Abstract
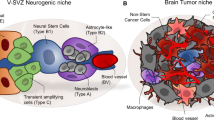
Neural stem cells have recently come to the forefront in neurobiology because of the possibilities for CNS repair by transplantation. Further understanding of the biology of these cells is critical for making their use in CNS repair possible. It is likely that these discoveries will also have spin-offs for neuro-oncology as primary brain tumors may arise from a CNS progenitor cell. An understanding of the normal migratory ability of these cells is also likely to have a very important impact on the knowledge of brain tumor invasion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wechsler-Reya R, Scott MP: The developmental biology of brain tumors. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 385–428, 2001
Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP: Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277: 1109–1113, 1997
Pietsch T, Waha A, Koch A, Kraus J, Albrecht S, Tonn J, Sorensen N, Berthold F, Henk B, Schmandt N, Wolf HK, von Deimling A, Wainwright B, Chenevix-Trench G, Wiestler OD, Wicking C: Medulloblastomas of the desmoplastic variant carry mutations of the human homologue of Drosophila patched. Cancer Res 57: 2085–2088, 1997
Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, Hebrink D, Alderete B, Fults DW, James CD: Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res 57: 842–845, 1997
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP: Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by sonic hedgehog. Neuron 22: 103–114, 1999
Potten CS, Loeffler M: Stem cells: attributes, cycles, spirals, pitfalls and uncertainties. Lessons for and from the crypt. Development 110: 1001–1020, 1990
Hall PA, Watt FM: Stem cells: the generation and maintenance of cellular diversity. Development 106: 619–633, 1989
Morrison SJ, Shah NM, Anderson DJ: Regulatory mechanisms in stem cell biology. Cell 88: 287–298, 1997
Gage FH: Stem cells of the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8: 671–676, 1998
Weiss S, van der Kooy D: CNS stem cells: where's the biology (a.k.a. beef)? J Neurobiol 36: 307–314, 1998
Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A: Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 97: 703–716, 1999
Johansson CB, Momma S, Clarke DL, Risling M, Lehdahl U, Frisen J: Identification of a neural stem cell in the adult mammalian central nervous system. Cell 96: 25–34, 1999
Morshead CM, van der Kooy DA: new ‘spin’ on neural stem cells? Curr Opin Neurobiol 11: 59–65, 2001
Reynolds BA, Weiss S: Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system (see comments). Science 255: 1707–1710, 1992
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A: Proliferating subventricular zone cells in the adult mammalian forebrain can differentiate into neurons and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 2074–2077, 1993
Morshead CM, Reynolds BA, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Staines WA, Morassutti D, Weiss S, van derKooy D: Neural stem cells in the adult mammalian forebrain: a relatively quiescent subpopulation of subependymal cells. Neuron 13: 1071–1082, 1994
Weiss S, Dunne C, Hewson J, Wohl C, Wheatley M, Peterson AC, Reynolds BA: Multipotent CNS stem cells are present in the adult mammalian spinal cord and ventricular neuroaxis. J Neurosci 16: 7599–7609, 1996
Garcia-Verdugo JM, Doetsch F, Wichterle H, Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A: Architecture and cell types of the adult subventricular zone: in search of the stem cells. J Neurobiol 36: 234–248, 1998
Morshead CM, Craig CG, van der Kooy D: In vivo clonal analyses reveal the properties of endogenous neural stem cell proliferation in the adult mammalian forebrain. Development 125: 2251–2261, 1998
Temple S, Alvarez-Buylla A: Stem cells in the adult mammalian central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9: 135–141, 1999
Hockfield S, McKay RD: Identification of major cell classes in the developing mammalian nervous system. J Neurosci 5: 3310–3328, 1985
Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB, McKay RD: CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell 60: 585–595, 1990
Gates MA, Thomas LB, Howard EM, Laywell ED, Sajin B, Faissner A, Gotz B, Silver J, Steindler DA: Cell and molecular analysis of the developing and adult mouse subventricular zone of the cerebral hemispheres. J Comp Neurol 361: 249–266, 1995
Zimmerman L, Parr B, Lendahl U, Cunningham M, McKay R, Gavin B, Mann J, Vassileva G, McMahon A: Independent regulatory elements in the nestin gene direct transgene expression to neural stem cells or muscle precursors (published erratum appears in Neuron 1994 Jun; 12(6): following 1388). Neuron 12: 11–24, 1994
Frederiksen K, McKay RD: Proliferation and differentiation of rat neuroepithelial precursor cells in vivo. J Neurosci 8: 1144–1151, 1988
McKay R: Stem cells in the central nervous system. Science 276: 66–71, 1997
Hatten ME, Heintz N: Mechanisms of neural patterning and specification in the developing cerebellum. Annu Rev Neurosci 18: 385–408, 1995
Flax JD, Aurora S, Yang C, Simonin C, Wills AM, Billinghurst LL, Jendoubi M, Sidman RL, Wolfe JH, Kim SU, Snyder EY: Engraftable human neural stem cells respond to developmental cues, replace neurons, and express foreign genes. Nat Biotechnol 16: 1033–1039, 1998
Sah DW, Ray J, Gage FH: Bipotent progenitor cell lines from the human CNS. Nat Biotechnol 15: 574–580, 1997
Jacobson M: Developmental Neurobiology. Plenum Press, New York, 1991
Messier B, LeBlond CP, Smart I: Presence of DNA synthesis and mitosis in the brain of young adult mice. Exp Cell Res 14: 224–226, 1958
Smart I: The subependymal layer of the mouse brain and its cell production as shown by radioautography after thymidine-H3 injection. J Comp Neurol 116: 325–347, 1961
Altman J: Autoradiographic investigation of cell proliferation in the brains of rats and cats. Anat Rec 145: 573–591, 1963
Rakic P: Neurons in rhesus monkey visual cortex: systematic relation between time of origin and eventual disposition. Science 183: 425–427, 1974
Korr H: Proliferation of Different Cell Types in the Brain. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1980.
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH: Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus (see comments). Nat Med 4: 1313–1317, 1998
Alvarez-Buylla A, Lois C: Neuronal stem cells in the brain of adult vertebrates. Stem Cells (Dayt) 13: 263–272, 1995
Gage FH, Ray J, Fisher LJ: Isolation, characterization, and use of stem cells from the CNS. Annu Rev Neurosci 18: 159–192, 1995
Morshead CM, van der Kooy D: Postmitotic death is the fate of constitutively proliferating cells in the subependymal layer of the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci 12: 249–256, 1992
Gritti A, Parati EA, Cova L, Frolichsthal P, Galli R, Wanke E, Faravelli L, Morassutti DJ, Roisen F, Nickel DD, Vescovi AL: Multipotential stem cells from the adult mouse brain proliferate and self-renew in response to basic fibroblast growth factor. J Neurosci 16: 1091–1100, 1996
Tropepe V, Craig CG, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D: Transforming growth factor-alpha null and senescent mice show decreased neural progenitor cell proliferation in the forebrain subependyma. J Neurosci 17: 7850–7859, 1997
Gould E, Beylin A, Tanapat P, Reeves A, Shors TJ: Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat Neurosci 2: 260–265, 1999
Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E: Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410: 372–376, 2001
Cameron HA, Gould E: Adult neurogenesis is regulated by adrenal steroids in the dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 61: 203–209, 1994
Cameron HA, Tanapat P, Gould E: Adrenal steroids and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation regulate neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rats through a common pathway. Neuroscience 82: 349–354, 1998
Gould E, McEwen BS, Tanapat P, Galea LA, Fuchs E: Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult tree shrew is regulated by psychosocial stress and NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 17, 2492–2498, 1997
Traiffort E, Charytoniuk DA, Faure H, Ruat M: Regional distribution of Sonic Hedgehog, patched, and smoothened mRNA in the adult rat brain. J Neurochem 70: 1327–1330, 1998
van Praag H, Christie BR, Sejnowski TJ, Gage FH: Runningenhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 13427–13431, 1999
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH: Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 2: 266–270, 1999
Chiasson BJ, Tropepe V, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D: Adult mammalian forebrain ependymal and subependymal cells demonstrate proliferative potential, but only subependymal cells have neural stem cell characteristics. J Neurosci 19: 4462–4471, 1999
Hartfuss E, Galli R, Heins N, Gotz M: Characterization of CNS precursor subtypes and radial glia. Dev Biol 229: 15–30, 2001
Malatesta P, Hartfuss E, Gotz M: Isolation of radial glial cells by fluorescent-activated cell sorting reveals a neuronal lineage. Development 127: 5253–5263, 2000
Noctor SC, Flint AC, Weissman TA, Dammerman RS, Kriegstein AR: Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex. Nature 409: 714–720, 2001
Johansson CB, Svensson M, Wallstedt L, Janson AM, Frisen J: Neural stem cells in the adult human brain. Exp Cell Res 253: 733–736, 1999
Roy NS, Wang S, Jiang L, Kang J, Benraiss A, Harrison-Restelli C, Fraser RA, Couldwell WT, Kawaguchi A, Okano H, Nedergaard M, Goldman SA: In vitro neurogenesis by progenitor cells isolated from the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 6: 271–277, 2000
Roy NS, Benraiss A, Wang S, Fraser RA, Goodman R, Couldwell WT, Nedergaard M, Kawaguchi A, Okano H, Goldman SA: Promoter-targeted selection and isolation of neural progenitor cells from the adult human ventricular zone. J Neurosci Res 59: 321–331, 2000
Palmer TD, Schwartz PH, Taupin P, Kaspar B, Stein SA, Gage FH: Progenitor cells from human brain after death. Nature 411: 42–43, 2001
Hatten ME: Central nervous system migration. Annu Rev Neurosci 22, 511–539, 1999
Altman J: Autoradiographic and histologic studies of postnatal neurogenesis. III. Dating the time of production and onset of differentiation of cerebellar microneurons in rats. J Comp Neurol 136: 269–294, 1969
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A: Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264: 1145–1148, 1994
Lois C, Garcia-Verdugo J-M: Chain migration of neuronal precursors. Science 271: 978–981, 1996
Luskin MB: Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 11: 173–189, 1993
Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A: Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci 17: 5046–5061, 1997
Lin RCS, Matesic DF, Marvin M, McKay RD, Brustle O: Re-expression of the intermediate filament nestin in reactive astrocytes. Neurobiol Dis 2: 79–85, 1995
Frisen J, Johansson CB, Torok C, Risling M, Lendahl U: Rapid, widespread, and longlasting induction of nestin contributes to the generation of glial scar tissue after CNS injury. J Cell Biol 131: 453–464, 1995
Craig CG, Tropepe V, Morshead CM, Reynolds BA, Weiss S, van der Kooy D: In vivo growth factor expansion of endogenous subependymal neural precursor cell populations in the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci 16: 2649–2658, 1996
Kuhn HG, Winkler J, Kempermann G, Thal LJ, Gage FH: Epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 have different effects on neural progenitors in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci 17: 5820–5829, 1997
Kaltschmidt JA, Davidson CM, Brown NH, Brand AH: Rotation and asymmetry of the mitotic spindle direct asymmetric cell division in the developing central nervous system. Nat Cell Biol 2: 7–12, 2000
Embryonic vertebrate central nervous system: revised terminology. The Boulder Committee. Anat Rec 166: 257–261, 1970
Sidman RL, Rakic P: Neuronal migration, with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res 62: 1–35, 1973
Allendoerfer KL, Shatz CJ: The subplate, a transient neocortical structure: its role in the development of connections between thalamus and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 17: 185–218, 1994
Super H, Del Rio JA, Martinez A, Perez-Sust P, Soriano E: Disruption of neuronal migration and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex following ablation of Cajal– Retzius cells. Cereb Cortex 10: 602–613, 2000
O'Rourke NA, Dailey ME, Smith SJ, McConnell SK: Diverse migratory pathways in the developing cerebral cortex. Science 258: 299–302, 1992
Tan SS, Breen S: Radial mosaicism and tangential cell dispersion both contribute to mouse neocortical development. Nature 362: 638–640, 1993
O'Rourke NA, Sullivan DP, Kaznowski CE, Jacobs AA, McConnell SK: Tangential migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex. Development 121: 2165–2176, 1995
Pearlman AL, Faust PL, Hatten ME, Brunstrom JE: New directions for neuronal migration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8: 45–54, 1998
Schmechel DE, Rakic PA: Golgi study of radial glial cells in developing monkey telencephalon: morphogenesis and transformation into astrocytes. Anat Embryol (Berl) 156: 115–152, 1979
Culican SM, Baumrind NL, Yamamoto M, Pearlman AL: Cortical radial glia: identification in tissue culture and evidence for their transformation to astrocytes. J Neurosci 10: 684–692, 1990
Chanas-Sacre G, Rogister B, Moonen G, Leprince P: Radial glia phenotype: origin, regulation, and transdifferentiation. J Neurosci Res 61: 357–363, 2000
Rakic P: Neuron–glia relationship during granule cell migration in developing cerebellar cortex. A Golgi and electronmicroscopic study in Macacus Rhesus. J Comp Neurol 141: 283–312, 1971
Nadarajah B, Brunstrom JE, Grutzendler J, Wong RO, Pearlman AL: Two modes of radial migration in early development of the cerebral cortex. Nat Neurosci 4: 143–150, 2001
Tan SS, Kalloniatis M, Sturm K, Tam PP, Reese BE, Faulkner-Jones B: Separate progenitors for radial and tangential cell dispersion during development of the cerebral neocortex. Neuron 21: 295–304, 1998
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A: Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264: 1145–1148, 1994
Wichterle H, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A: Direct evidence for homotypic, glia-independent neuronal migration. Neuron 18: 779–791, 1997
Komuro H, Yacubova E, Rakic P: Mode and tempo of tangential cell migration in the cerebellar external granular layer. J Neurosci 21: 527–540, 2001
Edmondson JC, Liem RK, Kuster JE, Hatten ME: Astrotactin: a novel neuronal cell surface antigen that mediates neuron–astroglial interactions in cerebellar microcultures. J Cell Biol 106, 505–517, 1988
Zheng C, Heintz N, Hatten ME: CNS gene encoding astrotactin, which supports neuronal migration along glial fibers. Science 272: 417–419, 1996
Rio C, Rieff HI, Qi P, Khurana TS, Corfas G: Neuregulin and erbB receptors play a critical role in neuronal migration. Neuron 19: 39–50, 1997
Anton ES, Marchionni MA, Lee KF, Rakic P: Role of GGF/neuregulin signaling in interactions between migrating neurons and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex. Development 124: 3501–3510, 1997
Georges-Labouesse E, Mark M, Messaddeq N, Gansmuller A: Essential role of alpha 6 integrins in cortical and retinal lamination. Curr Biol 8: 983–986, 1998
Anton ES, Kreidberg JA, Rakic P: Distinct functions of alpha3 and alpha(v) integrin receptors in neuronal migration and laminar organization of the cerebral cortex. Neuron 22: 277–289, 1999
Jacques TS, Relvas JB, Nishimura S, Pytela R, Edwards GM, Streuli CH, French-Constant C: Neural precursor cell chain migration and division are regulated through different beta1 integrins. Development 125: 3167–3177, 1998
Cremer H, Lange R, Christoph A, Plomann M, Vopper G, Roes J, Brown R, Baldwin S, Kraemer P, Scheff S: Inactivation of the N-CAM gene in mice results in size reduction of the olfactory bulb and deficits in spatial learning. Nature 367: 455–459, 1994
Tomasiewicz H, Ono K, Yee D, Thompson C, Goridis C, Rutishauser U, Magnuson T: Genetic deletion of a neural cell adhesion molecule variant (N-CAM-180) produces distinct defects in the central nervous system. Neuron 11: 1163–1174, 1993
Chazal G, Durbec P, Jankovski A, Rougon G, Cremer H: Consequences of neural cell adhesion molecule deficiency on cell migration in the rostral migratory stream of the mouse. J Neurosci 20: 1446–1457, 2000
Wu W, Wong K, Chen J, Jiang Z, Dupulis S, Wu JY, Rao Y: Directional guidance of neuronal migration in the olfactory system by the protein Slit (see comments). Nature 400; 331–336, 1999
Zou Y, Stoeckli E, Chen H, Tessier-Lavigne M: Squeezing axons out of the gray matter: a role for slit and semaphorin proteins from midline and ventral spinal cord. Cell 102: 363–375, 2000
Alcantara S, Ruiz M, De Castro F, Soriano E, Sotelo C: Netrin1 acts as an attractive or as a repulsive cue for distinct migrating neurons during the development of the cerebellar system. Development 127: 1359–1372, 2000
Flanagan JG, Vanderhaeghen P: The ephrins and Eph receptors in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci 21: 309–345, 1998
Wilkinson DG: Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 155–164, 2001
Gerlai R: Eph receptors and neural plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 205–209, 2001
Conover JC, Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD, Alvarez-Buylla A: Disruption of Eph/ephrin signaling affects migration and proliferation in the adult subventricular zone. Nat Neurosci 3: 1091–1097, 2000
Powell EM, Mars WM, Levitt P: Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is a motogen for interneurons migrating from the ventral to dorsal telencephalon. Neuron 30: 79–89, 2001
Gage FH, Coates PW, Palmer TD, Kuhn HG, Fisher LJ, Suhonen JO, Peterson DA, SuhrST, Ray J: Survival and differentiation of adult neuronal progenitor cells transplanted to the adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11879–11883, 1995
Vescovi AL, Parati EA, Gritti A, Poulin P, Ferrario M, Wanke E, Frolichsthal-Schoeller P, Cova L, Arcellana-Panlilio M, Colombo A, Galli R: Isolation and cloning of multipotential stem cells from the embryonic human CNS and establishment of transplantable human neural stem cell lines by epigenetic stimulation. Exp Neurol 156: 71–83, 1999
Fricker RA, Carpenter MK, Winkler C, Greco C, Gates MA, Bjorklund A: Site-specific migration and neuronal differentiation of human neural progenitor cells after transplantation in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci 19: 5990–6005, 1999
Hammang JP, Archer DR, Duncan ID: Myelination following transplantation of EGF-responsive neural stem cells into a myelin-deficient environment. Exp Neurol 147: 84–95, 1997
Zhang SC, Ge B, Duncan ID: Adult brain retains the potential to generate oligodendroglial progenitors with extensive myelination capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 4089–4094, 1999
Brustle O, Choudhary K, Karram K, Huttner A, Murray K, Dubois-Dalcq M, McKay RD: Chimeric brains generated by intraventricular transplantation of fetal human brain cells into embryonic rats. Nat Biotechnol 16: 1040–1044, 1998
Aboody KS, Brown A, Rainov NG, Bower KA, Liu S, Yang W, Small JE, Herrlinger U, Ourednik V, Black PM, Breakefield XO, Snyder EY: From the cover: neural stem cells display extensive tropism for pathology in adult brain: evidence from intracranial gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 12846–12851, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dirks, P.B. Glioma Migration: Clues from the Biology of Neural Progenitor Cells and Embryonic CNS Cell Migration. J Neurooncol 53, 203–212 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012273922478
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012273922478