Abstract
A novel ‘nano’-tool based on metal clusters enables the transduction of changes of biorecognitive binding as well as conformation quantitatively into an optical signal which can be observed directly as a color change of a sensor-chip surface.
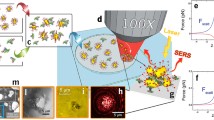
Proteins including various enzymes and serum proteins were spotted via micro-arraying onto the chip surface forming monolayer and thin film dots. Multi-layered (up to 300 nm thick) nano-gel-pads were stabilized by photo crosslinking the protein dots with UV-light. By deposition of metal-nano clusters, synthesized via chemical means or sputter coating on top of photo-crosslinked macromolecules an optical resonance effect was obtained.
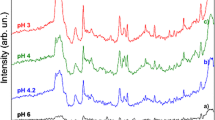
The response of the novel surface enhanced absorption cluster sensor-chip was transduced spectroscopically in the visible and IR range of the spectrum via an 8 μm resolution reflectance scanner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aussenegg F.R. et al., 1995. The metal island coated swelling polymer over mirror system (MICSPOMS): a new principle for measuring ionic strength. Sensors and Actuators B 29, 204–209.
Bauer G., F. Pittner & T. Schalkhammer, 1999. Metall nanocluster biosensors. Mikrochimica Acta 131(1–2), 107–114.
Bensberg, A., 1997. Swelling and shrinking of polyacid gels. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 9, 323–340.
Catanzano F. et al., 1998. Circular dichroism study of ribonuclease A mutants containing the minimal structural requirements for dimerization and swapping. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 23(4), 277–285.
Evans, D.J. Jr, D.G. Evans, S.S. Kirkpatrick & D.Y. Graham, 1991. Characterization of the Helicobacter pylori urease and purification of its subunits. Microb. Pathog. 10(1), 15–26.
Fagain C.O., 1995. Understanding and increasing protein stability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1252(1), 1–14.
Frens G., 1973. Preparation of gold dispersions of varying particle size: controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature 241, 20–22.
Gladilin A.K. & A.V. Levashov, 1998. Enzyme stability in systems with organic solvents. Biochemi. Mosc. 63(3), 345–356.
Johnson W.C., 1999. Analyzing protein circular dichroism spectra for accurate secondary structure. Proteins 35(3), 307–312.
Klibanov A.M. & A. Zaks, 1985. Enzyme-catalyzed processes in organic solvents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 82(10), 3192–3196.
Klibanov A.M. & T. Ke, 1998. On enzymatic activity in organic solvents as a function of enzyme history. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 57(6), 746–750.
Leitner A., Z. Zhao, H. Brunner, F.R. Aussenegg & A. Wokaun, 1993. Optical properties of a metal island film close to a smooth metal surface. Appl. Optics 31, 102–110.
Nguyen Q.T., Z. Bendjama, R. Clément & Z. Ping, 1999. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) crosslinked in different conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 2761–2766.
Philippopoulos M. & C. Lim, 1999. Exploring the dynamic information content of a protein NMR structure: comparison of a molecular dynamics simulation with the NMR and X-ray structures of Escherichia coli ribonuclease H1. Proteins 36(1), 87–110.
Schalkhammer T. et al., 1995a. The use of metal-island-coated pH-sensitive swelling polymers for biosensor applications. Sensors and Actuators B 24, 166–172.
Schalkhammer T. et al., 1995b. Metal Island Coated Polymer Sensor for Direct Determination of the Volume Effect of Chaotropic Agents. Mikrochim. Acta 121, 259–268.
Schalkhammer T. et al., 1995c. New Urea sensor based on a metal island coated ion sensitive swelling polymer device. SPIE 2508, 102–110.
Turbett G.R., P.B. Hoj, R. Horne & B.J. Mee, 1992. Purification and characterization of the urease enzymes of Helicobacter species from humans and animals. Infect. Immun. 60(12), 5259–5266.
Wiese H. & R. Rupaner, 1999. Influence of metal ions on the alkali-swelling behavior of carboxylated acrylic polymer latexes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 277, 372–375.
Zerovnik E. et al., 1999. Differences in the effects of TFE on the folding pathways of human stefins A and B. Proteins 36(2), 205–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer, C., Palkovits, R., Bauer, G. et al. Surface Enhanced Resonance of Metal Nano Clusters: A Novel Tool for Proteomics. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 3, 359–369 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012564029052
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012564029052