Abstract
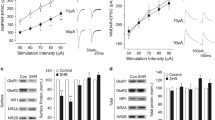
Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) are used as a genetic model for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), since they have behavioral characteristics that mimic the major symptoms of ADHD. We have previously shown that dopaminergic and noradrenergic systems are altered in the prefrontal cortex of SHR compared to normotensive Wistar–Kyoto (WKY) control rats. We also showed that neural circuits that use glutamate as a neurotransmitter increased norepinephrine release from rat prefrontal cortex slices and that glutamate caused significantly greater release of norepinephrine from prefrontal cortex slices of SHR than from those of WKY. The effect of glutamate did not appear to be mediated by NMDA receptors, since NMDA did not exert any effect on norepinephrine release and the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 did not reduce the effect of glutamate. In this investigation we show that the stimulatory effect of glutamate is greater in SHR than in WKY and that the effect can be antagonised by the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX). The results suggest that glutamatergic neuron terminals in rat prefrontal cortex establish synaptic contacts with noradrenergic terminals to enhance norepinephrine release by activation of AMPA receptors and that this enhancement is amplified in SHR.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bailey, C.H., Giustetto, M., Huang, Y.-Y., Hawkins, R.D., and Kandel, E.R. (2000). Is heterosynaptic modulation essential for stabilizing hebbian plasticity and memory? Nature Rev. Neurosci. 1:11–20.
Honore, T., Davies, S.N., Drejer, J., Fletcher, E.J., Jacobsen, P., Lodge, D., and Nielsen, F.E. (1988). Quinoxalinediones: Potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science 241:701–703.
Lockhart, B., Iop, F., Closier, M., and Lestage, P. (2000). (S)-2,3-dihydro-[3,4]cyclopentano-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-1,1-dioxide: (S18986-1) A positive modulator of AMPA receptors enhances (S)-AMPA-mediated [3H]noradrenaline release from rat hippocampal and frontal cortex slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 401:145–153.
Malinow, R., Mainen, Z.F., and Hayashi, Y. (2000). LTP mechanisms: From silence to four-lane traffic. Curr. Opin. Neuroobiol. 10:352–357.
O'Brien, R.J., Kamboj, S., Ehlers, M.D., Rosen, K.R., Fischbach, G.D., and Huganir, R.L. (1998). Activitydependent modulation of synaptic AMPA receptor accumulation. Neuron 21:1067–1078.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C. (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press, New York.
Petralia, R.S., Esteban, J.A., Wang, Y.X., Partridge, J.G., Zhao, H.M., Wenthold, R.J., and Malinow, R. (1999). Selective acquisition of AMPA receptors over postnatal development suggests a molecular basis for silent synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2:31–36.
Russell, V.A. (in press). Hypodopaminergic and hypernoradrenergic activity in prefrontal cortex slices of an animal model for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder – the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Behav. Brain. Res.
Russell, V.A., Allie, S., and Wiggins, T. (2000). Increased noradrenergic activity in prefrontal cortex slices of an animal model for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder – the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Behav. Brain. Res. 117:69–74.
Russell, V.A., de Villiers, A., Sagvolden, T., Lamm, M., and Taljaard, J. (1995). Altered dopaminergic function in the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen of an animal model of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Brain. Res. 676:343–351.
Russell, V.A., de Villiers, A.S., Sagvolden, T., Lamm, M.C.L., and Taljaard, J.J.F. (1996a). Impaired vesicular storage of dopamine in an animal model for Attention-deficit Hyperactivity disorder – the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 22:2082.
Russell, V.A., de Villiers, A., Sagvolden, T., Lamm, M., and Taljaard, J. (1998). Differences between electrically-, ritalin-and d-amphetamine-stimulated release of [3H]dopamine from brain slices suggest impaired vesicular storage of dopamine in an animal model for Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 94:163–171.
Russell, V.A., Lamm, M.C.L., de Villiers, A.S., Reyneke, L., and Taljaard, J.J.F. (1996b). [3H]Dopamine and [14C]acetylcholine release from rat prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen slices. Neurosci. Protocols 96-060-05-01-18.
Russell, V.A. and Wiggins, T. (2000). Increased glutamate-stimulated norepinephrine release from prefrontal cortex slices of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 15:297–304.
Sagvolden, T., Hendley, E.D., and Knardahl, S. (1992a). Behavior of hypertensive and hyperactive rat strains: Hyperactivity is not unitarily determined. Physiol. Behav. 52:49–57.
Sagvolden, T., Metzger, M.A., and Sagvolden, G. (1993a). Frequent reward eliminates differences in activity between hyperkinetic rats and controls. Behav. Neural Biol. 59:225–229.
Sagvolden, T., Metzger, M.A., Schiørbeck, H.K., Rugland, A.-L., Spinnangr, I., and Sagvolden, G. (1992b). The spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) as an animal model of childhood hyperactivity (ADHD): Changed reactivity to reinforcers and to psychomotor stimulants. Behav. Neural Biol. 58:103–112.
Sagvolden, T., Pettersen, M.B., and Larsen, M.C. (1993b). Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) as a putative animal model of childhood hyperkinesis: SHR behavior compared to four other rat strains. Physiol. Behav. 54:1047–1055.
Sagvolden, T. and Sergeant, J.A. (1998). Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder – from brain dysfunctions to behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 94:1–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, V.A. Increased AMPA Receptor Function in Slices Containing the Prefrontal Cortex of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Metab Brain Dis 16, 143–149 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012584826144
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012584826144