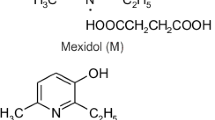
Abstract
The intensity of hydroxyl radical (OH?) formation in the myocardium during reperfusion after ischemia of different duration was evaluated using microdialysis with sodium salicylate. 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, a product of OH? trapping by salicylic acid, was used as a marker of OH? generation in the postischemic myocardium. Experiments were performed on open-chest anesthetized and jet-ventilated Wistar rats. The concentrations of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid in the dialysate were measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. Experiments showed that the intensity and duration of free oxygen radical generation during reperfusion after 30-min ischemia far surpassed those observed after 20-min ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. Bolli, M. Zughaib, X. Y. Li, et al., J. Clin. Invest., 96, No. 2, 1006-1084 (1995).
D. K. Das, A. George, X. Liu, and P. S. Rao, Biochem Biophys. Res. Cornmun., 165, 1004-1009 (1989).
N. S. Dhalla, R. M. Temsah., and T. J. Netticadan, Hypertention, 18, 655-673 (2000).
A. I. Kuzmin, A. V. Gourine, A. I. Molosh, et al., Basic Res. Cardiol., 95, No. 2, 127-136 (2000).
R. D. Lasley, P. J. Konyn, J. O. Hegge, and R. M. Mentzer, Am. J. Physiol., 269, H1460-H1466 (1995).
J. M. McCord, N. Engl. J. Med., 312, No. 3, 159-163 (1985).
T. Obata, M. Aomine, and Y. Yamanaka, J. Physiol. (Paris), 93, 213-218 (1999).
T. Obata, H. Hosokawa, and Y. Yamanaka, Am. J. Physiol., 266, H903-H908 (1994).
K. T. Spencer, P. D. Lindower, G. R. Buettner, and R. E. Kerber, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 32, No. 3, 343-348 (1998).
A. Tosaki, D. Bagchi, T. Pali, et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 45, No. 4, 961-969 (1993).
A. Tosaki, T. Pali, and M. T. Droy-Lefaix, Diabetologia., 39, No. 11, 1255-1262 (1996).
C. Vergely, V. Maupoil, M. Benderitter, and L. Rochette, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 24, No. 3, 470-479 (1998).
C. S. Yang, P. J. Tsai, W. Y. Chen, and J. S. Kuo, Redox. Rep., 3, 295-301 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorodetskaya, E.A., Kalenikova, E.I. Formation of Hydroxyl Radicals during Myocardial Reperfusion after Experimental Ischemia of Different Duration. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 131, 533–535 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012338232265
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012338232265