Abstract
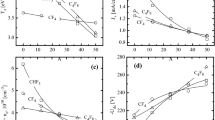
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) films were deposited, at room temperature, from a CH4/Ar plasma produced by a radio frequency (r.f.) glow discharge system at 13.56 MHz, and different power values. Two different characterisation techniques, Raman and FTIR spectroscopies, have been used to investigate correlations between deposition conditions and properties of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. The composition of the initial gaseous mixture and the r.f. power input are shown to affect significantly both mechanical and microstructural properties of deposited films. As the fraction of argon in the feed gas is increased, the deposition rate increases and the deposited film shows a higher friction coefficient, thus suggesting the production of a softer material. On the other hand, Raman measurements suggest the occurrence of a lower degree of structural order in the sp2 lattice. Experimental findings are discussed in terms of the different chemical composition of the plasma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Tsai and D. B. Bogy, J. Vac. Sci. Technology A 5 (1987) 3287.
D. M. Gruen, C. D. Zuiker, A. R. Krauss and X. Pan, ibid. 13 (1995) 1628.
O. Matsumoto, H. Toshima and Y. Kanzaki, Thin Solid Films 128 (1985) 341.
H. C. Shish, C. P. Sung and W. T. Hsu, Diamond and Related Materials 2 (1993) 531.
H. C. Shish, C. P. Sung and W. L. Fan, Surf. Coat. Technology 54/55 (1992) 380.
W. Zhu, A. Inspektor, A. R. Badzian, T. Mckenna and R. Messier, J. Appl. Phys. 68(4) (1990) 1489.
N. Mutsukura and K. Yoshida, Diamond and Related Materials 5 (1996) 919.
N. Mutsukura and K. Saitoh, J. Vac. Sci. Technology A 14 (1996) 2666.
T. G. McCauley, D. M. Gruen and A. R. Krauss, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 (1998) 1646.
N. Fourches, G. Turban and B. Grolleau, Appl. Surf. Sci. 68 (1993) 149.
J. C. Angus, P. Koidl and S. Domitz, Plasma Deposited Thin Films (1986) 89.
J. W. Zou, K. Reichelt, K. Schimdt and B. Dischler, J. Appl. Phys. 65(10) (1989) 3914.
Idem., ibid. 67(1) (1990) 487.
F. Tuinstra and J. L. Konig, J. Chem. Phys. 53(3) (1970) 1126.
N. Wada, P. J. Gaczi and S. A. Solin, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 35/36 (1980) 543.
G. Mariotto, F. L. Freire and C. A. Achete, Thin Solid Films 241 (1994) 255.
L. Valentini, J. M. Kenny, H. Haefke and A. Perret, to be published.
R. O. Dillon, J. A. Woollam and V. Katkanant, Phys. Rev. B 29 (1984) 3482.
J. H. Lee, Y. H. Lee and B. Farouk, J. Vac. Sci. Technology A 14 (1996) 2702.
C. Riccardi, R. Barni, M. Fontanesi and P. Tosi, to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valentini, L., Kenny, J.M., Mariotto, G. et al. Deposition of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films from CH4/Ar plasmas: Ar dilution effects. Journal of Materials Science 36, 5295–5300 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012422618327
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012422618327