T.M., and Dorsa, D.M. (1996). Estrogen protects primary cortical neurons from glutamate toxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 212:13–16.
Southgate, G.(1999). An Investigation Into the Neuroprotective Properties of Melatonin, PhD thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown 6140, South Africa, pp. 111–115.
Stone, T.W. (1993). Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol. Rev. 48:309.
Torand-Allerand, C.D., Hashimoto, K., Greenough, W.T., and Saltarelli, M. (1983). Sex steroids and the development of the newborn mouse hypothalamus and preoptic area in vitro:III. Effects of estrogen on dendritic differentiation. Brain Res. 283:97–101.
Tsuzuki, K., Iino, M., and Ozawa, S. (1989). Change in calcium permeability caused by quinolinic acid in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 105:269–274.
Weaver, C.E., Park-Chung, M., Gibbs, T.T., and Farb, D.H. (1997). 17β-Estradiol protects against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity by direct inhibition of NMDA receptors. Brain Res. 761:338–341.
Weiland, N.G. (1992). Estradiol selectively regulates agonist binding sites on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Endocrinology 131:662–668.
Woolley, C.S. and McEwen, B.S. (1994). Estradiol regulates hippocampal dendritic spine density via an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent mechanism. J. Neurosci. 14:7680–7687.
Yamamura, H.I., Enna, S.J., and Kuhar, M.J. (1990). Methods in Neurotransmitter Receptor Analysis, 1st edn., Raven, New York, pp. 10–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heron, P., Daya, S. 17β-Estradiol Attenuates Quinolinic Acid Insult in the Rat Hippocampus. Metab Brain Dis 16, 187–198 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012593027961
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012593027961