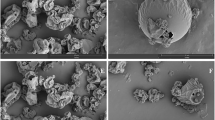
Abstract
Purpose. The long-term and high-temperature storage of dry, micron-sized particles of lysozyme, trypsin, and insulin was investigated. Subsequent to using supercritical carbon dioxide as an antisolvent to induce their precipitation from a dimethylsulfoxide solution, protein microparticles were stored in sealed containers at -25, -15, 0, 3, 20, 22, and 60°C. The purpose of this study was to investigate the suitability of supercritical antisolvent precipitation as a finishing step in protein processing.
Methods. Karl Fisher titrations were used to determine the residual moisture content of commercial and supercritically-processed protein powders. The secondary structure of the dry protein particles was determined periodically during storage using Raman spectroscopy. The proteins were also redissolved periodically in aqueous buffers and assayed spectrophotometrically for biological activity and by circular dichroism for structural conformation in solution.
Results. Amide I band Raman spectra indicate that the secondary structure of the protein particles, while perturbed from that of the solution state, remained constant in time, regardless of the storage temperature. The recoverable biological activity upon reconstitution for the supercritically-processed lysozyme and trypsin microparticles was also preserved and found to be independent of storage temperature. Far UV circular dichroism spectra support the bioactivity assays and further suggest that adverse structural changes, with potential to hinder renaturation upon redissolution, do not take place during storage.
Conclusions. The present study suggests that protein precipitation using supercritical fluids may yield particles suitable for long-term storage at ambient conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. E. Creighton, in Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties, 2nd ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, 1993; p 327.
H. R. Costantino, R. Langer, and A. M. Klibanov. J. Pharm. Sci. 83:1662-1669 (1994).
M. C. Manning, K. Patella, and R. T. Borchardt. Pharm. Res. 6:903-915 (1989).
A. M. Klibanov. Advances in Applied Microbiology 29:1-28 1983.
M. W. Townsend, and P. P. DeLuca. J. Pharm. Sci. 79:1083-1086 (1990).
S.-D. Yeo, G.-B. Lim, P. G. Debenedetti, and H. Bernstein. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41:341-346 (1993).
S.-D. Yeo, P. G. Debenedetti, S. Patro, and T. M. Przybycien. J. Pharm. Sci. 83:1651-1656 (1994).
M. A. Winters, B. L. Knutson, P. G. Debenedetti, H. G. Sparks, T. M. Przybycien, C. L. Stevenson, and S. J. Prestrelski. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:586-594 (1996).
C. A. Eckert, B. L. Knutson, and P. G. Debenedetti. Nature, 383:313-318 (1996).
D. J. Dixon, K. P. Johnston, and R. A. Bodmeir. AIChE J. 39:127-139 (1993).
D. J. Dixon, and K. P. Johnston. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 50:1929-1942 (1993).
S.-D. Yeo, P. G. Debenedetti, M. Radosz, and H.-W. Schmidt. Macromolecules 26:6207-6210 (1993).
T. W. Randolph, A. D. Randolph, M. Mebes, and S. Yeung. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 9:429-435 (1993).
S.-D. Yeo, P. G. Debenedetti, M. Radosz, R. Giesa, and H.-W. Schmidt. Macromolecules 28:1316-1317 (1995).
G. Luna-Bárcenas, S. K. Kanakia, I. C. Sanchez, and K. P. Johnston. Polymer 36:3173-3182 (1995).
W. J. Schmitt, M. C. Salada, G. C. Shook, and S. M. Speaker III. AIChE J. 41:2476-2486 (1995).
R. Bodmeir, H. Wang, D. J. Dixon, S. Mawson, and K. P. Johnston. Pharm. Res. 12:1211-1217 (1995).
M. J. Pikal. Biopharm 3:18-27 (1990).
A. Dong, S. J. Prestrelski, S. D. Allison, and J. F. Carpenter. J. Pharm. Sci. 84:415-424 (1995).
H. R. Constantino, K. Griebenow, P. Mishra, R. Langer, and A. M. Klibanov. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1253:69-74 (1995).
S. J. Prestrelski, N. Tedeschi, T. Arakawa, and J. F. Carpenter. Biophys. J. 65:661-671 (1993).
B. S. Kendrick, A. Dong, S. D. Allison, M. Manning, and J. F. Carpenter. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:155-158 (1996).
T. Arakawa, S. J. Prestrelski, W. C. Kenney, and J. F. Carpenter. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 10:1-28 (1993).
T. M. Przybycien, and J. E. Bailey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 995:231-245 (1989).
L. A. Decker, Ed. Worthington Enzyme Manual: Enzymes, Enzyme Reagents, Related Biochemicals; Worthington Biochemical Corp.: Freehold, NJ, 1977; pp 185-188, 221–224.
N. Greenfield, G. D. Fasman. Biochem. 8:4108-4116 (1969).
D. C. Phillips. Proc. N. A. S. 57:484-495 (1967).
T. M. Przybycien, and J. E. Bailey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1076:103-111 (1991).
D. Z. Frankel, Protein Purification with Compressed Carbon Dioxide, B. S. Thesis, Princeton University, 1997.
V. Sluzky, J. A. Tamada, A. M. Klibanov, and R. Langer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:9377-9381 (1991).
V. Sluzky, A. M. Klibanov, and R. Langer. Biotech. Bioeng. 40:895-903 (1992).
W. R. Liu, R. Langer, and A. M. Klibanov. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 37:177-184 (1991).
M. W. Townsend, and P. P. DeLuca. J. Pharm. Sci. 80:63-66 (1991).
P. F. Mullaney. Nature 210:953 (1966).
W. Goldbach, and R. Herzog. Nahrung 11:145-147 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winters, M.A., Debenedetti, P.G., Carey, J. et al. Long-Term and High-Temperature Storage of Supercritically-Processed Microparticulate Protein Powders. Pharm Res 14, 1370–1378 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012112503590
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012112503590