Abstract
Purpose. Understanding how chemical structures influence transport across the intestinal mucosa will greatly enhance the discovery of orally available drugs. In an attempt to accelerate defining such relationships between structure and transport, six arbitrary mixtures of N-substituted glycine (NSG) peptoids containing 24 physicochemically diverse compounds were evaluated in the Caco-2 model of intestinal absorption.
Methods. Samples were analyzed by HPLC and the areas of the peaks representing the components of each mixture were summed to measure 'aggregate' apparent permeability coefficients (P app) a score of the influence of the common structural element within each mixture towards absorption. Mass spectrometry was used to identify the chemical structure of Caco-2 permeable compounds.
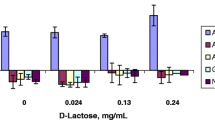
Results. Three linear trimeric mixtures were examined and, for each mixture, none of the components was detected in receiver chambers. It was concluded that the components of these mixtures each had a P app value less than 0.8 × 10−6 cm/sec, a permeability less than mannitol. Three dimeric mixtures were examined and they exhibited aggregate P app values of 9.2 × 10−6 , 14 × 10−6 and 6.9 × 10−6 cm/sec. These transport rates reflected the transport of most of the components of each mixture. Furthermore, the components of the dimeric mixtures which were transported at a rate greater than mannitol were apparently transported by passive mechanisms.
Conclusions. This study demonstrated that mixtures can be used to study structure-transport relationships in the Caco-2 model. The information obtained from this type of study will be integrated into the design of future chemical libraries. Other potential uses of chemical mixtures with the Caco-2 model are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W. H. Moos, G. D. Green, and M. R. Pavia. Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 28:315–324 (1993).
R. J. Simon, R. S. Kania, R. N. Zuckermann, V. D. Heubner, D. A. Jewell, S. Banville, S., Ng, L. Wang, S. Rosenberg, C. W. Marlowe, D. C. Spellmeyer, R. Tan, A. D. Grankel, D. V. Santi, F. E. Cohen, and P. A. Bartlett. Proc. Natl. Sci. Acad. U.S.A. 89:9367 (1992).
R. N. Zuckermann, J. M. Kerr, M.A. Siani, and S.C. Banville. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 40:497–506 (1992).
R. N. Zuckermann, E. J. Martin, D. C. Spellmeyer, G. B. Stauber, K. R. Shoemaker, J. M. Kerr, G. M. Figliozzi, D. A. Goff, M. A. Siani, R. J. Simon, S. C. Banville, E. G. Brown, L. Wang, L. S. Richter, and W. H. Moos. J. Med. Chem. 37:2678–2685 (1994).
S. M. Miller, R. J. Simon, S. Ng. R. N. Zuckermann, J. M. Kerr, and W. H. Moos. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 4:2657–2662 (1994).
R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, N. F. H. Ho, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 8:1453–1460 (1991).
R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, N. F. H. Ho, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 9:435–439 (1992).
P. S. Burton, R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, N. F. H. Ho, and L. L. Maggiora. J. Control. Release 19:87–98 (1992).
K. Palm, K. Luthman, A. L. Ungell, G. Strandlund, and P. Artursson. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:32–39 (1996).
A. R. Hilgers, R. A. Conradi, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 7:902–909 (1990).
I. J. Hidalgo, T. J. Raub, and R. T. Borchardt. Gastroenterology 96:736–749 (1989).
R. A. Conradi, K. F. Wilkerson, B. D. Rush, A. R. Hilgers, M. J. Ruwart, and P. S. Burton. Pharm. Res. 10:1790 (1993).
W. Rubas, N. Jezyk, and G.M. Grass. Pharm. Res. 10:113–118 (1993).
E. J. Martin, J. M. Blaney, M. A. Siani, D. C. Spellmeyer, A. K. Wong, W. H. Moos. J. Med. Chem. 38:1431 (1995).
C. H. Gochoco, F. M. Ryan, J. Miller, P. L. Smith, and I. Hidalgo. Int. J. Pharm. 104:187 (1994).
G. Wilson, I. F. Hassan, C. J. Dix, I. Williamson, R. Shah, M. Mackay, and P. Artursson. J. Conrtol. Release 11:25–40 (1990).
I. J. Hidalgo and R. T. Borchradt. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1028:25–30 (1990).
P. Artursson, A. L. Ungell, and J. E. Lofroth. Pharm. Res. 10:1123–1129 (1993).
J. J. Burbaum, M. H. Ohlmeyer, J. C. Reader, I. Henderson, L. W. Dillard, G. Li, T. L. Randle, N. H. Sigal, K. Chelsky, and J. J. Baldwin. Proc. Natl. Sci. Acad. U.S.A. 92:6027–6031 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, E.W., Gibbons, J.A. & Braeckman, R.A. Intestinal Absorption Screening of Mixtures from Combinatorial Libraries in the Caco-2 Model. Pharm Res 14, 572–577 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012140709158
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012140709158