Abstract
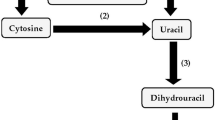
Reductive catabolism of the pyrimidine bases uracil and thymine was found to occur in Pseudomonas putida biotype B. The pyrimidine reductive catabolic pathway enzymes dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, dihydropyrimidinase and N-carbamoyl-β-alanine amidohydrolase activities were detected in this pseudomonad. The initial reductive pathway enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase utilized NADH or NADPH as its nicotinamide cofactor. The source of nitrogen in the culture medium influenced the reductive pathway enzyme activities and, in particular, dihydropyrimidinase activity was highly affected by nitrogen source. The reductive pathway enzyme activities in succinate-grown P. putida biotype B cells were induced when uracil served as the nitrogen source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248-254
De Vos P & De Ley J (1983) Intra-and intergeneric similarities of Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas ribosomal ribonucleic acid cistrons. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 13: 487-509
French CE, Boonstra B, Bufton KA & Bruce NC (1997) Cloning, sequence, and properties of the soluble pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Bacteriol. 179: 2761-2765
Kaplan NO (1955) Pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenase. Methods Enzymol. 2: 681-687
Kim S & West TP (1991) Pyrimidine catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 77: 175-179
Ogawa J, Kaimura T, Yamada H & Shimizu S (1994) Evaluation of pyrimidine-and hydantoin-degrading enzyme activities in aerobic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 122: 55-60
Patel BN & West TP (1987) Oxidative catabolism of uracil by Enterobacter aerogenes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 40: 33-36
Stanier RY, Palleroni NO & Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J. Gen. Microbiol. 42: 159-271
Tamaki N & Mizutani N (1987) Purification and properties of β-ureidopropionase from the rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem. 169: 21-26
Vogels GD & van der Drift C (1976) Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol. Rev. 40: 403-468
West TP (1989) Isolation and characterization of thymidylate synthetase mutants of Xanthomonas maltophila. Arch. Microbiol. 151: 220-222
West TP (1991) Pyrimidine base and ribonucleoside utilization by the Pseudomonas alcaligenes group. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 59: 263-268
West TP (1997) Reductive catabolism of uracil and thymine by Burkholderia cepacia. Arch. Microbiol. 168: 237-239
West TP (1998) Isolation and characterization of an Escherichia coli B mutant strain defective in uracil catabolism. Can. J. Microbiol. 44: 1106-1109
West TP, Traut TW, Shanley MS & O'Donovan GA (1985) A Salmonella typhimurium strain defective in uracil catabolism and β-alanine synthesis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 131: 1083-1090
Xu G & West TP (1992) Reductive catabolism of pyrimidine bases by Pseudomonas stutzeri. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138: 2459-2463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
West, T.P. Pyrimidine base catabolism in Pseudomonas putida biotype B. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 80, 163–167 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012275512136
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012275512136