Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of this study was to test whether structural modifications improve the intestinal absorption of DMP 728 (cyclo(D-Abu-NMeArg-Gly-Asp-Amb)), a GPIIb/IIIa receptor antagonist.
Methods. In vitro permeabilities of prodrugs and analogs of DMP 728 across excised rat intestinal segments were determined.
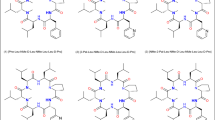
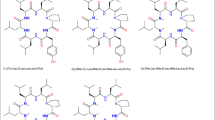
Results. n-Butyl and n-octyl esters of DMP 728 were relatively stable during in vitro permeation of rat intestine. Intestinal permeation rates of these compounds were no greater than that of DMP 728, even though the octyl ester was much more lipophilic. A pivaloyloxymethyl ester, which was hydrolyzed to DMP 728 during intestinal permeation, also did not improve permeability. In another approach, analogs with an additional methyl substituent on various amide nitrogens were evaluated. Cyclo(D-Val-NMeArg-Gly-Asp-NMeAmb), cyclo(D-Abu-diN-MeLys-Gly-Asp-Amb), and cyclo(NMeGly-NMeArg-Gly-Asp-Amb) each had about 2-fold greater permeability than DMP 728. Two other analogs with improved permeability were linear Ac-D-Abu-NMeArg-Gly-Asp-Amb and a DMP 728 derivative in which the Asp was rearranged. An analog in which the charged amino acids were replaced by neutral amino acids had permeability similar to DMP 728.
Conclusions. Within this series of peptides, hydrogen bonding tendency and structural constraint influenced intestinal permeation, but not always in ways consistent with the literature, whereas charge and lipophilicity were not shown to influence intestinal permeability. The failure of these approaches to improve permeation more significantly could be due to the influence of secretory transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. A. Mousa, J. M. Bozarth, M. S. Forsythe, S. M. Jackson, A. Leamy, M. M. Diemer, R. P. Kapil, R. M. Knabb, M. C. Mayo, S. K. Pierce, W. F. DeGrado, M. J. Thoolen, and T. M. Reilly. Circulation 89:3–12 (1994).
S. A. Mousa, W. F. DeGrado, D.-X. Mu, R. P. Kapil, B. R. Lucchesi, and T. M. Reilly. Circulation 93:537–543 (1996).
D. L. Burcham, B. J. Aungst, M. Hussain, M. A. Gorko, C. Y. Quon, and S.-M. Huang. Pharm. Res. 12:2065–2070 (1995).
R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, N. F. H. Ho, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 8:1453–1460(1991).
R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, N. F. H. Ho, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 9:435–439(1992).
B. J. Aungst and H. Saitoh. Pharm. Res. 13:114–119 (1996).
H. Saitoh and B. J. Aungst. Pharm. Res. 12:1304–1310 (1995).
S. Hsing, Z. Gatmaitan, and I. M. Arias. Gastroenterology 102:879–885 (1992).
P. F. Augustijns, T. P. Bradshaw, L.-S. L. Gan, R. W. Hendren, and D. R. Thakker. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 197:360–365 (1993).
P. S. Burton, R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, and N. F. H. Ho. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 190:760–766 (1993).
J. Hunter, B. H. Hirst, and N. L. Simmons. Pharm. Res. 10:743–749 (1993).
M. Rozencweig, M. Staquet, and J. Klastersky. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:592–597 (1976).
B. J. Aungst, J. A. Blake, N. J. Rogers, H. Saitoh, M. A. Hussain, C. L. Ensinger, and J. R. Pruitt. Pharm. Res. 12:763–767 (1995).
S. Gangwar, S. D. S. Jois, T. J. Siahaan, D. G. Vander Velde, V. J. Stella, and R. T. Borchardt. Pharm. Res. 13:1657–1662 (1996).
F. W. Okumu, G. M. Pauletti, D. G. Vender Velde, T. J. Siahaan, and R. T. Borchardt. Pharm. Res. 14:169–175 (1997).
S. Jackson, W. DeGrado, A. Dwivedi, A. Parthasarathy, A. Higley, J. Krywko, A. Rockwell, J. Markwalder, G. Wells, R. Wexler, S. Mousa, and R. Harlow. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 116:3220–3230 (1994).
A. C. Bach, II, C. J. Eyermann, J. D. Gross, M. J. Bower, R. L. Harlow, P. C. Weber, and W. F. DeGrado. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 116:3207–3219 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saitoh, H., Aungst, B.J. Prodrug and Analog Approaches to Improving the Intestinal Absorption of a Cyclic Peptide, GPIIb/IIIa Receptor Antagonist. Pharm Res 14, 1026–1029 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012149227756
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012149227756