Abstract
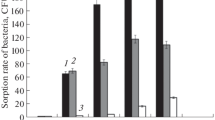
Nodulation, rhizospheral, and saprophytic types of competitiveness (NC, RC, and SC, respectively) were studied in the highly active strains CXM1-105 and CXM1-188 of the alfalfa rhizobium Sinorhizobium meliloti.The competitiveness was estimated with the use of markers of antibiotic resistance. It was found that the mutant strain T37, which was characterized by a drastically decreased NC, had higher SC and RC than the parental strain. The mutant T107 (with a moderately decreased NC) did not differ from the parental strain with respect to RC but had a higher SC. The mutant T27 (with the lowest NC) did not differ from the parental strain with respect to SC or RC. In the mutant Tb1, the NC and RC were decreased and the SC was the same as in the parental strain. In Tb7, the SC was decreased and RC was increased. In the mutant T795, all of the three types of competitiveness were decreased. The difference between the mutants studied and the parental strain with respect to NC and RC was confirmed using an indirect method (the ability to form effective symbiosis after mixed inoculation together with the an ineffective tester strain CXM1-48) and the X-Gluc staining method (using the S. melilotiRmM4gustester strain carrying the gene of β-glucuronidase). However, the decreased SC that the mutants exhibited when they were cultivated together with parental strains in a plant-growth substrate (vermiculite) was not observed in the case of their cocultivation in liquid media. The independent variation of different types of competitiveness indicate that rhizobia have several separate gene systems determining their survival in in plantaandex plantaecological niches.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Onishchuk, O.P. and Simarov, B.V., Genetic Variation in Nodulation Competitiveness of Nodule Bacteria and Its Application in Selection, Genetika (Moscow), 1995, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 293-303.
Onishchuk, O.P. and Simarov, B.V., Genes Controlling Nodulation Competitiveness of Nodule Bacteria, Genetika (Moscow), 1996, vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 1157-1166.
Vlassak, K.M. and Vanderleyden, J., Factors Influencing Nodule Occupancy by Inoculant Rhizobia, Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 1997, vol. 16, pp. 163-229.
Bittinger, M.A., Milner, J.L., Saville, B.J., and Handelsman, J., RosR, a Determinant of Nodulation Competitiveness in Rhizobium etli, Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1997, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 180-186.
Triplett, E.W. and Barta, T.M., Trifoliotoxin Production and Nodulation Are Necessary for the Expression of Superior Nodulation Competitiveness by Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii Strain T24 on Clover, Plant Physiol., 1987, vol. 95, no. 2, pp. 335-342.
Brewin, N.J., Wood, E.A., and Young, J.P., Contribution of the Symbiotic Plasmid to the Competitiveness of Rhizobium leguminosarum, J. Gen. Microbiol., 1983, vol. 129, no. 1, pp. 2973-2977.
Onishchuk, O.P., Chesnokova, O.N., Sharypova, L.A., and Simarov, B.V., Genetic Analysis of the T37 Rhizobium meliloti Mutant with Lower Nodulation Rate and Competitiveness, Genetika (Moscow), 1990, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 560-562.
Onishchuk, O.P., Sharypova, L.A., and Simarov, B.V., Isolation and Characterization of the Rhizobium meliloti Tn5-Mutants with Impaired Nodulation Competitiveness, Plant Soil, 1994, vol. 197, no. 2, pp. 267-274.
Fedorov, S.N. and Simarov, B.V., Generation of Rhizobium meliloti Mutants with Changed Symbiotic Properties by Means of UV Irradiation, S–kh. Biol., 1987, no. 9, pp. 44-49.
Sharypova, L.A. and Simarov, B.V., A Procedure of Comparing Effective Rhizobium meliloti Strains with Respect to Competitiveness, Tr. Vses. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. S–kh. M., 1985, vol. 55, pp. 85-90.
Selbitschka, W., Dresing, U., Hagen, M., et al., A Biological Containment System for Rhizobium meliloti Based on the Use of Recombination-Deficient (recA) Strains, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 1995, vol. 16, pp. 223-232.
van Dillewijn, P., Martinez-Abarca, F., and Toro, N., Multicopy Vectors Carrying the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifA Gene Do Not Enhance the Nodulation Competitiveness of Sinorhizobium meliloti on Alfalfa, Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1998, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 839-842.
Kurchak, O.N., Krol, L.A., Ushakov, K.V., et al., Sinorhizobium meliloti lpsL Mutant Causes a Disruption of Symbiosis with Alfalfa, Abstracts 9th Int. Congr. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact., Amsterdam (July 25–30), Elsevier, 1999, p. 58.
Yurgel', S.N., Sharypova, L.A., and Simarov, B.V., The Tn5 Mutations That Increase Redox Potential of Free-Living Cells and Symbiotic Efficiency on Alfalfa in Rhizobium meliloti, Genetika (Moscow), 1998, vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 742-748.
Araujo, R.S., Robleto, E.A., and Handelsman, J., A Hydrophobic Mutant of Rhizobium etli Altered in Nodulation Competitiveness and Growth in the Rhizosphere, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, vol. 60, pp. 1430-1436.
Fedorov, S.N., Fokina, I.G., and Simarov, B.V., Evaluation of Symbiotic Properties of Alfalfa Nodule Bacteria Rhizobium meliloti in Laboratory Conditions, S–kh. Biol., 1986, no. 1, pp. 112-118.
Novikova, N.I. and Simarov, B.V., Transduction in Rhizobium meliloti, Genetika (Moscow), 1984, vol. 20, no. 4, p. 542.
Lakin, G.F., Biometriya (Biometrics), Moscow: Vysshaya Shkola, 1990.
Onishchuk, O.P., Kurchak, O.N., Sharypova, L.A., et al., Genetics of Competitiveness of Sinorhizobium meliloti, Proc. 22nd EUCARPIA Fodder Crops and Amenity Grasses Section Meet., St. Petersburg, 2000, pp. 141-144.
Dorosinskii, L.M., Problems of Ecology of Nodule Bacteria, Usp. Mikrobiol., 1970, no. 10, pp. 201-213.
Andronov, E.E., Rumyantseva, M.L., Sagulenko, V.V., and Simarov, B.V., The Effect of the Host Plant on Genetic Diversity of a Natural Sinorhizobium meliloti Population, Genetika (Moscow), 1999, vol. 35, no. 10, pp. 1358-1365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onishchuk, O.P., Kurchak, O.N., Sharypova, L.A. et al. Analysis of Different Types of Competitive Capacity in the Alfalfa Rhizobia (Sinorhizobium meliloti) Tn5 Mutants. Russian Journal of Genetics 37, 1266–1271 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012552908063
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012552908063